* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.2 Hormones that Affect Blood Sugar - Ms. Pasic
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
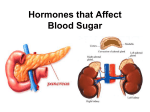
Hormones that Affect Blood Sugar Pancreatic Hormones • Produced in the islets of Langerhans. – Beta (β) cells produce insulin. – Alpha (α) cells produce glucagon. Hormonal Response to High Blood Sugar • ↑ blood sugar = release of insulin. • Causes muscle, liver and other body cells to become permeable to glucose. • Glucose stored as glycogen. • Result = ↓ blood sugar. Hormonal Response to Low Blood Sugar • ↓ blood sugar = release of glucagon. • Promotes breakdown of glycogen into glucose, which is released into the blood. • Result = ↑ blood sugar. Adrenal Glands • Each composed of two glands. 1. Adrenal medulla short-term stress. 2. Adrenal cortex long-term stress. Adrenal Medulla • Produces epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). • “Fight-or Flight Response”. – ↑ blood sugar (glycogen glucose). – ↑ HR, breathing rate & cell metabolism. – Dilation of blood vessels. – Pupil dilation. Adrenal Cortex • Produces 3 types of hormones: – Glucocorticoids. – Mineralcorticoids. – Sex hormones. Adrenal Cortex • Glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol): – Promotes conversion of amino acids to glucose – Promotes breakdown of fats to fatty acids – Decreased glucose uptake by muscles – Increased blood sugar in response to stress Fight or Flight and Blood Sugar Why block insulin during fight-or-flight response? Hormones that Affect Metabolism Two Major Glands • Thyroid Gland • Parathyroid Gland Thyroid Gland • Thyroxine (T4) • Triiodothyronine (T3) – Both need iodine to be produced. – Used to oxidize sugar and other nutrients. – More T4 in the blood will “boost metabolism” Hypothyroid or Hyperthyroid If the thyroid gland produces T4 and T3, hormones that regulate metabolism, what would happen if: a) The thyroid stopped producing T4 and T3? (hypothyroidism) b) The thyroid could not stop producing T4 and T3? (hyperthyroidism) Acronyms: • TRH – Thyroid Releasing Hormone • TSH – Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Parathyroid Glands • Four groups of cells on the thyroid gland. • Release a hormone called parathyroid hormone, or “PTH”. – PTH raises the calcium levels in the blood. Negative Feedback Calcitonin Calcitonin is also released by the thyroid, and it counter-acts parathyroid hormone (PTH) by: • Inhibiting Ca2+ absorption by the intestines • Inhibits Ca2+ reabsorption in the nephrons of the kidney Human Growth Hormone (HGH) • Too much? - Giantism • Too little? - Dwarfism • Produced in and released from the anterior pituitary gland. Andre the giant 7 ft 4 inches 520 lb. Human Growth Hormone • Cause cells to grow in size and in number. • Promotes protein synthesis. • Promotes the breakdown of fats. – ↑ GH, muscles use fatty acids as energy – Loss of fat during growth spurts