* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cholesterol and Heart Disease
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
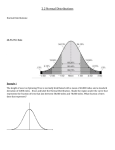
Cholesterol and Heart Disease Plaques • Buildup in arteries is composed of proteins, lipids, and cholesterol • When blood vessels are plugged up, you get heart attacks or strokes. • 1.5 million deaths per year from heart attacks • 600,000 deaths from cancer Deaths in Thousands 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 00 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 06 Years Deaths from cardiovascular disease (United States: 1900–2006 preliminary). Source: NCHS and NHLBI.3 100 85.9 Percent of Population 90 80 73.3 72.6 79.3 70 60 50 37.9 38.5 40 30 20 10 15.9 7.8 0 20-39 40-59 60-79 Men 80+ Women Prevalence of CVD in adults age 20 and older by age and sex (NHANES: 2005-2006). Source: NCHS and NHLBI. These data include coronary heart disease, heart failure, stroke and hypertension. 4 16 Per 1,000 Persons 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 35-44 White Men 45-54 Black Men 55-64 White Women 65-74 Black Women Annual rate of first heart attack by age, sex and race. (ARIC Surveillance:1987-2004). Source: NHLBI. 5 15.1 16 Prevalence (%) 14 11.4 12 10.4 10 8.3 8 6 5.1 7.9 8.6 6.2 5.6 5.1 3.6 4 2.2 2 0 All 1971-75 Women 1976-1980 1988-1994 Men 1999-2002 Prevalence of low CHD risk, overall and by sex, ages 25-74 (NHANES :1971-2002). Source:Personal communication with NHLBI 6/28/07. “Low risk” is defined as SBP <120 mm Hg and DBP<80 mm Hg; cholesterol < 200 mg/dL and BMI <25 kg/m2 and currently not smoking cigarettes and no prior MI or DM. 6 Cholesterol • What is it used for? – Lipid bi-layer – half of all lipids in your cell membranes are cholesterol, half of all your cholesterol in your body is in cell membranes – You liver uses it to create bile that helps digest fats • Where does it come from? – Diet – eggs, butter, etc – Endogenous synthesis – your liver makes it Cholesterol • Cholesterol is too waxy to move through the blood, so it is esterified • Low density lipoproteins (LDL) – Very large particles – 220 angstroms – 1600 cholesterols • High density lipoprteins (HDL) • Very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) LDLR PDB code: 1N7D • The low-density lipoprotein receptor mediates cholesterol homeostasis through endocytosis of lipoproteins. • Mutations in this gene cause the autosomal dominant disorder, familial hypercholesterolemia. • The LDL receptor gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 19, and the protein is composed of 860 amino acids. LDL receptors • Liver normally clears out 75% of cholesterol to bring the level down through a regulatory process • It also produces cholesterol – Acetic acid -> HMG CoA reductase -> cholesterol Acetyl-CoA-> HMG CoA reductase -> cholesterol Cholesterol Liver Bile Acids Cholesterol Diet LDL extracellular space cytosol receptor-mediated endocytosis LDL receptor Cholesterol Familial Hypercholesterolemia • Hypercholesterolemia – too much cholesterol in the blood • Familial – transmitted in families – +/+ normal people 150mg/deciliter • Heart att – +/- you got the mutation from one of your parents 300 mg/deciliter – -/- you got the mutation from both of your parents 600 mg/deciliter Background • In 1972, Michael S. Brown and Joseph L. Goldstein hypothesized that surmised that cholesterol overproduction results from defect in the control mechanisms that normally regulate cholesterol biosynthesis. • In 1974, Brown and Goldstein demonstrated that the lesion in FH cells is a defect in LDL binding to a receptor on the surface. What is your solution • Reduce cholesterol in diet – If reduce drastically, you only get a 10% reduction in -/- patients • Your body is more efficient at using cholesterol • Your liver produces more when the level decreases • Feed people bile acid-binding resins – Your liver will then up regulate its LDL receptors, and use more cholesterol from the blood stream – Get 20-25% reduction, but liver still increases production Solutions? • You could give them HMG CO-A reductase inhibitors that stop the liver from producing cholesterol – Statin drugs inhibit pathway to producing cholesterol – When combined with diet and bile acid-binding resins +/- patients are reduced to normal levels – This same strategy helps people that arent FH – The only people who don’t benefit are FH -/- What about FH -/• Gene therapy – Since the liver regenerates quickly, you can take out some cells, fix the mutation and inject them back and they will have the correct receptor