* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MAST_-_Introduction2MET
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
The Weather Channel wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
National Severe Storms Laboratory wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Space weather wikipedia , lookup
Satellite temperature measurements wikipedia , lookup
Thunderstorm wikipedia , lookup
Weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Storm Prediction Center wikipedia , lookup
Weather Prediction Center wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Convective storm detection wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
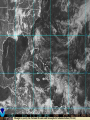
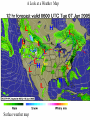
MET 200 Introduction to Meteorology Dr. R. Suseela Reddy Weather and Climate A Satellite’s View of the Weather Storms of All Sizes A Look at a Weather Map Weather and Climate in Our Lives Special topic: Meteorology: A Brief History Weather Elements Temperature Precipitation Air Pressure Visibility Humidity Wind Clouds Weather Elements Air Temperature – the degree of hotness or coldness of the air. Air pressure – the force of the air above an area. Humidity – a measure of the amount of water vapor in the air. Clouds – a visible mass of tiny water droplets and/or ice crystals that are above the earth’s surface. Precipitation – any form of water, either liquid or solid (rain or snow), that falls from clouds and reaches the ground. Visibility – the greatest distance on can see. Wind – the horizontal movement of air. Key Terms Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at any particular time and place. Weather Elements: The elements of air temperature, air pressure, humidity, clouds, precipitation, visibility, and wind that determine the present state of the atmosphere, the weather. Climate: The accumulation of daily and seasonal weather events over a long period of time. A Satellite’s View of the Weather Geostationary Satellite – A satellite that orbits the earth at the same rate that the earth rotates and thus remains over a fixed place above the equator 36,000 km (22,300 mi). Polar Orbiting Satellite – A satellite whose orbit closely parallels the earth’s meridian lines and thus crosses the polar regions(800 km) on each orbit. A Satellite’s View of the Weather Meridians – The dotted lines running from pole to pole on a satellite picture. Longitude – depicts how far east or west, in degrees, it is from the prime meridian. Parallels of latitude – The dotted lines that parallel the equator. GOES East Hurricane SECTOR Visible Image Satellite’s View of the Weather Hurricane Tracking Sector (VIS) View Movie of the Visible Sector Brought to you by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Key Terms Meridian: A great circle of the earth passing through the poles and any given point on the earth’s surface. Longitude: The angular distance east or west on the earth’s surface from the Prime Meridian(zero meridian). Latitude: The angular distance north or south from the equator of a point on the earths surface, measured on the meridian of the point. Parallels of latitude: The dotted lines that parallel the equator. Middle latitudes: The region of the world typically described as being between 30° and 50° latitude. Storms of All Sizes Mid-Latitude Cyclonic Storm (Extratropical Cyclone): A cyclonic storm that most often forms along a front in middle and high latitudes. (also called a depression or a low). Hurricane: A severe tropical cyclone having winds in excess of 64 knots (74 miles per hour). Thunderstorm: A local storm produced by cumulonimbus clouds. Always accompanied by lightning and thunder. Tornado: An intense, rotating column of air that protrudes from a cumulonimbus cloud in the shape of a funnel or a rope whose circulation is present on the ground. A Look at a Weather Map Surface Weather Map Surface weather map Regional Surface Map JSU Meteorology Program Weather Observations Date Observer’s Name Time of Observation 6/06/05 Monesa Watts 10:02a.m. Yesterday’s High Temperature This Morning’s Low Temperature Total rain/snow last 24 hours 92 F 67 F 1.06 in Current Temperature Current Sky Conditions Weather 72.1 F/ 22.3 C BKN 040 (7/8 Sc) RA Wet-Bulb Temperature Relative Humidity (%) Dewpoint Temperature 70.1 F 92 % 67.0 F/19.4 C Current Pressure Pressure Tendency Wind Direction & Speed 30.12 in Rising (Code 0) VAR @ 5 MPH Special or Additional Remarks/Comments: METAR CODED OBSERVATION: SPECI KJSU 061502Z VRB04KT 9SM RA BKN 040 22/19 A3012 RMK SLP 200 70106 8/5// T02230194 50xxx Key Terms Wind: Air in motion relative to the earth’s surface. Wind Direction: The direction from which the wind is blowing. Front: The transition zone between two distinct air masses. Meteorology: The study of the atmosphere and atmospheric phenomena as well as the atmosphere’s interaction with the earth’s surface, oceans, and life in general. Cumulonimbus Clouds reaching high into the atmosphere Cumulonimbus clouds (Cb) are much larger and more vertically developed than fair weather cumulus. They can exist as individual towers or form a line of towers called a quall line. Fueled by vigorous convective updrafts (sometimes in excess 50 knots), the tops of cumulonimbus clouds can easily reach 39,000 feet (12,000 meters) or higher. Lower levels of cumulonimbus clouds consist mostly of water droplets while at higher elevations, where temperatures are well below 0 degrees Celsius, ice crystals dominate. Under favorable atmospheric conditions, harmless fair weather cumulus clouds can quickly develop into large cumulonimbus clouds associated with powerful thunderstorms known as supercells. Photograph by: Knupp Supercells are large thunderstorms with deep rotating updrafts and can have a lifetime of several hours. Supercells can produce frequent lightning, large hail, damaging winds, and tornadoes. These storms tend to develop during the afternoon and early evening when the effects of heating by the sun are strongest. For more information about supercells and other types of severe weather phenomena, visit the Severe Storm Spotters Guide. Weather and Climate in Our Lives Weather often dictates the type of clothing we wear, while climate influences the type of clothing we buy. Climate determines what crop to plant and when. Weather affects how we feel(ex. Arthritis pain is most likely to occur when rising humidity is accompanied by falling pressure. Headaches are common on days when we are forced to squint due to hazy skies or a thin, bright overcast layer of high clouds. Heavy fog can restrict visibility at airports, causing flight delays and cancellations. Key Terms Wind Chill Factor: The cooling effect of any combination of temperature and wind, expressed as the loss of body heat (effects tells us its much colder than it really is). Chinook Wind: A warm dry wind on the eastern side of the Rocky Mountains (some people often become irritable and depressed). Severe Thunderstorm: An intense thunderstorm capable of producing heavy showers, flash floods, hail, strong and gusty surface winds, and tornadoes. Flash Flood: A flood that rises and falls quite rapidly with little or no advance warning, usually as the result of intense rainfall over a relatively small area. Downburst: A severe localized downdraft that can be experienced beneath a severe thunderstorm. Wind shear: The rate of change of wind speed or wind direction over a given distance. NOTES On a hot, humid day we normally feel uncomfortably warm and blame it on the humidity. If our bodies overheat, heat exhaustion or heat stroke may result. Each summer scorching heat waves take many lives. Each year, the violent side of weather influences the lives of millions. Tornadoes have not only taken many lives, but annually cause damage to building and property totaling in the hundreds of millions of dollars, as a single tornado can level and entire section of a town. On the average, more people die in the United States from floods and flash floods than from any other natural disaster. About the NWS Weather Forecast/Professional Organizations TV Broadcast Meteorologist(I.e. Weather Channel, Local News) National Weather Service NOAA Weather Radio Website(UCAR, University websitesweather.jsums.edu) American Meteorological Society National Weather Association NWS Services Working Together Keeps Weather Hazards from Becoming Weather Disasters Make Sure Your School/Home/Office Has an All-Hazards NOAA Weather Radio Thank YOU!!