* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20 The Heart
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
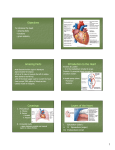
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART o The adult heart is approximately the size of _________________________. o The heart is located in the _________ cavity, between _________________. o Base is directed ____________, and the apex is directed ___________________. o The membrane surrounding and protecting the heart is called ______________. o Pericardium consists of two parts; outer is the ______________ and the inner is the __________________. o Serous pericardium is double layered; outer is ___________________ and inner is called ________________. o Visceral pericardium is also called the _______________. o Space between the parietal and the visceral pericardium is called the _____________________ cavity filled with the ____________ fluid. o Inflammation of the pericardium leads to ______________________. o The outermost layer of the heart wall is called the _______________. o The middle layer of the heart wall is called the _______________. o The innermost layer of the heart wall is called the _______________. Chambers of the Heart o How many chambers does the heart have? ____________. o The superior chambers are called ___________ and the inferior chambers are called ________________. o Each atria has a flap like extension called ______________, which functions to _____________________________. o An external groove separating the atria from the ventricles is called ________________________. o Right atrium receives blood from _______________, ________________ and ______________________. o _______________________ is an opening in the fetal heart in the inter-atrial septum, it closes after birth and becomes _________________________. o Blood moves from the right atrium to the right ventricle by passing through the ___________________ valve. o Inner wall of Ventricles have irregular ridges and folds, which are called ___________________________. o Left and right ventricles are separated from each other by _____________________ septum. o Blood passes from the right ventricle to the _________________________, through a valve called the _____________________________ . o Left atrium receives blood from the ___________ via ________________ veins. o Blood passes from the left atrium to the left ventricle through a valve called the _________________, also known as the ________________________. o Blood passes from the _________________to the aorta through a valve called the _________________________. o During fetal life, a temporary blood vessel called ________________, connects pulmonary trunk to the aorta, this blood vessels closes shortly after birth, leaving a remnant called _________________ . o What is the function of ductus arteriosus? ______________________________________________. o Between the atria and ventricles which one has a thicker myocardial wall? Why? __________________________________________ o Wall of the ________ ventricle is 2-4 times thicker than the wall of _________ ventricle, since it has to pump blood long distance to all body parts. HEART VALVES AND CIRCULATION OF BLOOD o Heart Valves open and close in response to ___________________ changes in the heart chambers. o The valve is made up of 2-3 _____________ or __________________. o Valves prevent the ____________________________. o Where are the papillary muscles located? ____________________________. o Papillary muscles are connected to the cusps by ___________________________________. o Contraction of the right ventricle causes the ____________ valves to close and the _____________ valves to open, causing the blood to flow in to ______________________________. o Where is the bicuspid valve? __________________________. o Why is it called the bicuspid valve? ____________________________. o Bicuspid valve is also called the ________________________ valve. o With each beat of the heart, the blood is pumped into two closed circuits called _____________________ and ______________________ circulation. o The ________ side of the heart is for _________________________ circulation. it receives oxygenated blood from the _____________ and distributes it to the _____________________. o The ________ side of the heart is for _________________________ circulation. it receives de-oxygenated blood from the _____________ and sends it to the _______________ for oxygenation. o Blood from the systemic circulation enters the _______________ of the heart and then passes through the tricuspid valve to the _____________________ of the heart. o Contraction of the right ventricle forces the blood to flow into the _____________________ and finally to the _______________ where gas exchange takes place. o Oxygenated blood returns to the ________________________ by four ______________________ veins. o Blood then passes through the mitral valve to the _______________________. o Contraction of the left ventricle forces the blood to flow into the _____________________ and finally distributed to the _______________ . o The two major arteries supplying blood to the myocardium are called: _______________________ and ________________________________. o Blood is drained from the atria and ventricles by _________________________ which empties into the right atrium. CARDIAC MUSCLE TISSUE AND THE CARDIAC CONDUCTION SYSTEM o Cardiac muscles fibers are connected to each other by ____________________. o Intercalated discs are rich in _______________ which allow cell-cell communication. o Cardiac muscle cells are rich in _______________ which produce ________________ for muscle contraction. o Specialized cardiac muscle cells capable of generating spontaneous action potentials are called ________________________________. o Sinoatrial node is located in the wall of ____________________. o Sinoatrial node is also called the _______________________. Why? o Atrioventricular node is located in the _______________________. o At the AV node the action potential is delayed by _______________, which allows for _________________________. o AV node passes the action potential to the ______________________________, which divides to form __________________________ and ___________________________ o The Bundle branches are located in the __________________________ and they transfer the action potential finally to the _________________________. o On its own, SA node is capable of generating an action potential every ____________ sec, which results in contraction at the rate of _________ beats/min. o Signal form the ______________ nervous system and ___________ (hormone) can modify the rate of heartbeat. • Action Potential and Contraction of Contractile Fibers o Depolarization begins by the opening of ____________ channels, causing an influx of ________________ causing rapid depolarization. o What is the plateau phase? ________________________. o Plateau phase is characterized by the opening of ________ channels, increasing the influx of ____________ which triggers muscle contraction. o o Repolarization is due the closure of _________ channels and opening of ____________ channels. o Define refractory period? ____________________________________________________. o The longer refractory period in the cardiac muscle fibers allows _______________________________________________. o What is ECG or EKG? ______________________________________________. o The instruments used to record ECG is called ___________________________. o P wave is the result of _______________________________________ and signals the onset of __________________________. o QRS complex results from ______________________________________ and signals the onset of _________________________________. o T wave results from ______________________________________ and signals the onset of _________________________________. o What does the PQ interval represent? o An abnormal ECG can indicate _____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ________________. CARDIAC CYCLE o Cardiac cycle refers to ____________________________________________________. o The average duration of cardiac cycle in an adult is ______________ sec. o The term _______________ means to contract. o The term ________________ means to relax. o The major phases of the caridac cycle are: _________________________________________________. o Atrial systole lasts _________ sec and involves the contraction of _______________. o Contraction of the atria opens the _________ valve, causing the blood to flow into the ventricles. o The total volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of this phase is called the _______________________________. o As ventricular systole begins, the pressure in the ventricle _________________, causing the closure of __________ valves. o All four valves close at this time and this brief period is called _________________________________. o When the ventricular pressure becomes grater than the pressure in the pulmonary trunk and the aorta the ___________ valves are pushed open and blood begins to flow out of the ventricles. o At the end of all ejection the volume of blood still left behind in the ventricles is called ___________________________________. o As the ventricular diastole begins, the pressure in the ventricles _______________ , causing the blood to flow back into the _________________ which closes the ____________ valves. HEART SOUNDS: o Heart sounds are caused by _________________________________________. o The act of listening to the heart sounds with the help of stethoscope is called ____________________. o Each cardiac cycle produces _________ sounds, only the first _________ are loud enough to be heard through the stethoscope. o The first heart sound is called ___________________, and is caused by ________________________. o The second heart sound is called ___________________, and is caused by ________________________. o An abnormal heart sound is called ________________________________. CARDIAC OUTPUT (CO) • Define cardiac output? _______________________________________________________ _. • Cardiac output is equal to _______________________ times _________________________. • Define heart rate? ___________________________________________________________. • Define stroke volume? __________________________________________________________. • Three factors that regulate stroke volume are ______________________, _____________ and ____________________________. • Define Frank-Starling law of the heart ___________________________________________________. • Substance that increase contractility are called ___________________________ agents, e.g. __________________________________. • Substance that decrease contractility are called ___________________________ agents, e.g. __________________________________. • What is cardiac reserve? ________________________________________________________. • How is cardiac reserve affected by exercising?_____________________________________________. Regulation of Heart Rate: o Cardiovascular center in the ___________________ is the main control center for controlling heart rate. o Receptors sending information to medulla oblongata include __________________________________________________. o Sympathetic impulses tend to _____________________ heart rate, whereas parasympathetic impulses tend to __________________ heart rate. DISORDERS o ________________________________ is a condition in which the heart muscle does not receives the required amount of blood. o _________________________ is the deposition of fatty substances, especially cholesterol and triglycerides (neutral fats) in the walls of the arteries. o __________________________ is a defect that exists at birth. o A congenital birth defect in which a segment of the aorta is too narrow, thereby reducing the flow of blood to the body ______________________________. o A condition characterized by the failure of ductus arteriosus to close after birth ___________________________. o An opening in the septum that allows oxygenated blood to mix with deoxygenated blood ___________________. o ______________________ is an irregularity in heart rhythm resulting from a defect in the conduction system of the heart. o A condition characterized by slower than normal heart rate is called ____________________. o A condition characterized by an abnormally high heart rate is called ____________________. o A condition characterized by rapid, uncoordinated heart beats ___________________. o ______________________________ is a chronic or acute state that results when the heart is not capable of supplying the oxygen demands of the body.