* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Potential
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
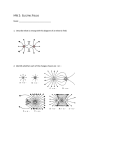
Electric Potential I Electric Potential Energy 1. A negative test charge q = -0.6 C moves through a uniform electric field of magnitude 5 N/C from point A to point B to point C, as in the picture below. A E = 5 N/C 0.5m B 0.5m C A. What is the force on the charge due to the electric field as it moves from point A to point B? from B to C? B. Recall the definition of work from Physics 1. How much work was done by the electric net force as the charge moves from point A to point B? from B to C? C. The electric force is a conservative force so there is a potential energy associated with it. What is the change in electric potential energy of the test charge as it moves from A to B? from B to C? 2. Three protons are being held at the corners of an equilateral triangle with sides of length 0.25 meters? A. What is the potential energy of the arrangement? B. If the three are released simultaneously, what is the speed of each on when they are very far apart? II Electric Potential (Voltage) 1. Consider the definition of electric potential. A. How is electric potential different from electric potential energy? B. Look again at problem I.1. 1. What is the difference in potential from point A to point B, and which point is at a higher potential? 2. What is the difference in potential from point B to point C, and which point is at a higher potential? 2. Four charges are arranged on the corners of a square with sides of length 0.25 meters. A. What is the electric field at the center of the square? +4 μC -2 μC B. What is the electric potential at the center of the square? -2 μC +4 μC 3. An electron traveling at a speed v passes through a potential difference ∆V = +2 V. Does the electron speed up, slow down, or continue at constant speed? 4. Consider the diagram of equipotential planes below. The planes are separated by 0.04 m. A. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field in the region? B. A proton is released from rest at point B. What direction will it move, or will it stay stationary?