* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download epidermolysis bullosa
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
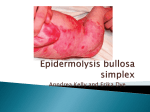
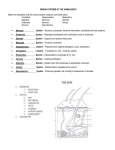
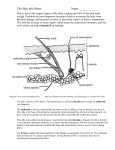
What is EB? What is EB? EB is a genetic condition. What does that mean? EB is a genetic condition. What does that mean? EB is a family of rare genetic disorders involving the skin and skin-like tissues is a family of rare genetic disorders involving the skin and skin-like tissues thatEB share a common way in which wounds are formed that share a common way in which wounds are formed epidermolysis epidermolysis bullosa bullosa refers to to thethe outer layer refers outer layer of skin (epidermis) of skin (epidermis) means breakdown means breakdown People with EBEB have extremely fragile skin People with have extremely fragile skin leading to constant blisters oror skin tears that leading to constant blisters skin tears that cancan cause wounds that are difficult to heal. cause wounds that are difficult to heal. and wounds areare caused byby These blisters and wounds caused These blisters proteins that help hold layers ofof changes to to proteins that help hold layers changes skin structure skinskin together and support skin structure together and support Blisters wounds can occur from friction, Blisters andand wounds can occur from friction, such as something rubbing or scratching such as something rubbing or scratching skin or tissue. They can form anywhere thethe skin or tissue. They can form anywhere on the skin, and sometimes inside the body, on the skin, and sometimes inside the body, such as the lining mouth such as the lining of of thethe mouth Normally, certain genes Normally, certain genes provideinstructions instructionstoto provide makeproteins proteins make These protein changes These protein changes impact structure impact thethe structure andand strength skin strength of of thethe skin aakind kindof ofblister blister There Thereare are44types typesof of EB: EB: 1 1 EBS EBS EB EBsimplex simplex 22 JEB JEB JunctionalEB EB Junctional DEB 33 DEB DystrophicEB, EB, Dystrophic includingDominant Dominant including DEB(DDEB) (DDEB) and and DEB RecessiveDEB DEB (RDEB) (RDEB) Recessive KindlerSyndrome Syndrome 44 Kindler What are some key factsabout aboutEB? EB? What are some key facts a chronic disease that a chronic disease that can worsen with age can worsen with age In EB, mutated genes In EB, mutated genes provide altered instructions provide altered instructions that change the function or that change the function or amount of protein being made amount of protein being made Genetic conditions are Genetic conditions are caused by mutations caused by mutations in genes in genes affects males and females affects males and females equally and can occur equally and can occur in all ethnicities in all ethnicities is EB EB inherited? inherited? How is !! Sometimes,EB EBoccurs occursspontaneously spontaneously individual because a new genetic Sometimes, inin anan individual because of of a new genetic mutationthat thathis hisororher herparents parentsdid did not have mutation not have But oror both parents who either have EBEB or or Butusually, usually,EB EBisisinherited inheritedfrom fromone one both parents who either have carry carryaamutated mutatedEB EBgene gene RECESSIVE (JEB, RDEB, RECESSIVE (JEB, RDEB, KINDLER SYNDROME) KINDLER SYNDROME) DOMINANT DOMINANT(EBS, (EBS,DDEB) DDEB) •• IfIf 11 parent parentisisaffected affectedby byEB EBand and1 parent 1 parent is not affected, there is about a 50% is not affected, there is about a 50% chance chancethat thateach eachchild childborn borncould could have EB have EB •• A A child childwho whodoes doesnot notinherit inherita amutated mutated gene from an affected parent gene from an affected parentwill willnot not develop EB or pass it on to his or develop EB or pass it on to his or her children her children Affected Affected •A child must inherit 2 copies of aof a •A child must inherit 2 copies recessive mutated gene to be affected recessive mutated gene to be affected parents areare carriers of aofmutated • If• both If both parents carriers a mutated gene but are not affected by EB, there is is gene but are not affected by EB, there about a 25% chance that each child born about a 25% chance that each child born could have EB could have EB • If• a only inherits 1 copy of aof a If person a person only inherits 1 copy mutated gene, that person is a carrier mutated gene, that person is a carrier Carrier Carrier Unaffected Unaffected Carrier Carrier signs and symptoms signs and symptoms vary widely vary widely not contagious not contagious estimated to affect estimated to affect about 500,000 500,000 about individuals worldwide individuals worldwide causes pain and can causes painand and can physically physically and emotionally impact emotionally daily living impact daily living 50% Affected 50% Affected 50% Unaffected 50% Unaffected 25% Affected 25% Affected 50% Carrier 50% Carrier 25% Unaffected 25% Unaffected What do these words mean? What do these words mean? Anemia A condition in which a person has fewer red blood cells or hemoglobin than normal, resulting in fatigue Anemia A condition Dermis in which a person has fewer red blood cells or hemoglobin than normal, resulting in fatigue The inner layer of skin Dermis TheDNA inner layer of skin Basic unit that allows for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to DNA the next and contains instructions, or code, for making proteins Basic unit that allows for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the Epidermis next and contains instructions, or code, for making proteins The outer layer of skin Epidermis TheEsophagus outer layer of skin The tube that leads from the mouth through the throat to the stomach Esophagus TheGene tube that leads from the mouth through the throat to the stomach A part of a chromosome in a cell transferred from parent to offspring that influences inherited traits Gene Mutation A part of a chromosome in a cell transferred from parent to offspring that influences inherited traits A permanent error in the DNA code Mutation Reflux A permanent error in the DNA code A backward flow of the stomach contents into the esophagus Reflux Squamous cellofcarcinoma A backward flow the stomach contents into the esophagus A type of skin cancer Squamous cell carcinoma A type of skin cancer Want to learn more? A VISUAL A VISUAL G U I D E GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING TO UNDERSTANDING EPIDERMOLYSIS EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA BULLOSA Want Talk toto yourlearn doctor ormore? nurse. These additional resources can also provide support and information to help you to understand EB*: Talk to your doctor or nurse. These additional resources can also provide support and Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Research National Institute of Arthritis and information to help you toInternational understand EB*: Association (DEBRA) Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS) debra-international.org Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Research National Institute of Arthritis and niams.nih.gov Association (DEBRA) International Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases debra of America (NIAMS) debra-international.org National Organization for Rare debra.org niams.nih.gov Disorders (NORD) debra of America rarediseases.org DEBRA UK National Organization for Rare debra.org debra.org.uk Disorders (NORD) European Organization for Rare rarediseases.org Disorders (EURORDIS) DEBRA UK EB Research Partnership (EBRP) eurordis.org debra.org.uk ebresearch.org European Organization for Rare Disorders (EURORDIS) EB Research Partnership Sohana Research Fund(EBRP) eurordis.org sohanaresearchfund.org ebresearch.org Sohana Research Fund sohanaresearchfund.org *Please note that the opinions expressed by the organizations above do not necessarily reflect those of Amicus. Amicus does not maintain and is not responsible for the content of communications for the listed organizations or their websites. *Please note that the opinions expressed by the organizations above do not necessarily reflect those of Amicus. Amicus does not maintain and is not responsible for the content of communications ©Amicus Therapeutics, Inc. Cranbury, NJ. for the listed organizations or their websites. NP/NPS/01/0280/GLO916 ©Amicus Therapeutics, Inc. Cranbury, NJ. NP/NPS/01/0280/GLO916 INFORMATION FOR INFORMATION PEOPLE WITH FOR PEOPLE WITH BULLOSA EPIDERMOLYSIS EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA (EB) AND THEIR FAMILIES (EB) AND THEIR FAMILIES What might someone with EB experience? What might someone with EB experience? SKIN STRUCTURE: SITES OF PRIMARY BLISTER FORMATION EBS SKIN STRUCTURE: SITES OF PRIMARY BLISTER FORMATION • Symptoms range from mild to severe EBS INDIVIDUALS WITH EB EXPERIENCE: INDIVIDUALS WITH EB EXPERIENCE: • Blisters form on the top layer of skin, • Symptoms range from mild to severe known as the epidermis • Blisters form on the top layer of skin, • Blisters appear on the hands and feet knowntypically as the epidermis but can be widespread over the hands entire and skinfeet • Blisters typically appear on the Fragile Blisters Itching Pain skin Fragile Blisters Itching Pain skin Symptoms usually first appear in babies and Symptoms toddlers but sometimes don'tinappear usually first appear babies untiland adolescence toddlers but sometimes don't appear until adolescence Symptoms can range from mild to severe Symptoms can range from mild to severe All areas of the skin can be affected, areasand of the skin can affected, bothAll inside outside thebe body both inside and outside the body Signs and symptoms differ depending Signs and on the type ofsymptoms EB, but alldiffer typesdepending can cause onand the chronic type of EB, acute painbut all types can cause acute and chronic pain How does EB affect daily living? How does EB affect daily living? • Blisters formrange between epidermis • Symptoms fromthe mild to severeand dermis • Blisters occur on the skin and inside body, • Blisterscan form between the epidermis and the dermis such as incan theoccur linings the mouth and esophagus • Blisters onof the skin and inside the body, DERMAL-EPIDERMAL JUNCTION DERMAL-EPIDERMAL JUNCTION such as in the linings of the mouth and esophagus DEB DEB • Symptoms range from mild to severe • Symptoms mild to severe • Blisters formrange in thefrom dermis • Blisters in the • There areform 2 types of dermis DEB: • There are 2 types of DEB: 1 DOMINANT 1Wounds DOMINANT appear on hands, elbows, knees, and feet DERMIS DERMIS • Skin sunburns • A rare type of EB easily • Skin sunburns • Blisters form easily on any layer • Blisters form of skin or on any layer internal of skin or organs internal organs • There is increased risk • There is increased risk of squamous of squamous cell carcinoma cell inside carcinoma the mouth inside the mouth Wounds appear on hands, elbows, knees, and feet 2 RECESSIVE 2 RECESSIVE Widespread blistering and scarring occur, and Widespread blistering and scarring occur, and there is increased risk of a type of skin cancer there is increased risk of a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma called squamous cell carcinoma Chronic Chronicwounds woundsmay maycause causescar scar tissue, tissue, which which may lead to deformities of hands and feet may lead to deformities of hands and feet that limit dexterity limit dexterityand andmobility mobility Itchingisisa acommon commonproblem problemthat that may may lead lead to Itching disruptionofofsleep sleepand andthe theability ability to to focus. focus. disruption Duringsleep, sleep,scratching scratchingcan cancause cause or or During worsenwounds wounds worsen The clearouter outerlayer layerof ofthe theeye eye(cornea) (cornea) The clear can become injured, which may cause pain, pain, can become injured, which may cause excessivetear tearformation, formation,or ordischarge discharge excessive Gastrointestinal issues and malnutrition Gastrointestinal issues and malnutrition may result from difficulty swallowing, may result from difficulty swallowing, narrowing of the esophagus due to scar tissue, narrowing of the esophagus due to scar tissue, reflux, lactose intolerance, and constipation reflux, lactose intolerance, and constipation Anemia and fatigue, which can vary across Anemia andcan fatigue, which can vary across EB types, be due to having a chronic EBdisease, types, or canfactors be due to having a chronic such as chronic blood disease, or factors such as chronic blood loss or malnutrition loss or malnutrition Social isolation can result from fear of further trauma Social isolationlimitations can result from fear of further trauma and physical and physical limitations Stress and depression may be related to changes in Stress and depression may be to changes in appearance and limitations in related daily activities appearance and limitations in daily activities Adapted with permission from Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa with Research Association of America (debra of America). Adapted permission from Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Research Association of America (debra of America). How is EB treated? How is EB treated? Currently, there is no cure for EB; Currently, there is no cure for EB; however, potential treatments however, potential treatments being investigated: areare being investigated: Symptomsare areaddressed addressed with daily Symptoms with daily wound care and bandaging, along wound care and bandaging, along withprescription prescriptionmedication medication itch with forfor itch andpain painmanagement management and Prevention scarring, Preventionofofinfection, infection, scarring, and rigid joints and rigid joints Protein Protein replacement replacement Stem cellcell Stem transplant transplant Gene therapy Gene therapy Although this is a serious, life-altering condition, these daily tips may help Although this is a serious, life-altering condition, these daily tips may help with managing symptoms with managing symptoms Follow your doctor’s recommendations Follow your doctor’s for managing wounds recommendations for managing wounds Protect vulnerable skin sites by wearing gloves and padding Protect vulnerable skin sites around elbows and knees by wearing gloves and padding Keep skin cool by avoiding Keep skin cool by avoiding exposure to hot temperatures exposure to hot temperatures Keep skin moisturized to minimize itching, reduce friction, Keep skin moisturized to andminimize prevent skin fromreduce cracking itching, friction, and prevent skin from cracking Avoid tight clothing, hard shoes, internal seams, and Avoid tight clothing, hard tags to reduce friction shoes, internal seams, and tags to reduce friction GENETIC TESTING A blood sample is GENETIC taken toTESTING determine A blood sample is whether the condition taken determine wasto inherited whether theparent condition from one was inherited or both parents from one parent or both parents Wound Wound carecare advancements advancements What help? Whatare aresome somethings thingsthat thatmay may help? around elbows and knees A doctor suspects EB—what might happen next? A doctor suspects EB—what might happen next? SKIN BIOPSY A small sample of SKIN BIOPSYskin tissue affected A small fromsample open orofunhealed affected skinistissue wounds taken and fromexamined open or to unhealed find wounds is taken and protein deficiencies and structural examined to find flaws protein deficiencies and structural flaws • A rare type of EB SYNDROME EPIDERMIS • Symptoms range from mild to severe JEB Wounds Woundsand andblisters blisterscan canoccur occurall all over over the the body, which may make it difficult to perform body, which may make it difficult to perform daily activities daily activities PSYCHOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPACT IMPACT EPIDERMIS JEB but can be widespread over the entire skin Daily wound care can be painful and time Daily wound care can be painful and time consuming and can include soaking baths and consuming and can include soaking baths and constant dressing changes constant dressing changes PHYSICAL PHYSICAL IMPACT IMPACT KINDLER SYNDROME KINDLER PRENATAL TESTING When there is a PRENATAL TESTING family history of EB, When there is a may prenatal testing family history of EB, be performed prenatal testing may be performed Pad eyeglasses to protect the nose and ears Pad eyeglasses to protect the nose and ears Treat blisters when they appear as recommended by your doctor, and use Treat blisters when they appear as nonadhesive bandages and dressings recommended by your doctor, and use nonadhesive bandages and dressings Consider hobbies and noncontact sports to avoid risk of skin trauma Consider hobbies and noncontact sports to avoid risk of skin trauma Maintain a healthy diet; additional calories and protein are needed to ahelp with diet; skin healing Maintain healthy additional calories and protein are needed to help with skin healing A V I S U AL G U I D E T O U ND E R S T ANDING E P IDE RM OLYS IS BULLOS A ( E B) A V I SU A L G U I DE T O U N DE R S T A N D I N G E P I D E R M O L Y S I S B U L L O S A ( E B )