* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Epicenter Location
Seismic retrofit wikipedia , lookup
Casualties of the 2010 Haiti earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2009–18 Oklahoma earthquake swarms wikipedia , lookup
Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
1880 Luzon earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
1570 Ferrara earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2010 Pichilemu earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2009 L'Aquila earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2008 Sichuan earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1960 Valdivia earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1906 San Francisco earthquake wikipedia , lookup
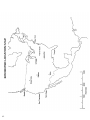
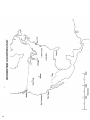
NAME_________________________________________ DATE________________ FINDING EPICENTERS VOCABULARY: FaultEpicenterFocusFocal Depth-P-WaveS-WaveSeismographSeismogramINTRODUCTION: Earthquakes occur when there is movement within the crust along a fault. This movement creates waves which travel through the Earth. These seismic waves are radiated in every direction from the focus. An earthquake occurs every 30 second, every day. Most of these earthquakes are so weak they wouldn’t be noticed without the use of seismographs. While seismologists use many stations to locate an epicenter, you will use three, the minimum number needed to triangulate the location of an epicenter. OBJECTIVE: Learn to read and interpret seismograms and using those seismograms locate the epicenter of an earthquake. 77 PROCEDURE A: The diagram below demonstrates how to use the difference in arrival times of P & S waves to determine the distance to the epicenter. Using the three seismograms provided and your “Earthquake P-wave and S-wave Travel Time” graph from your reference table to calculate: 1) Arrival times for P and S waves 2) Difference in arrival times 3) Distance to the epicenter 4) Length of time the P-wave traveled for each city and enter on Report Chart. PROCEDURE B: 1. a. To locate the epicenter on the map by constructing a circle whose radius is equal to the distance from the city to the epicenter. b. Use the scale of distance on your map to set the compass at the correct radius. 2. On the map identify the epicenter location by drawing all three circles, where all three circles meet is your epicenter, place and “X” at this location. 78 REPORT CHART Seismograph Station Arrival Time (clock time) “P” Wave “S” Wave Difference in Arrival Time Time (min and sec) Distance to Epicenter (km) “P” Wave Travel Time (min and sec) CHICAGO TAMPA WINK 79 80 REPORT CHART Seismograph Station Arrival Time (clock (clock time) “P” Wave “S” Wave Difference in Arrival Time (min and sec) Distance to Epicenter (km) “P” Wave Travel Time (min and sec) NEW YORK SAN DIEGO TAMPA 81 82 REPORT CHART Seismograph Station Arrival Time (clock time) “P” Wave “S” Wave Difference in Arrival Time (min and sec) Distance to Epicenter (km) “P” Wave Travel Time (min and sec) WINK SEATTLE MEMPHIS 83 1 84 DISCUSSION QUSTIONS: 1. What difference between P-waves and S-waves was used to find the earthquake’s epicenter? 2. What was the approximate location of the epicenter of: Earthquake 1: Earthquake 2: Earthquake 3: 3. Why is three the minimum number of stations necessary to locate and epicenter? 4. Why does the time between the arrival of the P-wave and S-wave become greater and greater as you get farther away from the epicenter? CONCLUSION: Describe step by step how an epicenter of an earthquake is located. 85 86