* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aversive Control of Behavior
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Shock collar wikipedia , lookup
Flagellation wikipedia , lookup
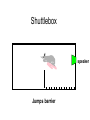
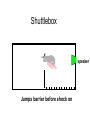
Aversive Control of Behavior: Punishment & Avoidance Lesson 16 Life: The School of Hard Knocks Learning with aversive stimuli pain sickness Positive Punishment B aversive outcome Negative RFT escape & avoidance Classical conditioning pair neutral stimulus w/ shock ~ B aversive SR What type of punishment? Positive punishment Difficult to do human, ethics but some human evidence Mostly animal research ~ Factors that influence efficacy Punishment is associative process Trials effect R punished B aversive S greater suppression Intensity (magnitude) greater intensity greater efficacy Delay of punishment longer delay less effective ~ Factors that influence efficacy History of punishment start w/ weak ineffective punishment more intense punishment less effective Habituation occurs Alternate routes of reinforcement Provide alternate responses to gain reward after punishment increases effectiveness ~ Human Case Study NOT an experiment 9 month old boy w/ chronic vomiting near death before treatment Recorded precise muscle activity identified muscle activity that preceded vomiting ~ Procedure Vomiting muscle activity observed Punished w/ shock produced startle response but not crying Results Vomiting eliminated after 5 trials over 3 days BUT… ~ Potential Side Effects Unintended & undesirable Response generalization other responses to aversive stimuli anger/fear/aggression avoidance Global effects can be worse than behavior punished ~ Monkey Study Learn to push button to get food opens a door Put toy snake in food dish quit pushing button after a few trials Side effects lost interest in eating lost social status lower in hierarchy ~ Painful Stimuli & Aggression College women 1 teaches another words 1 group of teachers hand in warm water Other while hand in ice water Results Ice water group verbally aggressive ~ Alternatives to Positive Punishment Time-out Remove opportunities for RFT Response cost Fines, loss of privileges Differential RFT of … Other Behaviors (DRO) Incompatible Behaviors (DRI) ~ Escape & Avoidance: Negative Reinforcement Escape / Avoidance Shuttle Box 2 compartments Can jump over barrier Electrified grid Speaker/light emits signal ~ Shuttlebox speaker Tone on Shuttlebox speaker Shock on Shuttlebox speaker Jumps barrier Shuttlebox speaker What is outcome? Shuttlebox Jumping over barrier terminates shock More trials responds more quickly learns to avoid shock ~ Shuttlebox speaker Tone on Shuttlebox speaker Jumps barrier before shock on Shuttlebox speaker What is outcome? Shuttlebox Results Early trials: escapes shock After may trials: avoidance Shift from escape avoidance Why? ~ Mowerer’s 2 Process Theory (1947) 2 processes involved in escape/avoidance Operant & Classical Conditioning Early trials escape (operant) shock (SD) jumping (B) escape (SR) Later trials avoidance (CC involved) Tone (CS) evokes fear (CER) B reduces fear drive strengthens response ~ So... Avoidance = escape from fear fear is classically conditioned D & CS Tone = S Avoidance no shock? Does extinction occur? 2 process view suggest cyclical performance ~ Observed performance Hi avoidance continues Avoidance Escape Lo # of trials But extinction does NOT occur ~ Avoidance & Extinction Avoidance behavior Persists Resistant to extinction Explanation? failure to avoid is punished Cognitive Theory (Annau & Kamin, 1961) Conservation of Anxiety Theory (Solomon & Wynne, 1954) ~ Expectancy Theory Cognitive theory Early trials consistent w/ 2 process tone Fear avoidance More experience expectancy expectancy = no shock Avoidance (B) satisfying outcome Avoidance response strengthened Difficult to extinguish ~ Conservation of Anxiety Theory Fear of CS doesn’t fully extinguish Immediate avoidance short latency Delayed avoidance Exposed CS longer No extinction for later portion CS Strengthens fear of early CS Behavior Therapy Exposure to sequential CSs Exposure therapy - fear hierarchy ~