* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15: The Digestive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
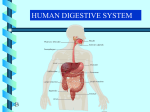
Chapter 15: The Digestive System 1. A) B) C) D) Ans: Food is digested so that it can be swallowed. it can be converted to waste. nutrients can cross the plasma membrane. for all of these reasons. C figure 15.1 2. Which letter in figure 15.1 points to the stomach? Ans: b 3. Which letter in figure 15.1 points to the esophagus? Ans: c 4. Which letter in figure 15.1 points to the liver? Ans: a 5. Which letter in figure 15.1 points to the appendix? Ans: d 6. Which letter in figure 15.1 points to the small intestine? Ans: e Page 118 7. A) B) C) D) E) Ans: The __________ digests only protein. large intestine stomach esophagus small intestine mouth B 8. A) B) C) D) E) Ans: The __________ only transports food. large intestine stomach esophagus small intestine mouth C 9. A) B) C) D) E) Ans: The __________ absorbs water. large intestine stomach esophagus small intestine mouth A 10. A) B) C) D) E) Ans: The __________ digests only starch. large intestine stomach esophagus small intestine mouth E 11. A) B) C) D) E) Ans: The __________ absorbs nutrients. large intestine stomach esophagus small intestine mouth D Page 119 12. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which are the wisdom teeth? incisors canines premolars last molars D 13. A) B) C) D) Ans: Fluoride treatment strengthens the enamel. dentin. pulp. periodontal membrane. A 14. A) B) C) D) Ans: The pharynx connects to the nose. the mouth. the larynx. all of these. D 15. A) B) C) D) Ans: Food leaving the stomach is called bolus. rugae. chyme. peristalsis. C 16. A) B) C) D) Ans: HCl is found in the stomach. esophagus. small intestine. large intestine. A 17. A) B) C) Ans: Heartburn is due to the heart's temperature rising. swallowing of hot food. contents of the stomach escaping into the esophagus. C Page 120 18. A) B) C) D) Ans: HCl digests food. activates an enzyme. acts as a lubricant. is described by all of these characteristics. B 19. A) B) C) D) Ans: Gastric glands are in the stomach. secrete juice containing HCl. secrete juice containing an enzyme. are described by all of these characteristics. D 20. A) B) C) D) Ans: What is the function of the small intestine? digests food absorbs nutrients transports undigested food to the large intestine all of these D 21. A) B) C) Ans: Which is the first portion of the small intestine? duodenum ileum jejunum A 22. A) B) C) D) Ans: Villi are in the stomach. the small intestine. the large intestine. all of these. B 23. A) B) C) D) Ans: Lacteals are located in villi. are part of the lymphatic system. absorb fat molecules. are described by all of these characteristics. D Page 121 24. A) B) C) D) Ans: The pancreas and liver are referred to as accessory organs because they are not needed for digestion. food does not enter them. they do not produce digestive enzymes. they are described by all of these characteristics. B 25. A) B) C) D) Ans: The pancreas secretes enzymes acting on proteins. fats. carbohydrates. all of these. D 26. A) B) C) Ans: The pancreas secretion of pancreatic juice is an endocrine function. exocrine function. endocrine function and an exocrine function. B 27. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which is the largest gland in the body? pancreas gallbladder liver gastric gland C 28. A) B) C) D) Ans: The emulsifying ingredient(s) in bile is(are) biliverdin. bilirubin. bile salt. all of these. C 29. A) B) C) Ans: Bile pigments are yellow substances synthesized in the gallbladder. formed from the breakdown of hemoglobin in the liver. synthesized in the pancreas. B Page 122 30. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which of these molecules is emulsified before digestion begins? protein sugar fat all of these C 31. A) B) C) D) Ans: The gallbladder is attached to the liver. is attached to the stomach. produces bile. is attached to the liver and produces bile. A 32. A) B) C) D) Ans: The liver stores glucose. converts amino acids to glucose and urea. produces blood proteins. is described by all of these characteristics. D 33. A) B) C) D) Ans: Pancreatic juice and bile are released into the duodenum. ascending colon. jejunum. descending colon. A 34. A) B) C) D) Ans: Jaundice results in a yellowish tint in the skin. may be due to red cell destruction. may be due to gallstones obstructing the bile duct. is described by all of these characteristics. D 35. A) B) C) Ans: __________ is liver damage that can be caused by the use of unsanitary needles. Cirrhosis Hepatitis Jaundice B Page 123 36. A) B) C) Ans: __________ is liver damage that can be caused by the use of alcohol. Cirrhosis Hepatitis Jaundice A 37. A) B) C) Ans: __________ is an overabundance of bile pigments. Cirrhosis Hepatitis Jaundice C 38. A) B) C) D) Ans: The large intestine includes the colon. the cecum. the rectum. all of these. D 39. A) B) C) D) Ans: The large intestine digests fat. absorbs water. stores food. is described by all of these characteristics. B 40. A) B) C) Ans: Bacteria in the large intestine break down undigested food. produce vitamins. break down undigested food and produce vitamins. C 41. A) B) C) Ans: What dietary components can help prevent constipation? water fiber water and fiber C 42. A) B) C) D) Ans: Appendicitis and diverticulosis are associated with the small intestine. large intestine. stomach. esophagus. B Page 124 43. A) B) C) D) Ans: Chemical digestion begins in the mouth. esophagus. stomach. small intestine. A 44. A) B) C) Ans: The __________ transports waste. stomach large intestine small intestine B 45. A) B) C) Ans: The __________ digests all food. stomach large intestine small intestine C 46. A) B) C) Ans: The __________ contains pepsin. stomach large intestine small intestine A 47. A) B) C) D) Ans: The hepatic portal vein carries nutrients to the small intestine. liver. pancreas. stomach. B 48. A) B) C) D) Ans: What is the most immediate energy source for the body? amino acids glucose glycogen any sugar B 49. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which is essential in the diet? glucose certain amino acids certain fatty acids certain amino acids and certain fatty acids D Page 125 50. A) B) C) Ans: Which organs of the digestive tract lack digestive enzymes? mouth and esophagus mouth and pancreas esophagus and large intestine C 51. Discuss all aspects of digestion occurring in the small intestine. Ans: In the small intestine, digestion takes place both chemically and mechanically. Absorption and transportation of the nutrients also occur. Chemical digestion takes place as a result of the actions of enzymes in the intestine and the pancreatic enzymes that are secreted into the duodenum. Absorption takes place through the villi, fingerlike projections in the intestine. 52. Discuss the liver and the pancreas as accessory glands of digestion. Ans: The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes which are transported to the duodenum for digestion. The liver produces bile, necessary for the emulsification of fats so they can be digested and absorbed. 53. Suppose you have just eaten a steak, baked potato with butter, and a salad. Explain in detail the changes that have to take place before the body can use the nutrients. Ans: The proteins in the meat will be digested by enzymes from the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine. The fats from the meat, butter, and salad dressing will be emulsified by bile from the liver and then digested by enzymes from the pancreas and small intestine. The carbohydrates from the potato will be digested by enzymes from the salivary glands, pancreas, and small intestine. 54. Explain what causes heartburn. Considering the fact that milk contains protein, would drinking milk help to get rid of heartburn. Ans: Heartburn occurs when some of the contents of the stomach escape into the esophagus. Drinking milk may temporarily stop heartburn, but the proteins in the milk will cause the stomach to increase gastric gland secretion, which could intensify the heartburn. 55. List the hormones of the digestive system and identify their sources and functions. Ans: See figure 15.8 in text. 56. List and explain the nondigestive functions of the liver. Ans: See text. 57. Why is linoleic acid considered an essential fatty acid? Ans: The liver is able to metabolize fats and convert the subunits into any form of fatty acid required by the body except for the fatty acid, linoleic acid. Linoleic acid must be present in food. 58. Compare vitamins and minerals with regard to composition. Ans: Vitamins are small organic molecules and minerals are inorganic elements. Page 126 59. How does the liver function to maintain a constant blood glucose level? Ans: Following a meal, excess glucose in the blood is removed by the liver and stored as glycogen. Between meals, as the blood glucose level begins to fall, the liver will break down glycogen molecules and release glucose into the blood. 60. Describe how the liver and kidneys work together when the liver converts amino acids into glucose. Ans: When glucose is unavailable, the liver can convert amino acids into glucose. During the process, a molecule of ammonia is removed from each amino acid. The ammonia molecules are converted into urea that is carried by the blood to the kidneys for excretion. 61. Explain the importance of sodium bicarbonate in pancreatic juice. Ans: Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the pH of chyme in the small intestine. Chyme is very acidic as a result of the stomach's secretion of HCl. The neutralization of the chyme allows for the functioning of the digestive enzymes in the small intestine, as these enzymes require a more neutral pH. 62. A) B) C) Ans: Which gastric gland cell type secretes HCL? chief mucous parietal C 63. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which enzyme produces maltose? amylase lisase maltase pepsin A 64. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which enzyme breaks down maltose? amylase lisase maltase pepsin C 65. A) B) C) D) Ans: What foods occupy the peak of the new food pyramid described in the text? cheese, milk fats, sweets red meat, white bread nuts, legumes C Page 127 66. A) B) C) Ans: Individuals with which eating disorder are most likely to hold a distorted body image? anorexia nervosa bulimia nervosa obesity A Page 128