* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topography of the Ocean Floor Notes
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
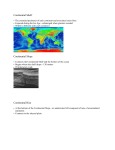
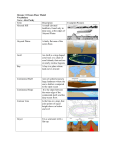
Continental Margin The edge of the continent, comprised of: Continental Shelf Continental Slope Continental Rise Continental Shelf Gently sloping part of the continent that is underwater Continental Slope The steep decline from the continental shelf to the ocean floor Continental Rise A mound of sediments at the bottom of the continental slope Turbidity Currents – An underwater mudslide of sediments Submarine Canyon – A deep, eroded area in the continental slope carved out by turbidity currents Abyssal Plain Flat area on the ocean floor, covered by a thick layer of sediment Mid-Ocean Ridges • Long underwater mountain chain • Produced by sea floor spreading at divergent plate boundaries Rift Valley A deep undersea valley, located along the center of the mid-ocean ridge Seamounts • Underwater mountains, usually volcanic. • The biggest mtn. on earth is Mauna Loa (Hawaii). • Build-up underwater (over a hot spot), & when they break the ocean surface they turn into islands. • Start to “deflate” & sink as the crust carries it away from the hot spot. Atolls Ring-shaped coral reef, encircling a shallow lagoon Trenches • Long, narrow, deep depression of the subduction sea floor caused by __________ Marianas • Deepest place on Earth - ________ Trench - 7 miles deep Guyots Flat-topped seamounts, formed from erosion above the sea surface Seamount/Volcanic Island Guyot