* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Erosion
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Overdeepening wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
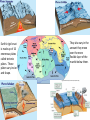
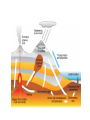
Physical Process of the Earth Create a pocket on the left hand side of your ISN On the left hand side. Title the Pocket List of Countries Create a pocket on the right hand side of your ISN Glue the following picture on the outside of your pocket Create a foldable Fold your piece of construction paper in half like a book. Lay it landscape on your desk. Glue the following items onto the front page of your foldable. Earth’s rigid crust is made up of 16 enormous plates called tectonic plates. These plates vary in size and shape. They also vary in the amount they move over the more flexible layer of the mantle below them. Type of plate movement Landforms Created Edge of one plate pushes up over another Mountains, volcanoes, ocean trenches Plate crush together, causing edges of both places to crumble and break Jagged mountain ranges Plates on ocean floor move apart New crust, islands The reasons the continents are labeled the way they are is because of continental drift. Each of the continents is on a different continental plate, therefore as the tectonic plates move, the continents move with them. Sudden Changes Fault: results when the rocks on one side or both dies of a crack in Earth’s crust have been moved by forces within Earth. Earthquakes: are caused by plate movement along fault lines. Earthquakes also can be caused by the force of erupting volcanoes. Pacific Plates Pacific plate lies at the bottom of the ocean. Over time, the edges of these plates were forced under the edges of the plates surrounding the Pacific Ocean. This plate movement created a long, narrow band of volcanoes called the Ring of Fire. The Ring of Fire stretches for more than 24,000 miles, 38,624 km, around the Pacific Ocean. Tsunamis The vibrations of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions transfer energy to the Earth’s surface and into the ocean’s water. This transfer of energy can create enormous waves to form on the water’s surface. Tsunamis create flooding and wide spread destruction to coastlines and coastal economies. Weathering Weathering is a process by which Earth’s surface is worn away by forces such as wind, rain, chemicals, and the movement of ice and flowing water. Even plants cause weathering. Plant roots and small seeds can grow into tiny cracks in rock, gradually splitting the rock apart as the roots expand. Erosion Erosion is a process by which weathered bits of tock are moved elsewhere by water, wind, or ice. Rain and moving water can erode even the hardest stone over time. When material is broken down by weathering, it can easily be carried away by the action of erosion. Categorize each of the following events as a slow change or a sudden change. Earthquake Glacier Tsunami Plate movement Volcanic eruption Wind erosion Water erosion