* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System Overview Major Glands
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
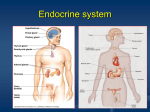
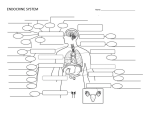
Endocrine System Overview target cell target cell hormone bloodstream receptor not a target cell • Glands: Major organs of the endocrine system • Glands make hormones Glands make hormones – Hormones: chemical signals • Hormones move through bloodstream • Hormone binds to cell receptor • Target cells produce proteins There are steroid hormones and nonsteroid There are steroid hormones and nonsteroid hormones Steroid hormone diffuses through the cell membrane Nonsteroid hormone binds to receptor on the cell membrane. Non‐steroid hormone receptor Steroid hormone binds to a receptor within the cell. within the cell. receptor t nucleus The hormone and receptor enter the nucleus and bind nucleus and bind to DNA Receptor stimulates g a second messenger with in the cell. Second messenger starts a series of chemical reactions in the cytoplasm. second messenger Chemical Ch i l reactions DNA Steroid hormone causes DNA to causes DNA to make proteins. proteins Second messenger reactions activate enzymes. activated enzymes All the below create hormones Hypothalamus – Stimulates the pituitary gland to release hormones PITUITARY – Controls growth, reproduction, body temp • Pituitary gland Pituitary gland – Controls cell growth and [H2O] in blood THYROID – Stimulates other glands • Thyroid gland y g THYMUS – Regulates metabolism, growth, development ADRENAL GLANDS • Thymus – Allows WBCs to mature to fight infection PANCREAS • Adrenal Glands FEMALE GONADS :OVARIES – Controls “fight or flight” response – Increases breathing, alertness, blood pressure • Pancreas – Controls glucose level in blood – Insulin, glucagon • Gonads: influence sexual development – Testes (males): testosterone MALE GONADS : TESTES – Ovaries (females): Estrogen, progesterone HYPOTHALAMUS – Steroid hormones enter into the cell. S id h i h ll – Nonsteroid hormones do not enter the cell. Steroid hormone Major Glands • Releasing hormones stimulate other glands to produce hormones produce hormones – Allow glands to communicate with one another – Are used in temperature regulation regulation Pituitary gland • Abnormal hormone levels affect homeostasis. • Hormonal imbalances might be treated with surgery or medicine. • Steroids, a pituitary tumor, or some prescription drugs can make the pituitary overactive and indirectly cause problems. REview Hypothalamus Thyroid y Thymus Adrenal glands d l l d Pancreas Ovaries Testes Hormonal imbalances can cause severe illness 1) What are glands and what do they release? 2) What do steroid and nonsteroid hormones direct cells to create? 3) Examine the diagram of the endocrine system on slide #7. Practice answering the 8 different glands. Practice answering the 8 different glands. 4) Which gland…. releases insulin to lower blood sugar levels? increases your alertness and blood pressure? helps your white blood cells mature? i l t d t is located atop your kidneys? kid ? are found in your brain (two answers)? is considered your body’s thermostat? y y