* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular - San Juan College
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
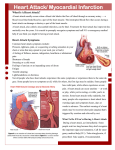
CARDIOVASCULAR Blood circulates through the body by the pumping action of the heart. The working of the heart supplies the entire body with its necessary blood and oxygen. We can keep our hearts healthy, and it is contrary to believe that heart disease is inevitable. There are several risk factors for heart disease that can be controlled. 1. Physical Inactivity Of course, people who are not physically active are more likely to have heart disease. A major misconception concerning heart disease is that to have a healthy heart that a person needs to do a heavy, duty exercise program. A walking program can accomplish the desired health affects. Other activities can be running, bicycling, swimming, and/or any other programs that will get the heart rate up to a good target heart rate. People who work out rigorously and regularly have the healthiest hearts. 2. Lipoproteins Cholesterol levels are related to the amount of lipoproteins in the blood. There is LDL, which is low-density lipoproteins, and HDL, which is high-density lipoprotein. HDL is the “good cholesterol”, while LDL contributes to deposits of fat on artery walls, that leads to heart disease. People with the least chance of cardiovascular disease have a high HDL, the higher the HDL to the ratio of total cholesterol, then the lower the possibility of having heart disease. Total cholesterol count should be under two hundred (200) with the ideal being one hundred and fifty (150). 3. Cigarette Smoking More smokers die each year from heart attacks than non-smokers, including cancer and lung disease. Smoking causes the blood vessels to the arms and legs to harden and clog. Other risk factors include coronary heart disease, cancer of the upper digestive tract and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. · · · · · Cigarette and cigar smoking, along with second hand smoke, damages the heart in a variety of ways. Nicotine over stimulates the heart Carbon monoxide replaces oxygen in the blood, reducing oxygen to the heart and other body parts Tars damage the lining of the coronary arteries Smoking increases blood clotting, raising clotting in coronary arteries and increasing the chances of heart attacks. Irreversible damage to arteries even in ex-smokers 4. High Blood Pressure Each time the heart beats the blood pressure goes up and down as the blood is forced through the walls of the blood vessels. High blood pressure, or hypertension, occurs when the walls of the blood vessels become blocked, restricting normal blood flow. When several factors are combined, including high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and high cholesterol, cardiovascular problems increase. 5. Triglycerides Triglycerides are the fats in the blood that are present after a meal. Triglycerides are usually higher in women and are more likely to contribute to heart disease. Diets high in calories, sugar, refined starches and alcohol raise triglyceride levels. 6. Weight Of course, obesity is one of the leading causes of heart problems. Even in slight obesity it is more likely to have chest pain or a heart attack than someone who is thinner. There are certain risk factors that cannot be controlled. 1. Age The older the more prone a person is to heart attacks. 2. Gender Men are more prone to heart attacks than women. 3. Male Pattern Baldness Those men that have baldness at the top of their head have an increased risk of heart attack. 4. Heredity If someone whose parents, siblings, or other close relatives have had a heart attack before the age of fifty (50), chances are increased.