* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Cumberland Gap Health Science
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
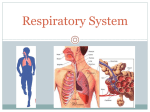
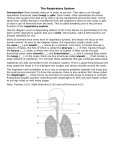
Consists of the right and left lungs the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and alveoli The respiratory system is responsible for taking in oxygen and removing carbon dioxide which is necessary for proper body function and life Lungs – right and left----left has two lobes – right has three lobes Process of respiration is controlled in the brain by the medulla oblongata. Has two openings called nostrils which air enters thru The nasal septum is a wall of cartridge that divides the nose into hollow spaces called nasal cavities Nasal cavities are lined with mucous membranes that are rich in blood vessels Air is warmed and filtered as it enters the nasal cavities Cilia – small hair like structures that filter and trap dust and other particles Cavities in the skull that provide resonance in the voice Can become inflamed and infected resulting in sinusitis Also known as the throat and lies behind the nasal cavities Divided into three sections: Nasopharynx – upper portion located behind the nasal cavities and houses the adenoids and pharyngeal tonsils Oropharynx – located behind the oral cavity ( mouth) Laryngopharynx – bottom section that branches off into the esophagus and trachea Voice box Has nine layers of cartilage with the largest thyroid layer of cartilage being the Adam’s Apple The epiglottis is a small flap that closes over the trachea when food is swallowed to prevent choking. Known as the windpipe Carries air between the pharynx and bronchi Bronchi are the right and left branches that come off of the trachea into the lungs and become smaller branches called bronchioles Apx 500 million little grape like clusters of air sacs that are located on the ends of the bronchioles This is where the gas exchange takes place in the lungs Capillaries – bring carbon dioxide from the body and carry oxygen back to cells Membrane that encloses the lungs Can become inflamed and cause lots of pain ..this is called pleurisy The diaphragm is a big muscle located under the lungs and the intercostal muscles located between the ribs are the main muscles used in respiration Process of breathing and involves two phases: Inspiration and expiration Inspiration –inhaling air into the lungs -diaphragm contract Expiration –exhaling air out of the lungs--diaphragm relaxes One inspiration and one expiration = one respiration Respiratory disorder caused by sensitivity to allergens or can be caused by stress, overexertion and infection Usually results in difficulty breathing ( dyspnea) , wheezing, coughing and tightness in the chest Inflammation of the bronchi and bronchial tubes used caused by an infection Symptoms are cough, dyspnea, rales and fever Non infectious respiratory illness that occurs when the walls of the alveoli deteriorate and lose their elasticity. This causes air to be trapped in the lungs resulting in a feeling of suffocation, dyspnea, barrel chest, pain cyanosis, prolonged expirations. Nosebleed Compress nostrils, apply cold compress and tilt head slightly forward Never tilt head back!!! Flu Symptoms include fever, chill, sore throat, muscle aches, runny inflamed nose (rhinitis), and fatigue No cure….just treat the symptoms Prevention Inflammation of the larynx and vocal cords usually caused by an infection Symptoms : sore throat , loss of voice, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) treatment: rest, no talking, meds Measurable decrease in oxygen as a result of periods of not breathing when sleeping. Very serious can lead to heart and respiratory problems if not corrected. Can be caused by obesity, smoking, high blood pressure, alcoholism, and sedatives CPAP – machine that forces air into the lungs and keeps the airway open. Inflammation of the mucous membranes resulting in a runny nose, which may be accompanied by a sore throat, sneezing nasal congestion and watery eyes. Treatment: treat symptoms Infectious respiratory illness that causes fatigue, fever, night sweats weight loss hemoptysis (coughing up blood) Health care workers have to be tested yearly Upper Respiratory Infection Highly contagious inflammation of the respiratory membranes which causes fever, runny nose, watery eyes congestion in chest and sinuses, sore throat, and hacking cough Inflammation or infection of the lungs characterized by mucous, fever, cough. Caused by a bacteria Tx with antibiotics Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Many other respiratory conditions can turn into COPD. Broad term Chronic cough, mucous and difficulty breathing Treatment includes: cough meds, bronchodilators, mucolytics