* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download autonomic nervous system
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
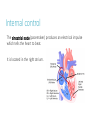
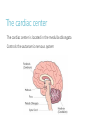
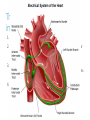
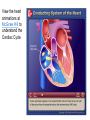
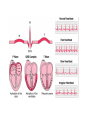
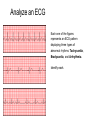
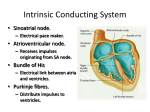
Do Now 11/5/14 1. Which chambers of the heart act as pumps? 2. Where does blood go after it leaves the right ventricle? Through what valve does it pass? 3. What are the substages of systole? Describe the relaxation/contraction of the chambers and the opening/closing of valves at each substage. 4. What are the substages of diastole? Describe the relaxation/contraction of the chambers and the opening/closing of valves at each substage. Regulation of the Heart agenda Do Now Quiz Regulation of the heart Practice RAFT ECG Exit Ticket 5 min 20 min 15 min 10 min 10 min 15 min 5 min Objectives By the end of today’s class period, I will be able to … Describe the control centers of the heart Describe how the heart receives electrical impulses Describe what an ECG is and how it is interpreted Regulation of the heart There are three regulation mechanisms of the heart 1 internal – sinoatrial node 2 external – medulla oblongata, endocrine system Internal control The sinoatrial node (pacemaker) produces an electrical impulse which tells the heart to beat. It is located in the right atrium. Two forms of external control Medulla Oblongata: located in the brain Endocrine system The cardiac center The cardiac center is located in the medulla oblongata Controls the autonomic nervous system The autonomic nervous system Baroreceptors located in the atria, aortic arch and carotid arteries monitor blood pressure and send info to the cardiac center Autonomic nervous system: Sympathetic branches increase heart rate Parasympathetic branches decrease the heart rate The endocrine system Glands in the endocrine system secrete hormones Epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine, and thyroxine increase the heart rate The Conduction system The conduction system transmits signals which control heart rate and contraction strength The pathway of an electrical impulse 1. The sinoatrial node creates the impulse 2. The impulse goes to the left atrium and the atrioventricular node (between the right atrium and right ventricle) – atria contract 3. The impulse travels down the atrioventricular bundles in the interventricular septum (middle of the heart) to millions of Purkinje fibers 4. The Purkinje fibers stimulate the ventricles to contract. The pathway of an electrical impulse 1. The sinoatrial node creates the impulse 2. The impulse goes to the left atrium and the atrioventricular node (between the right atrium and right ventricle) – atria contract 3. The impulse travels down the atrioventricular bundles in the interventricular septum (middle of the heart) to millions of Purkinje fibers 4. The Purkinje fibers stimulate the ventricles to contract. View the heart animations at McGraw Hill to understand the Cardiac Cycle Practice Discuss all of the following questions with your partner, but do not shout out. I will call on one person to answer each question Question #1 What are the 3 different mechanisms that regulate the heart? #1. Sinoatrial Node #2. Cardiac center in the medulla oblongata #3.Endocrine System Question #2 What is another term for the sinoatrial node? What does it do? Pacemaker. It creates electrical impulses to tell the heart to pump. Questions #3 The cardiac center has two branches of fibers that send messages to the brain. What is this nervous system called? What are the branches called? Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Branches Question #4 Describe the difference between the roles of the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches. Sympathetic increases HR Parasympathetic decreases HR Question #5 List the order in which an electrical impulse travels through the heart. #1 originates in the sinoatrial node #2 Travels to the Left Atrium and the Atrioventricular Node #3 Travels from the AV node down the center of the heart. #4 The signal splits to go to each ventricle through the Purkinje fibers RAFT (role audience format topic) The body contains many pathways for electrical impulses, of which the heart is just one pathway. Write a journal entry as if you are a nerve impulse the usually works in the muscular system but are sightseeing in the heart’s control center. Role – nerve impulse Audience – fellow nerve impulses working the muscular system Format – journal entry Topic – you usually work in the muscular system but you are sightseeing in the heart’s control center. Begin at the cardiac center and end at the Purkinje fibers. Electrocardiogram (ECG) Interpretation of the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time as detected by electrodes attached to the surface of the skin ECG – electrocardiogram – a recording of the electrical events (changes) during a cardiac cycle •P Wave – depolarization of the atria (atrial contraction – systole) •QRS Complex – depolarization of the ventricles (ventricular contraction, systole) •T Wave – Repolarization of the ventricles Heart Sounds – opening and closing of the valves, flow of blood into and out of the chambers, vibrations in muscle Interpreting ECGs An ECG is printed on paper covered with a grid of squares. Notice that five small squares on the paper form a larger square. The width of a single small square on ECG paper represents 0.04 seconds. A common length of an ECG printout is 6 seconds; this is known as a "six second strip." Types of Arrhythmia Arrhythmia – abnormal heart rhythm causing the heart to be unable to pump blood effectively Bradycardia – heart rate below normal range, resting heart rate under 60 BPM Tachycardia – heart rate exceeding normal range, resting heart rate over 100 BPM Analyze an ECG Each one of the figures represents an ECG pattern displaying three types of abnormal rhythms: Tachycardia, Bradycardia, and Arrhythmia. Identify each. Exit Ticket