* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download accessory digestive organs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
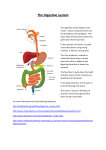
BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Rev. 2/15/07 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LECTURE 1 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 1 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli OVERVIEW OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Includes Organs of: Alimentary Canal Accessory Digestive Organs ALIMENTARY CANAL ~ Gastrointestinal Tract ~ “GIT” Muscular digestive tube . . . winds through ventral body cavity Includes: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Anus Function: Breaks down food to enable absorption through GI tract lining ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Aid digestive processes Mouth: Teeth . . . Tongue . . . Salivary Glands Liver Gall Bladder Pancreas DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 2 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli 6 FUNCTIONAL DIGESTIVE PROCESSES 1. Ingestion Intake of food 2. Propulsion ~ “Motility” Movement of food through the digestive tract Swallowing “voluntary” & reflex movement of food from mouth through the esophagus to the stomach “Peristalsis” “involuntary” movement of food through the remainder of the GI tract Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine The major mechanism of propulsion Alternate waves of contraction & relaxation of smooth muscles which surrounding GI tract organs ~ milking Peristalsis ~ longitudinal muscles Lateral movement of food thru GIT Segmentation ~ circular muscles ~ constriction Allows time for nutrients to be absorbed DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 3 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli 3. Mechanical Digestion ~ Mechanical Processing Physical process of compression, mixing or breaking food down into smaller fragments Chewing . . . Mixing . . . Churning ~ mouth & stomach Segmentation ~ intestine Local rhythmic constriction of intestine Mixes food with digestive enzymes absorption rate by moving different parts of intestine wall over food particles 4. Chemical Digestion & Secretion Secretion ~ release of water, acids, enzymes, buffers, mucous by glandular epithelium Catabolic steps & enzymatic action Carbohydrates. . . Proteins. . . Fats . . . broken down 5. Absorption Passage of digested food, minerals, water, vitamins from GI tract lumen, through wall, into blood 6. Defecation ~ Excretion of feces Elimination of “indigestible” substances through anus Both Involuntary & Voluntary Process DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 4 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM “DIGESTION REFLEXES” regulate digestive activity Extrinsic Innervation ~ CNS INVOLVED Involves long reflexes with CNS ~ via VAGUS nerve Smell, sight, thought of food ~ cerebral cortex Initiates secretion & motility ~ “stomach growling” Parasympathetic ~ stimulation increases activity Sympathetic ~ stimulation decreases activity Intrinsic Innervation ~ Autoregularion ~ No CNS Stimulated by the presence of food in GIT & stretch Short, immediate local reflex arc MAJOR hormone & enzyme secretion & motility Sensory Receptors in walls of GI tract Sense presence of digestive materials Mechanoreceptors ~ Stretch Receptors from “fill” Osmoreceptors ~ sense pH of contents Chemoreceptors ~ sense chemicals present Secretory ~ release of digestive enzymes & hormones Motility ~ peristalsis & segmentation DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 5 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli DIGESTIVE ORGAN WALLS & TISSUE LAYERS “Tube” Organs of the GI tract have same basic tissue pattern MUCOSA ~ innermost Layer ~ lines “lumen” Stratified Squamous or Simple Columnar epithelium Rapid epithelial cell turnover ~ replaced every 2-6 days Secretory Surface: mucous, enzymes, hormones Goblet Cells ~ secretes mucous lubricate & protects against bacteria & self digestion Enteroendocrine Cells ~ secretes digestive hormones Breaks down & absorbs ingested food materials Lamina Propria ~ Loose areolar connective tissue Capillaries ~ provide nourishment & allows absorption of digested materials Lymphatic tissue ~ destroy unwanted bacteria Muscularis Mucosa ~ thin muscle layer ~ initial motility Plical Folds ~ Folds in mucosa – Increases absorptive surface area DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 6 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli SUB-MUCOSA Deeper ~ beneath the mucosa layer Dense irregular connective tissue ~ tough Blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, & nerve fibers Submucosal Nerve Plexus ~ “intrinsic” autoregulation Parasympathetic & Sympathetic Innervation Regulates glands & smooth muscle in mucosa & sub-mucosa ~ “mostly secretion & initial motility” MUSCULARIS EXTERNA External to sub-mucosa layer Smooth muscle layer Inner circular layer ~ sphincters ~ “segmentation” Outer longitudinal layer ~ “peristalsis” Myenteric Nerve Plexus Innervates circular & longitudinal layers of Muscularis Externa Controls GI motility Peristalsis ~ longitudinal muscle Segmentation ~ circular muscles DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 7 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli SEROSA ~ “adventitia” layer Outermost epithelial & connective tissue layer Provides external surface to organs Covered by “visceral” peritoneum SEROUS MEMBRANES ~ Thin Serous Membranes Parietal Peritoneum Line & covering inside of abdominal wall Visceral Peritoneum Cover serosa or outer layer of digestive organs Continuous with parietal peritoneum PERITONEAL CAVITY ~ THE Abdominal Cavity Area between parietal & visceral peritoneum Contains serous fluid (transudate) which decreases friction during organ activity and movement “Peritonitis” ~ Inflammation of peritoneal membranes Very Painful . . . could be fatal Causes: Post surgical bacterial infection ~ #1 Ruptured appendix Trauma . . . Physical or chemical damage Gunshots & Stabbings Common DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 8 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli MESENTARIES ~ in peritoneal cavity Double sheets of serous membranes surrounded with fat Contain blood vessels, lymph vessels & nerves TIE-DOWNS ~ Stabilize attached & suspended organs & hold in place Prevent entanglement & twisting of digestive organs during sudden body movements Lesser Omentum ~ stabilizes portion of stomach Greater Omentum ~ stabilizes great curve of stomach Mesentery Proper ~ stabilizes small intestine Mesocolon ~ stabilizes large intestine BLOOD SUPPLY is via . . . Splanchnic Circulation Arteries branch off abdominal aorta Deliver oxygenated blood to digestive organs 25% of cardiac output normally delivered to digestive organs ~ Increases to 70% after meals Veins from digestive organs deliver venous blood to inferior vena cava Hepatic Portal Circulation ~ specialized veins that collect nutrients from digestive tract ~ Carry nutrients directly to Liver for processing via venous system DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 9 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Not All Covered in Lecture ~ Read in Text ORAL CAVITY ~ “Buccal Cavity” ~ THE MOUTH Boundaries: Lips - anterior Cheeks - lateral Tongue - inferior Palate - superior Continuous with oropharynx Oral Mucosa ~ Mucosal lined cavity Lined with stratified squamous epithelium ~ NON Keratin Protects against abrasion Superficial layers replaced hourly when sloughed off Gums (gingival), hard palate & tongue ~ ARE keratinized ORAL ORIFACE ~ opening ~ orbicularis oris muscle LIPS (labia) & CHEEKS Skeletal muscle covered with skin Lips extend from below nose to chin NO sebaceous or sweat glands in lips ~ must keep moist VESTIBULE ~ space between gum & cheek DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 10 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli PALATE Forms roof of mouth Hard Palate Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium Covers palatine bone Provides hard surface for tongue to push food against during chewing Raphae or Rugae ~ corrugated midline ridge which provides friction Prevents food from sticking to roof Soft Palate Mobile fold formed mostly of skeletal muscle Blocks nasopharynx for swallowing ~ reflex Uvula ~ finger like downward projection Separates nasopharynx from oral cavity Vibrates during expiration ~ causes snooring DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 11 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli TONGUE Interlacing skeletal muscle ~ covered by mucosa Anchors to floor of mouth ~ lingual frenulum Cannot speak normally if too restrictive ~ surgery Anterior Body ~ “oral” portion ~ NOT attached Intrinsic Muscles – confined within the tongue Allows tongue to change shape . . . NOT position Needed for speech & swallowing Posterior Root ~ “pharyngeal” portion ~ ATTACHED Extrinsic Muscles ~ connect tongue to skull Changes position of tongue, NOT shape Papillae ~ peg-like projections on surface of tongue Provides friction to manipulate food Contains “taste buds” & blood vessels ~ “GUSTATION” Mixes food with saliva ~ forms “BOLUS” for swallowing Secretes mucous ~ lubricant Secretes lingual lipase ~ enzyme that breaks fats Lingual Tonsil ~ posterior surface, lymph cells, IMMUNITY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 12 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LECTURE 2 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 13 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli SALIVARY GLANDS Inside Oral Cavity ~ “Buccal” Salivary Glands Outside Oral Cavity ~ Parotid, Sublingual, Submandibular Produce & secrete SALIVA ~ 1- 2 Liters per day FUNCTIONS & COMPOSITION of SALIVA Cleans mouth & Breaksdown food Moistens food & aids in “bolus” formation Contains: 99% H2O & Electrolytes Salivary Amylase ~ digests starch & CHO Mucin ~ mucous when dissolved in H2O Lysozyme & IgA ~ infection protection SALIVATION ~ stimulated by parasympathetic stimulation Food ingestion or thought of food stimulates chemoreceptors in mouth parasympathetic stimulation in brain stem stimulation of cranial nerves VII & IX output of watery, enzyme rich saliva SALIVATION ~ inhibited by sympathetic stimulation Dry mouth when nervous ~ “cotton mouth” DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 14 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Intrinsic Salivary Glands ~ Buccal Glands Many ~ Scattered throughout the oral cavity mucosa Continuously secrete saliva ~ keeps mouth moist Extrinsic Salivary Glands ~ MAJOR Exocrine Glands Secrete saliva only when food enters mouth ~ CNS reflex Parotid Salivary Gland Large gland anterior to ear ~ R & L Duct opens near second molar (feel flap inside cheek) Submandibular Gland Duct opens at base of lingual frenulum ~ R & L Feel smooth lumps medial to molars w/ tongue Sublingual Gland Small gland anterior under tongue Many ducts on floor of mouth MUMPS ~ contagious virus infects salivary glands ~ 5 to 9 yrs. old Vaccination ~ disease almost eliminated in US since 1967 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 15 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli MASTICAION Process of Chewing & “Bolus Formation” Teeth & Tongue mixes food with saliva & compacts food into “bolus” prior to voluntary swallowing Initial mechanical & chemical digestion of CHO with salivary amylase Initial mechanical & chemical digestion of Lipids with lingual lipase TEETH Lie in sockets within mandible & maxilla Gingiva ~ gum partial covering sockets for teeth Purpose: chew & masticate food Deciduous ~ “Temporary” Teeth ~ “Baby” Teeth 20 teeth ~ No roots ~fall out easily Erupt from 6 months of age to adolescence Permanent Teeth ~ “Secondary” teeth 32 total ~ large roots embedded in bone Erupt from 7 years to 25 years of age DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 16 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli NOT Covered in Lecture ~ Read in Text Types of Teeth Incisors ~ cutting ~ 1 root Cuspids ~ “Canine” ~ tearing ~ 1 root Bicuspids ~ “Premolars” ~ crush & mash ~ 1 or 2 roots Molars ~ crush & grind ~ 3+ roots Tooth Structure Crown Enamel covered ~ calcium ~ Hardest material in body Exposed ~ Extends above gingiva or gum Neck Below gum line ~ Connects crown & root Root Embedded in bone Incisors & Canine teeth have single root Pre-molars & Molars have 2 or 3 roots Cementum Calcified connective tissue Covers outer surface of root Attaches to root & Periodontal ligament Periodontal ligament ~ Secures tooth to bony alveolus Dentin Bone like material Forms bulk of tooth under enamel & cementum Surrounds central pulp cavity ~ Contains cells that secrete & maintain the dentin Pulp Cavity ~ central area beneath neck & crown “Pulp” ~ soft tissue structures (nerves, blood vessels, CT) DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 17 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli NOT Covered in Lecture ~ Read in Text Root Canal ~ area where pulp cavity extends into root Apical Foramen ~ opening at proximal end of each root canal ~ carries nerve & vessels TOOTH AND GUM DISEASE ~ “periodontal disease” Calculus ~ Dental Calculi Calcified dental plaque ~ “tartar” ~ Hard Common in gingival sulcus between tooth & gum Disrupts tooth-gum seal gum infection Results in “gingivitis” and/or “periodontal disease” Gingivitis ~ inflammation of the gums Usually caused by bacterial infection ~ bacteria trapping Attachment between gum & tooth breaks down ~ crevices Dental Plaque Carbohydrates (saliva), bacteria, & other mouth debris adheres to teeth . . . Bacteria metabolize CHO’s & produce acidic conditions which dissolve calcium of teeth Underlying softer tissue easily decays into dental caries Dental Caries ~ “cavities” Due to gradual demineralization of enamel & dentin Causes: bacterial decay ~ Streptococcus mutans Can lead to “root canal” ~ removal of nerve in pulp canal DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 18 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli PHARYNX ~ (Previously Discussed under Respiratory) Common passageway for food, liquids, & air Nasopharynx ~ between nasal cavity & pharynx ~ air ONLY Oropharynx ~ between mouth & pharynx ~ food, liquid, & air Laryngopharynx ~ between larynx & pharynx Mostly stratified squamous ~ some stratified columnar Skeletal muscles in wall move food toward esophagus ESOPHAGUS Muscular tube ~ 10” long between pharynx & stomach Passes from thoracic cavity through diaphragm at esophageal hiatus into abdominal cavity Joins stomach at cardiac oriface of stomach Surrounded by “gastroesophageal sphincter” SYN: Esophageal Cardiac Gastric Sphincter One way valve ~ clamps shut Keeps stomach closed when not swallowing Prevent regurgitation of gastric contents into esophagus Can relax ~ gastric fluid “refluxes” into esophagus Esophagus collapsed when food NOT passing through DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 19 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli ESOPHAGEAL LAYERS ~ same as other enteric organs Mucosa ~ Lines lumen . . . TOUGH & Abrasion resistant Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium Muscularis mucosa ~ smooth muscle Sub-mucosa ~ contains lubricating mucous glands Muscularis Externa ~ skeletal muscle anterior ~ superior ~ smooth muscle posterior ~ inferior Adventitia ~ Outer connective tissue layer DEGLUTINATION ~ SWALLOWING PHASES Buccal Phase ~ Voluntary Tip of tongue placed against hard palate Tongue contracts & propels bolus into oropharynx Pharyngeal & Esophageal Phases ~ Involuntary ~ Reflex Controlled by “swallowing center” in brain stem medulla Pharynx & esophagus are primary food conduits that propel food to stomach by peristalsis Gastroesophageal sphincter ~ Normally closed to prevent back flow into esophagus Relaxes when peristaltic wave of food approaches stomach ~ allows food to enter stomach DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 20 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli STOMACH C-shapped ~ Upper left quadrant of abdomen ~ 10” long Swallowing ---> Food bolus enters stomach gastroesophageal sphincter Begins Protein digestion Food blous converted to creamy paste ~ CHYME Stomach is Very Expandable with food & fluid ~ Up to 3X Empty stomach has large longitudinal folds ~ RUGAE Mechanical Grinding Gross Anatomy Cardiac Region ~ “cardia” nearest the heart Surrounds cardiac orifice ~ Food entry area Fundus ~ anterior dome shaped Body ~ mid-portion of stomach Greater Curvature ~ inferior ~borders intestine Lesser Curvature ~ superior ~ borders liver Pylorus ~ terminal area where stomach empties into duodenum Pyloric Sphincter ~ valve between stomach & small intestine DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 21 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Stomach Wall Muscularis Externa ~ 3 smooth muscle layers Allows churning & mixing of food Circular Layer Longitudinal layer Oblique layer Mucosa ~ Simple columnar epithelium Gastric Pits ~ deep folds in mucosa ~ entrapment Secretory “Gastric Glands” ~ MANY Produce stomach secretions ~ “Gastric Juices” Goblet cells ~ near surface ~ produce mucous Mucous Neck Cells ~ produce alkaline mucous Chief Cells pepsinogen ~ precursor to PEPSIN Parietal Cells HCL pH activates pepsin Enteroendocrine Cells Gastrin & Cholecystokinin GASTRIN ~ released by G-cells Stimulates gastric secretions & contractions CHOLECYSTOKININ Stimulates liver to produce BILE & pancreas to produce digestive enzymes DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 22 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli “Mucosal Barrier” ~ stomach lining ~ protection 3 liters of Gastric Juices produced daily ~ damaging Protects stomach from “self digestion” ~ from excess HCL Self Digestion ~ causes gastric ulcers . . . bleeding Damaged epithelial cells replaced quickly ~ in 3 to 6 days Alkaline mucous ~ neutralizes HCL acid Gastric Secretions ~ Review Table 25-2 Gastric Juices: Mucous, HCL, Pepsinogen, Gastrin, CKE Controlled by neural & hormonal Reflex PHASES Cephalic Phase ~ Long Reflex ~ Extrinsic ~ Brain controlled Smell, taste & food thought stimulates vagus nerve Digestive glands begin secretion of gastric juices before food Prepares stomach to receive food ~ stomach growling Gastric Phase ~ Intrinsic auto control ~ short reflex Stomach distension ~ stretch & chemoreceptor stimulated Releases: Mucous ~ HCL ~ Pepsinogen ~ Gastrin Intestinal Phase ~ stimulates & inhibits as acid chyme enters SI Cholecystokinin ~ stimulates liver & pancreas Secretin ~ inhibits stomach gastrin ~ ↓ gastric activity DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 23 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli SMALL INTESTINE (SI) ~ MAJOR “absorption” organ of body 90% GIT absorption of nutrients in SI ~ Takes 3-6 hours Convoluted: 20 feet long Diameter: 1.5 inches wide From stomach pylorus to large intestine at “ileocecal valve” Fills most of peritoneal cavity ~ stabilized by mesentery DUODENUM ~ first 10 inches ~ Mixing & Secretion JEJUNUM ~ Middle 7 ft. ~ MOST Absorption ~ 90% ILEUM ~ Last 10 ft. ~ Some Absorption ~ 10% H2O Gastric-Enteric Reflexes ~ stimulate secretions & motility “Intestinal Juices” secreted 1-2 liters/day Food leaving Stomach into Duodenum stimulates juices Mostly H2O . . . Lots of Mucous . . . HCO3- . . . Hormones Carrier Fluid . . . Lubrication . . . Protects against HCL Small Intestine Motility ~ takes 3 to 6 hours Mixes stomach chyme, bile & digestive juices Segmentation ~ Allows slow absorption & movement Peristalsis ~ occurs after most absorption completed Moves unabsorbed chyme into Large Intestine DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 24 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Mucosa ~ Simple Columnar Epithelium ~ absorption surface Intestinal Crypts & Plica Folds Many Villi & Microvilli ~ “brush border” 2200 feet of absorptive surface ~ 20 feet long Replaced every 3-6 days ~ rapid turnover & healing Goblet cells ~ numerous ~ produce mucous Crypts of Lieberkuhns ~ Duodenal mucosal glands Gastrin ~ stimulates secretion of mucous & motility Secretin ~ stops stomach secretions & stimulates pancreas to secrete HCO3Cholecystokinin ~ stimulates pancreas & liver Pancreas: amylase . . . lipase . . . protease Liver: Bile Brunner’s Glands ~ Duodenal sub-mucosal glands Secrete: HCO3- mucous ~ neutralize HCl chyme Lacteals ~ lymph capillaries ~ absorb fats into lymph Absorptive capillary beds ~ TO HEPATIC PORTAL VEINS Arterial Capillaries ~ O2 & nutrients DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 25 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli SMALL INTESTINE REGION ACTIVITY 90% absorption occurs in Duodenum & Jejunum (mostly) 10% absorption occurs in ileum . . . mostly H2O . . . vitamins MOST secretions occur in Duodenum Goblet Cells ~ secrete mucous Crypts of Lieberkuhns ~ Gastrin . . .CKE . . . Secretin Brunner’s Glands ~ secrete HCO3- rich mucous Hepato-pancreatic Sphincter ~ opening in duodenum Common bile duct ~ from gall bladder to duodenum Empties BILE into small intestine Pancreatic Duct ~ from pancreas to duodenum Delivers pancreatic enzymes into small intestine Amylase ~ Lipase ~ Proteases Peyer’s Patches ~ MALT ~ many lymphoid Follicles Found mostly throughout ileum Protects intestine from inhabitant bacteria ~ cleanses Ileum ~ Connects to large intestine thru ~ “ileocecal valve” DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 26 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli INTESTINAL NEURAL & ENDOCRINE REGULATION Intrinsic ~ short reflex arc ~ auto-regulation ~ MINOR Presence of food stimulates “local” cells to secrete digestive fluids & start movement ~ NO CNS involved Extrinsic ~ long reflex arc ~ MAJOR Stretch . . chemo . . taste . . smell ~ receptors stimulated Gastro-enteric Reflex ~ stimulates motility & secretion STIMULATED by Parasympathetic Nervous System Prepares stomach & small intestine to receive INHIBITED by Sympathetic Stimulation Gastro-ileal Reflex ~ opens ileocecal valve ~ “release” Gastrin secreted in stomach relaxes ileocecal sphincter & allows material to pass into cecum Vomiting Reflex ~ “Emesis” Irritation of pharynx, esophagus, stomach & small intestine causes a “protective” response Stimulates Vomit Reflex Center ~ Medulla Oblongata Reverse movement of materials from jejunum & duodenum into stomach thru pylorus Regurgitation of stomach contents into esophagus ~ expiratory muscles contract DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 27 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LECTURE 3 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 28 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli ASSOCIATED STRUCTURES TO SMALL INTESTINE PANCREAS ~ Review Table 25-3 Soft pink hand-shaped ~ Extends across abdomen Inferior to stomach ~ Between spleen & small intestine Broad Head ~ Slender Body ~ Short Blunt Tail Lumpy a & Lobular Mixed Gland ~ Both endocrine & exocrine function Endocrine ~ insulin (B) & glucagon (A) ~ hormones Regulation of blood sugar islets of langerhans ~ alpha(A) & beta cells(B) ~ 1% Exocrine ~ digestive enzymes & juices Ascinar Cells ~ Pancreatic Ascini ~ 99% Produce Digestive Enzymes ~ Digestive Juices Secretory cells ~ around pancreatic ducts Secrete: Amylase ~ Lipase ~ Protease Pancreatic Duct joins bile duct Carries pancreatic juices to duodenum Accessory Pancreatic Duct ~ Empties directly into duodenum DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 29 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Pancreatic Juices ~ contain Digestive Enzymes & HCO31200 to 1500 ml produced daily ~ 1/3 gallon Secretion controlled by Neural & Endocrine mechanism Neural Control Parasympathetic stimulation of Vagus Nerve Cephalic & Gastric Phases ~ smell & food Stimulates release of pancreatic juices Hormonal Control ~ MAJOR Mechanism Secretin ~ intestinal hormone Release stimulated by HCL in duodenum Stimulates “pancreatic cells” to produce HCO3rich juices & inhibits HCL release Bicarbonate ion ~ HCO3Neutralize acid chymes in SI from stomach Provides optimal pH for acinar enzymes Cholecystokinin ~ Gastric & Duodenal Hormone Release stimulated by food entering duodenum Stimulates pancreatic “ascinar cells” to produce digestive enzymes Amylase . . . lipase . . . protease DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 30 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Pancreatic Enzymes ~ produced by pancreatic Ascini Amylase . . . Lipase . . . Protease All must be activated in small intestines ~ protective Amylase ~ digests carbohydrates ~ EG: Sucrase Lipase ~ digests fats Protease ~ digests proteins ~ 70% Active protease will self-digest pancreas Proteases are secreted from pancreas as inactive forms ZYMOGENS ~ must be converted in small intestine Pancreas ~ inactive Zymogens Activated in Duodenum Trypsinogen trypsin Chymotrypsinogen chymotrypsin Procarboxypepditase carboxypepditase Pancreatitis ~ inflammation of the pancreas Very painful & could be life threatening in 10-15% Pancreatic enzymes could self digest pancreas Causes: Bacterial & Virus Infections Blocked Pancreatic Ducts Drugs & Alcohol DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 31 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli LIVER ~ Largest Visceral Organ Major Metabolic, Synthesis, & Detoxifying Functions Mostly in right hypochondriac & Epigastric Regions Weighs 1.5kg ~ 3.5lb ~ firm . . . dark reddish color 2 Liver Lobes ~ separated by “falciform ligament” Right & Left Lobes ~ main lobes Caudate Lobe ~ part of right lobe ~ posterior Quadrate Lobe ~ part of right lobe ~ posterior Hepatic Portal Vein Carries “nutrient & toxin rich venous blood” from the intestine directly to liver for detoxification Portal Triad ~ at “Hilus” Hepatic Portal Vein Hepatic Artery Bile Duct Hepatic Lobules – 100,000 in each lobe “Lobule” ~ basic functional unit of liver Contains: Hepatocytes . . . Sinusoids Kupffer Cells (macrophages) DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 32 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Liver Structure & Function Large blood reservoir ~ receives 25% of cardiac output Detoxify & removes metabolic wastes & drugs Hepatocytes ~ individual liver cells in stacked plate format Produces Bile ~ lipid & cholesterol metabolism Synthesizes proteins from amino acids Regulates composition of blood ~ heme . . . Hb . . . Fe Stores glucose Stores fat soluble vitamins ~ A, D, E, K, B12 Stores minerals ~ Fe from blood cell graveyard Liver Sinusoids Large porous venous capillaries between hepatocytes Receives blood from Hepatic Portal Veins “Percolates” blood in purification process Contain Kupffer Cells ~ Phagocytic Macrophages Filters & removes foreign debris& toxins from blood Removes & breaks down damaged red blood cells Central Veins ~ center of each lobule Carries “cleansed” venous blood to interlobular veins --> Hepatic Vein ---> inferior vena cava ---> return to heart DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 33 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Bile Duct System of Liver Liver continuously produces Bile ~ stored in Gall Bladder Bile ~ necessary for cholesterol & fat metabolism & removal Bile Composition ~ yellow/green base Aqueous water soluble substance Cholesterol ~ fatty substances Electrolytes ~ salt characteristics Bile pigments ~ heme & bilirubin Bilirubin ~ metabolized to urobilinogen by small intestine bacteria ~ feces color Heme ~ gives hemoglobin & RBC’s color Bile Flow ~ “enterohepatic circulation” Bile produced in hepatocytes Empties into bile canaliculi ~ tiny bile canals Run between adjacent hepatocytes Flows into hepatic ducts ---> common hepatic duct Common Bile Duct ~ direct to duodenum For immediate use or ---> Cystic Duct ---> Gall Bladder for storage DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 34 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli GALL BLADDER Thin walled green muscular sac on posterior surface of liver Stores bile not immediately needed for digestion Bile secreted into “cystic duct” when bladder walls contract Intestinal hormones stimulate bile production in liver & secretion from gall bladder Secretin ~ released from duodenum cells Cholecystokinin ~ released when acids & fats enter duodenum Relaxes “hepato-pancreatic sphincter” Bile & pancreatic juices released into duodenum via “duodenal ampulla” ~ Hepato-Pancreatic Duct Gall Stones ~ biliary calculi ~ “cholelithiasis” Caused by crystallation of cholesterol in bile Too much cholesterol or too little bile salts Pressures walls of gall bladder or block common bile duct Very painful in right thoracic area in some cases Remove gall bladder surgically ~ cholecystectomy Bile duct becomes new gall bladder for storage DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 35 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli ABNORMAL CONDITIONS: LIVER & GALL BLADDER Hepatitis ~ Inflammation of the liver Due to Viral or Bacterial infection or Alcohol Cirrhosis Diffuse & progressive chronic inflammation of the liver Liver has limited ability to regenerate after injury Involves a permanent scarring of liver with fibrous CT Due to long term alcohol intake or chronic hepatitis Treatment: liver transplant for survival Jaundice Yellow colored skin or sclera of eyes from increase bile in the blood Caused by: Blocked bile duct Overproduction of bile ~ liver disease Excess breakdown of hemoglobin Portal Hypertension High BP due to restricted blood flow through liver Causes: Blood Clot or damage to hepatocytes Can result in ascites or ruptured blood vessels & hemorrhage DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 36 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli LARGE INTESTINE ~ “large bowel” Horseshoe Shaped ~ Surrounds Small Intestine on three sides Located Between Small intestine & Anus Small intestine connects to large intestine at ileocecal valve Shorter than Small Intestine ~ much larger diameter ~ 5 ft Primary Functions: Water Reabsorption Forms & stores feces Eliminates waste ~ “defecation” Bacteria Flora ~ Synthesize B-complex vitamins & Vit. K LARGE INTESTINE ~ Cecum . . . Colon . . . Rectum . . . Anus CECUM ~ Short first part of large intestine Empties small intestine thru ileocecal valve Gastro-ileal Reflex (Gastrin) ~ relaxes sphincter Begins process of fecal compaction ~ removes water Contains ~ Vermiform Appendix ~ “Appendix” Blind pouch below ileocecal valve Lymphoid tissue ~ part of MALT Appendicitis ~ inflammation due to bacteria impaction DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 37 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli COLON ~ Long Middle portion of Large Intestine Ascending Colon ~ receives cecal material Transverse Colon Descending Colon Sigmoid Colon ~ empties into rectum “Diverticulitis” ~ Pockets in mucosa of sigmoid colon Become impacted ~ recurrent inflammation & Infection . . . Very painful CECUM & COLON ~ SPECIAL STRUCTURES Taenia Coli ~ longitudinal muscle with 3 bands Allows Colon to form pocket like sacs ~ “pucker” Haustra ~ pocket like sacs circular segmentation Epiploic Appendages ~ Fatty Appendages Small fat-filled sacs ~ provide energy & padding Connect large intestines to mesenteries ~ support Columnar Epithelium ~ few microvilli ~ very smooth Goblet Cells ~ MANY ~ Mucous ~ lubricate feces DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 38 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Rectum ~ last 6 inches ~ distends & stores feces Anal Columns Long ridges in anal canal ~ form feces shape Stratified squamous cells ~ tough & anti-abrasive Anal Sinuses Depressions of anal canal Produce mucous when compressed by feces Aids passage of feces through anal canal Anal Canal ~ last portion of rectum Anus ~ “anal orifice” ~ opening of canal to exterior Internal Anal Sphincter ~ involuntary smooth muscle External Anal Sphincter ~ voluntary skeletal muscle Hemorrhoids Superficial venous network ~ irritated & inflammed Due to faulty valves, pressure & straining, sitting too much & improper wiping after defecation Varicosities result ~ tortuous & dilated ~ irritated & itchy DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 39 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli LARGE INTESTINE PROCESSES NO breakdown processes in large intestine ~ NO villi Can function with large portions of intestine removed Large intestine propels feces toward rectum Haustral contractions occur every 30 minutes Peristalsis occurs only 3-4 times daily Absorption Large amounts of water reabsorbed Less than 10% nutrients absorbed ~ vitamins mostly 1500 ml of material enters colon ~ 200 ml excreted Feces = 75% water ~ 5% bacteria ~ 20% solid waste Defecation ~ Process of emptying feces out of anus Rectum usually empty until feces passes Defecation Reflex ~ involuntary Parasympathetic Stimulation ~ rectal stretch Sigmoid colon & rectum contract Internal anal sphincter relaxes External Anal Sphincter ~ voluntary control DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 40 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli DIGESTIVE SYSTEM IMBALANCES ~ important terminology KNOW Colon Cancer ~ common Can be fatal if not detected early ~ early detection a must Detected by: red blood in feces & colonscopy Diarrhea ~ frequent watery bowel movements Could be explosive ~ can cause severe loss of fluids Many causes: diet, irritants, viral, bacterial Treatment: anti-motility drugs Constipation ~ infrequent defecation ~ firm or hard feces Caused by excessive reabsorption of water Treatment: cathartics (laxative) & stool softner, fiber Ulcers ~ peptic, gastric, & duodenum ~ tarry blood in stool Gastritis ~ inflammation of the stomach ~ pain & nausea Enteritis ~ inflammation of the small intestine ~ cramps/gas Watery Diarrhea DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 41 BSC 1086 – Dr. Scialli Colitis ~ inflammation of the large intestine ~ mucous & watery diarrhea Inflammatory Bowel disease Chrohn’s Disease Ulcerative Colitis Ileus ~ Paralyzed Gut ~ Gas buildup ~ painful & flattulance Pyloric Stenosis ~ congenital ~ closed pyloric sphincter Diaphragmatic Hernia ~ any tear or herniation of any structure thru the diaphragm Hiatal Hernia ~ protrusion of stomach thru diaphragm hiatus Hiccups ~ spasms of the diaphragm ~ causes unknown Food Poisoning ~ Salmonella & Shigella ~ vomit & nausea Stomach Cancer ~ Gastric Cancer ~ Common Lethal Cancer Highest in countries with pickled & fermented food Treatment: Gastrectomy ~ stomach removal DIGESTIVE SYSTEM – Chapter 24 5/1/2017 42