* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics Lecture #28
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
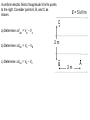
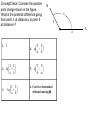
Mon. Feb. 9 – Physics Lecture #28 Electric Potential 1. Electric Work & Electric Potential Energy 2. Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential 3. Electric Potential due to Point Charges 4. Electric Potential and Electric Field Vocabulary Pile-Up Warm-Up: Discuss with your neighbors. Discuss and distinguish between Electric Charge Electric Force Electric Field Electric Work Electric Potential Energy Electric Potential Electric v. Electrostatic ConceptCheck: Would a free electron move towards higher potential or lower (electric) potential? 1. Move towards higher potential 2. Move towards lower potential 3. Neither 4. Not enough information to decide ConceptCheck: An electron and a proton are each accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 9 V. Consider the following choices: 1. Electron 2. Proton 3. Same 4. Not enough information a) Which has the larger final kinetic energy? b) Which has the larger final speed? A proton passes point A, traveling with speed 3 x 104 m/s to the right. A uniform electric field of magnitude 4.7 x 103 V/m points to the left. Describe the subsequent motion of the proton, qualitatively and quantitatively. A uniform electric field of magnitude 5 kV/m points to the right. Consider points A, B, and C as shown. E = 5 kV/m C a) Determine DVAB = VB – VA b) Determine DVBC = VC – VB c) Determine DVCA = VA – VC 2m B 2m A ConceptCheck: Consider the positive point charge shown in the figure. What is the potential difference going from point A at distance a to point B at distance b? B q b + 1. 0 1 1 a b 4. kq 1 1 a b 2. kq 1 1 a b 3. kq 1 1 b a 5. kq 6. Can’t be determined without knowing q. a A Consider four identical point charges –q held fixed at the corners of a square of side length d as shown in the figure. a) What is the electric field at the center of the square? b) What is the electric potential at the center of the square (with respect to infinity)? A fifth identical particle is placed at the center of the square and released from rest. d - - - - d A solid conducting sphere with radius 0.03 m has a net charge of +2 mC. Assume the sphere has reached static equilibrium and that there are no other charges around. a) Plot the magnitude of the electric field as a function of the distance from the center r. b) Plot the electric potential as a function of the distance from the center r. 0.03 m For some charge configuration, the potential as a function of position in a region is given by: V(x) 3x 2x 2 x 3 Where V is in volts when x is in meters. Determine the maximum magnitude of the electric field associated with this potential.