* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PLANT REPRODUCTION AND BREEDING
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
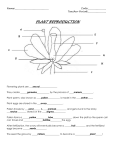
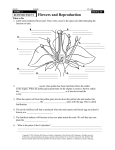
TOPIC 3 PLANT REPRODUCTION AND BREEDING - people adapt plants to meet their needs. - selective breeding is choosing specific for their special characteristics. plants - the plants are cross-pollinated and their offspring inherit the characteristics of both parents. - scientists can change plants by going inside the plant cell and changing some of the genetic material Watch Video - the part of the plant that control the characteristics is the genes PLANT REPRODUCTION Asexual Reproduction (Vegetative Reproduction) - one parent plant grows new plants from its roots, stems or leaves. - the young plant is identical to the parent. Layering - produces plants from the stems - branch from the parent bends to the ground and covers with soil then grows roots. Grafting - take a branch from one tree and attach it to another Cuttings - cut a small section of a leaf or stem to grow a new plant Sexual Reproduction - involves two parents that produce seed - plants are slightly different from the parents - reproduce using seeds - helps plants adapt to changes Cone Bearing Plants - female cone contains ovules (eggs) - male cone has pollen (sperm) - pollen blows in the wind to female cone - egg is fertilized inand the seed coneis formed Flowering Plants --Parts of the Flower Pollination Pollination occurs when pollen has been transferred from the anther to the stigma. When the pollen grain germinates on the stigma it creates a burrow called the pollen tube as it travels toward the ovary. When the sperm cell from the pollen grain reaches the ovary or ovule the sperm joins with the egg. This is called fertilization. The fertilized zygote will become a tiny new plant inside the seed. We call this tiny new plant the embryo. Fruit - fruit is the growing ovary of the plant - protects the seeds of the plant until they are ripe Seed Dispersal Read page 127 and describe the six ways plants can disperse seeds. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Germination - the development of the seed into a plant