* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 17: Bohr Model of the Atom
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Measurement in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Ensemble interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
James Franck wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
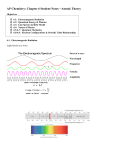
Plan for Fri, 31 Oct 08 • Lecture – Emission spectrum of atomic hydrogen (7.3) – The Bohr model of hydrogen (7.4) – Quantum mechanical model (7.5) • Quiz 5 Emission Photon Emission • Relaxation from one energy level to another by emitting a photon. • With DE = hc/l • If l = 440 nm, DE = 4.5 x 10-19 J Atomic Emission When we heat a sample of an element, the atoms become excited. When the atom relaxes it emits visible light. The color of the light depends on the element. Li When the light emitted from excited atoms is passed through a prism, we see discrete bands of color at specific wavelengths. Na K Ca Sr H Li Ba Emission spectrum of H (cont.) Light Bulb Hydrogen Lamp Quantized, not continuous Emission spectrum of H (cont.) We can use the emission spectrum to determine the energy levels for the hydrogen atom. The Bohr Model • Niels Bohr uses the emission spectrum of hydrogen to develop a quantum model for H. • Central idea: electron circles the “nucleus” in only certain allowed circular orbitals. • Bohr postulates that there is Coulombic attraction between e- and nucleus. However, classical physics is unable to explain why an H atom doesn’t simply collapse. The Bohr Model of the atom Principle Quantum number: n An “index” of the energy levels available to the electron. The Bohr Model (cont.) 2 Z 18 E 2.178x10 J 2 n • Energy levels get closer together as n increases • at n = infinity, E = 0 Identify the energy level diagram that best represents hydrogen: A B C D The Bohr Model (cont.) • We can use the Bohr model to predict what DE is for any two energy levels DE E final E initial 1 1 18 DE 2.178x10 J 2 (2.178x10 J) 2 ninitial n final 1 1 18 DE 2.178x10 J 2 2 n final ninitial 18 The Bohr Model (cont.) • Example: At what wavelength will emission from n = 4 to n = 1 for the H atom be observed? 1 1 DE 2.178x10 J 2 2 n final ninitial 18 1 4 1 DE 2.178x10 J1 2.04x1018 J 16 18 18 DE 2.04x10 J hc l l 9.74 x108 m 97.4nm The Bohr Model (cont.) • Example: What is the longest wavelength of light that will result in removal of the e- from H? 1 1 DE 2.178x1018 J 2 2 n final ninitial 1 DE 2.178x1018 J0 1 2.178x1018 J 18 DE 2.178x10 J hc l l 9.13x108 m 91.3nm The n = 4 to n = 1 transition in hydrogen corresponds to a wavelength of 97.4 nm. At what wavelength is the n = 4 to n = 2 transition expected? A. l41 > l42 B. l41 < l42 C. l41 l42 D. l42 0 Extension to Higher Z • The Bohr model can be extended to any single electron system….must keep track of Z (atomic number). 2 Z 18 E 2.178x10 J 2 n Z = atomic number n = integer (1, 2, ….) • Examples: He+ (Z = 2), Li+2 (Z = 3), etc. Extension to Higher Z (cont.) • Example: At what wavelength will emission from n = 4 to n = 1 for the He+ atom be observed? 1 1 DE 2.178x1018 JZ 2 2 2 n final ninitial 2 1 4 1 DE 2.178x10 J41 8.16x1018 J 16 hc 18 l 2.43x108 m 24.3nm DE 8.16x10 J l l H > l He 18 So what happened to the Bohr Model? Although it successfully described the line spectrum of hydrogen and other one-electron systems, it failed to accurately describe the spectra of multi-electron atoms. The Bohr model was soon scrapped in favor of the Quantum Mechanical model, although the vocabulary of the Bohr model persists. However, Bohr pioneered the idea of quantized electronic energy levels in atoms, so we owe him big. Thanks Niels Bohr! Quantum Concepts • The Bohr model was capable of describing the discrete or “quantized” emission spectrum of H. • But the failure of the model for multielectron systems combined with other issues (the ultraviolet catastrophe, workfunctions of metals, etc.) suggested that a new description of atomic matter was needed. Quantum Concepts (cont.) • This new description was known as wave mechanics or quantum mechanics. • Recall, photons and electrons readily demonstrate wave-particle duality. • The idea behind wave mechanics was that the existence of the electron in fixed energy levels could be though of as a “standing wave”. Quantum Concepts (cont.) • What is a standing wave? • A standing wave is a motion in which translation of the wave does not occur. • In the guitar string analogy (illustrated), note that standing waves involve nodes in which no motion of the string occurs. • Note also that integer and halfinteger values of the wavelength correspond to standing waves. Quantum Concepts (cont.) • Louis de Broglie suggests that for the e- orbits envisioned by Bohr, only certain orbits are allowed since they satisfy the standing wave condition. h h l p mv l wavelength m mass v velocity h Planck's constant not allowed Quantum Concepts (cont.) • Erwin Schrodinger developed a mathematical formalism that incorporates the wave nature of matter: Hˆ E • H, the “Hamiltonian,” is a special kind of function that gives the energy of a quantum state, which is by the wavefunction, Y. described Quantum Concepts (cont.) • What is a wavefunction? = a probability amplitude • Probability of finding a particle in space: Probability = * With the wavefunction, we can describe spatial distributions. The Probability Distribution for the Hydrogen 1s Orbital in ThreeDimensional Space (b) The Probability of Find the Electron at Points Along a Line Drawn From the Nucleus Outward in Any Direction for the Hydrogen 1s Orbital Hydrogen’s Electron Cross Section of the Hydrogen 1s Orbital Probability Distribution Divided into Successive Thin Spherical Shells (b) The Radial Two Representations of the Hydrogen 1s, 2s, Probability Distribution and 3s Orbitals (a) The Electron Probability Distribution (b) The Surface Contains 90% of the Total Electron Probability (the Size of the Oribital, by Definition) Quantum Concepts (cont.) • Another limitation of the Bohr model was that it assumed we could know both the position and momentum of an electron exactly. • Werner Heisenberg development of quantum mechanics leads him to the observation that there is a fundamental limit to how well one can know both the position and momentum of a particle. h Dx Dp 4 Uncertainty in position Uncertainty in momentum where… Dp D(mv) mDv Quantum Concepts (cont.) • Example: What is the uncertainty in velocity for an electron in a 1 Å radius orbital in which the positional uncertainty is 1% of the radius. (1 Å = 10-10 m) Dx = (1 Å)(0.01) = 1 x 10-12 m 34 6.626x10 J.s h 23 Dp 5.27x10 kg.m /s 12 4 Dx 4 1x10 m Dp 5.27x1023 kg.m /s 7m Dv 5.7x10 s m 9.11x1031 kg huge Quantum Concepts (cont.) • Example (you’re quantum as well): What is the uncertainty in position for a 80 kg student walking across campus at 1.3 m/s with an uncertainty in velocity of 1%. Dp = m Dv = (80kg)(0.013 m/s) = 1.04 kg.m/s 34 6.626x10 J.s h Dx 5.07x1035 m 4Dp 4 1.04kg.m /s Very small……we know where you are.