* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
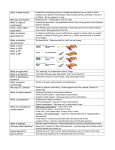
Learning Chapter Six Classical Conditioning • Definition: a simple form of learning in which a stimulus (a trigger) produces a response (a desired reaction) Ivan Pavlov’s Research 1. Taught a dog to salivate/ drool at the sound of a bell. 2. Dogs (and people) produce saliva to digest food. When we smell or see food, we often begin producing saliva. 3. Pavlov rang a bell (the stimulus) when he fed the dog. Since the dog saw the food, he began to drool. 4. After a while, the bell alone made the dog drool (the response). Taste Aversion • We also learn to dislike certain foods. 1. If we become ill after eating something (perhaps it was spoiled), we often won’t want to eat that item again. Operant Conditioning • Definition: learning from the consequences of our actions • If we like the consequences we will repeat the behavior, if we don’t we are more likely to avoid the behavior again. Reinforcement • Used to increase the chance that the behavior will happen again. • Can be positive (we are given something we like following a certain behavior). • Can be negative (we are given something we do not like following a certain behavior). Cognitive Factors in Learning • Remember—cognitive is what’s taking place in our minds; our thoughts. • Latent Learning: remains hidden until it is needed. • Observational Learning: we imitate others; there is thought (and concern) that we receive learning from the media. The PQ4R Method • This is a specific process designed to encourage learning. P=Preview: skim through a chapter/section to see what the material will cover; glance at pictures, bold words, or titles. Q=Question: create questions about what you just skimmed through. R=Read: read the material. R=Reflect: make some connections with what you’re reading. R=Recite: repeating information helps you remember it quickly. R=Review: spend time each night reviewing instead of studying the entire content the night before a test. Other Strategies • What other learning strategies have you learned? • Mnemonic Device: a word or words that stand for something else • HOMES=the Great Lakes: Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, and Superior Chapter 6 Review • Give a new example of Classical Conditioning • Give an example of a positive and a negative reinforcement • Think of an example of both Latent and Observational Learning that you’ve experienced • Apply the PQ4R Method to chapter 9—list out the letters and what you learned • Give two examples of mnemonic devices