* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
Lagrangian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs paradox wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Uncertainty principle wikipedia , lookup
Monte Carlo methods for electron transport wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Mass in special relativity wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
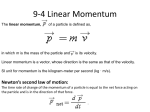
AP PHYSICS C Momentum Background A particle’s momentum p is defined as the product of its mass and velocity: p=mv Momentum is a vector quantity that may be thought of as a measurement of the effort needed to bring a particle to rest. Newton’s second law can be written in terms of the momentum of a particle. Differentiating the previous equation, we obtain: dp d(mv) dv = = m = ma dt dt dt Then substituting the force Fnet for ma, we get † Fnet = dp dt Thus the net force acting on a particle equals the time rate of change of the particle’s linear † momentum. The total momentum P of a system of many particle is the sum of the momenta of the individual particles: P = Â m i vi = Â p i i † i The momentum sum equals the total mass M times the velocity of the center of mass: P = Â mi vi = Mvcm i Differentiating with respect to time, we obtain: † dP dv = M cm = Macm dt dt But according to Newton’s second law, Macm equals the net external force acting on the system: † ÂF = F ext i net .ext = dP dt When the net external force acting on a system of particles is zero, the rate of change of the total momentum is zero, and the total momentum of the system remains constant: † P = Â mi vi = Mvcm = cons tan t i The result is known as the law of conservation of momentum: If the net external force on a system is zero, the total momentum of the † system remains constant. Example 1: During repair of the Hubble Space Telescope, an astronaut replaces two solar panels whose frames are bent. Pushing the detached panels away into space, she is propelled in the opposite direction. The astronaut’s mass is 60 kg and the panel’s mass is 80 kg. The astronaut is at rest relative to her spaceship when she shoves away the panel and she shoves it at 0.3 m/sec relative to the spaceship. What is her subsequent velocity relative to the space ship? Example 2: A runaway 14000 kg railroad car is rolling at 4 m/sec toward a switchyard. A sudden downpour fills the open-topped car with 2000 kg of rainwater. After the rainstorm, how long does it take the car to cover the 500 m distance to the switchyard? Assume that the rain comes straight down and that slowing due to friction is negligible. Example 3: A 40 kg skateboarder on a 3 kg board is training with two 5 kg weights. Beginning from rest, she throws the weights horizontally one at a time from her board. The velocity of each weight is 7 m/sec relative to her and the board after it is thrown. How fast is she propelled in the opposite direction after throwing the second weight? Assume the board rolls without friction. Example 4: A thorium 227 nucleus decays into a radium-223 nucleus (mass 223 u) by emitting an alpha particle (mass 4 u). The kinetic energy of the alpha particle is found to be 6.00 MeV. What time is the kinetic energy of the recoiling radium nucleus?