* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 2-4 Review
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
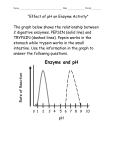
Ch. 2-4 Review Biology Name __________________________ Date __________________________ Period ______ Multiple Choice: Circle the one best choice that answers the question or completes the statement. 1. Which statement is true concerning the structure of proteins? a. The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids. b. Alpha helices and beta sheets are examples of secondary structure. c. Side chains (R-groups) of amino acids can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic. d. Proteins made of two or more polypeptide chains have quaternary structure. e. All statements are true. 2. Which statement regarding enzyme function is true? a. Higher temperatures allow greater contact between enzymes and substrates; therefore, the higher the temperature the better the enzyme will function. b. Enzymes cannot function at a pH lower than 6. c. Most coenzymes are inorganic substances such as ions of iron or potassium. d. Excessive salt ions can cause an enzyme to denature. e. All of the above. 3. A cell uses energy released by ____ reactions to drive the ____ reaction that makes ATP. Then it uses the energy released by the hydrolysis of ATP, an ____ reaction, to do various kinds of work in the cell. a. exergonic…exergonic…endergonic d. endergonic…endergonic…exergonic b. endergonic…exergonic…endergonic e. exergonic…endergonic…endergonic c. exergonic…endergonic…exergonic 4. The mechanism of enzyme action is _____. a. to create an energy barrier between substrates b. to lower the energy of the activation of a reaction c. to change the direction of thermodynamic equilibrium d. to change endergonic into exergonic reactions e. to allow substrates to move more freely in solution 5. If the tertiary structure of an enzyme is changed _____. a. its substrate may not fit properly in the active site b. it will be missing one of its polypeptides c. the helical coil will be stretched out d. the product of the reaction will be a different molecule e. its substrate will bond covalently with the wrong part of the molecule 6. Why does heating interfere with the activity of an enzyme? a. It kills the enzyme. b. It changes the enzyme’s shape. c. It decreases the energy of substrate molecules. d. It causes the enzyme to break up. e. It decreases the chance that the enzyme will meet a substrate molecule. 7. An enzyme is specific. This means a. it has a certain amino acid sequence. b. it is found only in a certain place. c. it functions only under certain environmental conditions. d. it speeds up a particular chemical reaction. e. it occurs in only one type of cell. 8. An enzyme and four different molecules are shown in the diagram below. The enzyme would most likely affect reactions involving a. molecule A, only b. molecule C, only c. molecules B and D d. molecules A and C Completion: On the lines provided, complete the following sentences. 9. Chemical reactions that ___________________ energy often occur spontaneously. 10. During a chemical reaction, chemical bonds are 11. Biological catalysts, or enzymes, act by lowering the ___________________ required for a reaction. 12. The reactants of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction are known as Defining Terms: On the lines provided, describe how the words in each set are related. 13. catalyst, enzyme, activation energy 14. reactant, product, chemical reaction Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the parts of the reaction asone of the following: products, reactants, or activation energy. 15. _____________________________ 16. _____________________________ 17. _____________________________ Interpreting Graphics: Use the two diagrams of chemical reactions to answer questions 18 to 20. Graph I Graph II B A C Course of Reaction Course of Reaction 18. Which pathway has the greatest activation energy? 19. Which graph shows a reaction that absorbs energy? 20. Why are two pathways shown in the graph on the right? Use the diagram below and your knowledge of biology to answer the following questions. 21. Pepsin: a. What is the optimal pH for pepsin? _________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ b. Is this pH acid or basic? ________________________________________________ c. In what organ of the digestive system does pepsin work? ______________________ 22. Trypsin: a. What is the optimal pH for trypsin? ________________________________________ b. Is this pH acid or basic? ________________________________________________ c. In what organ of the digestive system does trypsin work? ______________________ 23. Neither enzyme works at a pHs of _______________________________________________ Forming a Hypothesis: 24. Most enzymes in the human body work best at 37°C Imagine scientists have discovered an enzyme in the body that works best at 39°C. What processes or functions might this enzyme be involved in?