* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ADAPTATION: RELATIONSHIPS IN NATURE
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
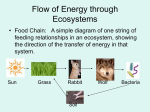
ADAPTATION: RELATIONSHIPS IN NATURE ADAPTATION • Symbiosis • Feeding relationships with an ecosystem • How cooperation and competition exist in nature. ADAPTATION • A trait that makes a living thing better able to survive in its surroundings. • Controlled by genes in the DNA of the organism. • Examples: – Speed of a cheetah. – Clear fur and black skin of a polar bear to help it blend in and absorb solar heat. – Ability of chameleon to blend into its background. – Venom of a rattlesnake to ward catch prey. NATURAL SELECTION • Process by which a condition in an organisms environment determines if it will survive long enough reproduce offspring. – Something in nature (temperature, precipitation, disease, etc…) does the selecting. – Organisms that are best suited to their environment are the ones who will most likely survive and reproduce. SYMBIOSISRelationship between species living in direct contact with each other; exchange of benefits • PARASITISM- One species benefits; other is harmed – Food/shelter in exchange for decrease in warmth and reproduction. • Fleas on a dog • MUTUALISM- Both species benefit from each other. • E. Coli bacteria in human intestines provides body with vitamin B12 while human provides home for bacteria • COMMENSALISM- One species benefits; the other is unaffected. • Sea anemone provides food and shelter; fish provides nothing. COMMUNITIES • A geographic area full of different species dependent on one another for survival • Habitat – place where an organism lives • Niche – an organism’s job within a community. • Types of organisms: – Producer – Consumer – Decomposer Feeding Relationships within an Ecosystem • Ecosystem is composed of varieties of food webs, made up of various food chains. • Each chain consists of producers, consumers and decomposers. – Producer – green plants (receive energy from sun) – Consumer • Primary (animals who eat plants) • Secondary (animals who eat other animals) – Decomposer – bacteria (breaks down organic matter; makes soil fertile) Energy Flow COOPERATION & COMPETITION IN NATURE • COOPERATION Populations within an environment interact with and assist other populations for food, shelter and protection. • COMPETITION Different populations try to occupy the same environment and end up competing for food, shelter and protection. ie: trees in a forest for sunlight; herbivores eating different plants or different plant parts Parts of the Food Web • Energy • Nutrients • Organisms Parts of the Food Web • Autotrophs – Producers – Make their Own Food using the Sun’s Energy Parts of the Food Web • Heterotrophs – Consumers – Eat plants and other organisms that can’t make their own food Herbivores • Animals that live off of and only consume Plant Material. Carnivores • Only Eat Meat Omnivores • Eat both Plants and Animals Decomposers • Decomposers breakdown dead material and return nutrients to the soil.