* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Welcome to Biology 11
Survey
Document related concepts
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point accepted mutation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular biology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
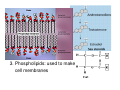
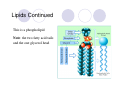
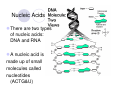
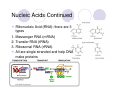
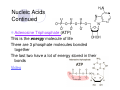
Welcome to Biology 11 Topics Chemicals of life Cells Evolution Taxonomy Microbio Animals Plants Ecology Biology this year! Adaptation and Evolution: A theory to explain relationships between living things Microbiology: The study of microscopic organisms Viruses Kingdom Monera Kingdom Protista Mycology: The study of fungus Animal biology: The study of animals (you may be surprised!) Kingdoms Porifera and Cnidaria Kingdoms Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, and Annelida Kingdoms Mollusca and Echinodermata Kingdom Arthropoda Kingdom Chordata, Subphylum Vertebrata Plant biology: The study of plants Green Algae, Mosses, Ferns Gymnosperms Angiosperms Ecology: The study of the interrelationships between organisms and their environment Biology 11 Life & its Major Molecules Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 8 characteristics of life Draw the structure of the 4 molecules of life State the function and examples of the 4 molecules of life The 8 Characteristics of Life 1. All life is made up of at least one cell 2. All life has to eat 3. All life grows - increasing its biomass 4. All life reproduces itself The 8 Characteristics of Life 5. All life responds to its environment 6. All life adapts - evolves - to survive in its environment 7. All life maintains internal and external homeostasis 8. All life ends 4 Molecules of Life Cytoplasm is made of 4 types of molecules 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids These molecules are composed mostly of four elements: H, O, C, & N Video Carbohydrates Function: energy for cell and structure There are 3 types: 1. Monosaccharides 2. Disaccharides 3. Polysaccharides Carbohydrates Continued Monosaccharides are a single unit of sugar If two monosaccharides are combined together, the result is called a disaccharide If there are many monosaccharides combined, the resulting molecule is a polysaccharide Examples of Carbohydrates Monosaccharides: glucose, fructose, galactose Disaccharides: sucrose, lactose, maltose Polysaccharides: Amylose, chitin, glycogen, cellulose Lipids (Fats) There are 3 types: 1. Triglycerides: long term energy storage 2. Steroids: hormones 3. Phospholipids: used to make cell membranes Lipids Continued This is a phospholipid Note: the two fatty acid tails and the one glycerol head Proteins Proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids The amino acids link together to form a chain These long chains of amino acids fold up in a very specific way The differences between proteins is the sequence of the amino acids and how they are folded up Nucleic Acids There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA A nucleic acid is made up of small molecules called nucleotides (ACTG&U) Nucleic Acids Continued Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Largest molecule on earth! Fits in to the nucleus and is twisted into a double helix Nucleic Acids Continued Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): there are 3 types 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) 2. Transfer RNA (tRNA) 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) All are single stranded and help DNA make proteins Has a U base instead of the T base Nucleic Acids Continued Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) This is the energy molecule of life There are 3 phosphate molecules bonded together The last two have a lot of energy stored in their bonds Video Your Turn! Complete the Bio-Mols Chart ☺