* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Krokodil - UCLA Brain Research Institute
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Urban legends about drugs wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
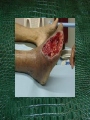
Opiates By Neal Deot & Adrina Kocharian Background on Opiates Opiates derived from poppy Some types of Opiates Heroin Morphine Codeine Background on Opiates What are they used for? Some are medically prescribed as a longterm pain killer Some are non- medically used as a drug to get high What primary effect do they have? Analgesia Krokodil UCLA Brain Institute Outreach Introduction to Krokodil Consists of Desomorphine morphine Desomorphine is similar to morphine It was intended to be created as another prescription pain killer Had very potent and severe effects so it was removed from market In Russia it resurfaced Homemade krokodil desomorphine Legality Schedule 1 Drug Absolutely prohibited in the United States Controlled internationally under Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961 So How Do People Get a Hold of It? Krokodil is made from Codeine, which is legal It is cooked and combined with extremely toxic chemicals Red phosphorous Gasoline Hydrochloric Acid Paint thinner Effects Side Effects High Effects Same drug effects as other opioids Analgesia Sedation Muscle Relaxation Euphoria Venous damage and skin and soft issue infections Rapidly followed by tissue necrosis and gangrene Scaly, gray-green dead skin forms • Thrombosis of major vessels and errosive bleeding • Large open ulcers, and gangrene • Respiratory depression • Skin and soft tissue infections to bone • Meningitis • Rotting gums and tooth loss • Bone infection, decayed structure of jaw and other facial bones • Limb rotting • Pneumonia • Sepsis • Coronary artery rupture • Sores and ulcers on forehead and skull • Gangrenous wounds • Speech impediments • Motor skill impairment • Rotting ears, nose, and lips • Liver and kidney injury Pharmacology About 10 times more potent than heroin Faster onset so more instant gratification Stronger effect than morphine and heroin The high typically lasts longer than heroin high Hard to know exact details Mode of Action dopamine Inhibitory GABA NO DOPAMINE IN SYNAPSE Mode of Action Inhibitory GABA Dopamine Krokodil DOPAMINE IN SYNAPSE Effects of Withdrawal Physical/ psychological Feeling horrible physical and psychological pain Anxiety Increased sensitivity to pain Diarrhea Runny nose Treatment in Addiction Antagonist Therapy N Overdoses are treated with a drug called Naloxone which blocks the receptor to which desomorphine binds Later, patients are maintained with Naltrexone N N Pre-Synaptic Neuron N Opioid Receptor N N Treatment for Addiction B Subsitution Therapy B Given a medication that binds to the same receptor but induces a milder effect So it’s less harmful and reduces horrible withdrawal = buprenorphine B B Pre-Synaptic Neuron B Opioid Receptor B B Heroin Background Artificially produced from morphine Gets into brain FASTER(“the rush”) Was used for pain relief but TOO ADDICTIVE Is Schedule 1 (MOST ILLEGAL) Effects Extreme euphoric rush (lasts 15-45min) Followed by relaxation state (1-3 hours) Pain relief Cough suppressant Constipation Death stop breathing dirty needle (HIV) Mode of Action Slows down neuron (brain cell) firing Increases dopamine levels High + relaxed Depressant Pharmacokinetics High begins within 30 min Lasts up to 5 hours Methods Injection (fastest, shortest lasting) Crosses blood brain barrier FAST Faster onset = more addictive Breakdowns into morphine Orally (slowest, longest lasting) Smoked Snorted Withdrawal Strong comedown Anxiety and depression Dependence Receptors are desensitized so you need MORE to feel high again Treatment Naltroxone IMMEDIATE ACTION: prevents overdose Kicks morphine off the receptors Methadone (substitution) longer lasting and less comedown Instead of stopping use, it slows it Suboxone (substitution) feels good if ingested but bad if injected Relevance Robert Downey Junior (ex-user) Philip Seymour Hoffman (death) Chris Farley (death)