* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Inheritance
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
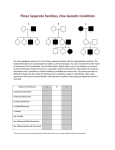
Human Inheritance Section 2-1 Human Inheritance Human Inheritance Pick a trait you inherited from a parent, such as widow’s peak, smile dimples, or curly hair. List the people in your family. Circle the family members who have the traits you chose. Identify any inheritance patterns you find. Human Inheritance Human traits Single genes such as Widow’s peak Multiple alleles such as Blood type Many genes such as Height Sex-linked genes such as Colorblindness controlled by Human Inheritance Human Inheritance A circle represents a female. A horizontal line connecting a male and female represents a marriage. A square represents a male. A vertical line and a bracket connect the parents to their children. A half-shaded circle or square indicates that a person is a carrier. A completely shaded circle or square indicates that a person has the trait. A circle or square that is not shaded in green indicates that a person neither has the trait nor is a carrier. Human Inheritance Section 2-2 Human Genetic Disorders Human Inheritance Genetic Disorder: An abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosomes. Caused by: Mutations or changes in a person’s DNA. Mutation: any change in a gene or chromosome Human Inheritance Genetic Disorders Human Inheritance Cystic Fibrosis Genetic Disorders Human Inheritance Cystic Fibrosis: •Body produces abnormally thick mucus in the lungs and intestines •Mucus makes it hard to breathe, allows bacteria to grow and makes digestion difficult •Mutation that causes cystic fibrosis is carried on a recessive allele •No cure, but treatments are given for symptoms Human Inheritance Cystic Fibrosis Genetic Disorders Human Inheritance Cystic Fibrosis Genetic Disorders Sickle-Cell Disease Human Inheritance Sickle-Cell Disease: •Genetic disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin •Makes the red blood cells sickle shaped •Blood can’t carry as much oxygen •The sickle-cell trait is codominant with the normal trait •No cure, but treatments are given for symptoms Human Inheritance Cystic Fibrosis Genetic Disorders Sickle-Cell Disease Human Inheritance Cystic Fibrosis Genetic Disorders Hemophilia Sickle-Cell Disease Human Inheritance Hemophilia: •Genetic disorder in which a persons blood clots slowly or not at all •One of the proteins for clotting is not produced •Sex-linked – caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome •No cure, but treatments are given for symptoms Human Inheritance Cystic Fibrosis Genetic Disorders Hemophilia Sickle-Cell Disease Human Inheritance Cystic Fibrosis Down Syndrome Genetic Disorders Hemophilia Sickle-Cell Disease Human Inheritance Down Syndrome: •Genetic disorder in which a person has an extra copy of chromosome #21 •Caused when chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis •People with Down syndrome have some degree of mental retardation •Heart problems associated with this disorder can be treated