* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download first heart sound - Easymed.club
Survey
Document related concepts
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
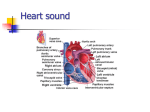
HEART SOUNDS HEART SOUNDS Heart sounds are made by the closure of the heart valves and the acceleration and deceleration or vibration of valves due to blood flow in the cardiac chambers. First and second heart sounds are normally heard during each cardiac cycle. One may hear a 3rd or 4th heart sound. Guyton and Hall WHERE WE CAN HEAR THE HEART SOUNDS Guyton and Hall FIRST HEART SOUND (S1) First heart sound is produced due to the closure of Atrioventricular valves (Tricuspid and Mitral). • It occurs at the beginning of the systole • Sounds like LUB • Frequency: 25-45 CPS (cycles per second) or Hz. • Soft when the heart rate is slow because ventricles are well filled with blood and the leaflets of the A-V valves float together before systole begins. • Time: 0.14 sec [Guyton]; 0.15 Sec [Ganongs] Guyton and Hall Ganongs FIRST HEART SOUND (S1) • First component due to turbulent rushing of blood towards A-V valves • 2nd component occurs due to the closure of the A-V valves • 3rd component is produced when semi-lunar valves open • 4th component produced due to turbulent blood flow into large arteries • The mitral component heard at the apex beat area [left 5th intercostal space at midclavicular line] • The tricuspid component is best heard in the 4th intercostal space at the left sternal border SECOND HEART SOUND (S2) • This sound is produced by the vibration associated with the closure of the semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonary) at the end of ventricular systole. • ECG relationship: The second heart sound occur soon after the T-wave of ECG. • Duration: 0. 11 sec [Guyton]; 0.12 [Ganong]. • Frequency: 50 Hz or CPS. • This sound is sharp and loud and described as “DUB.” • Two sub components • Pulmonary component heard at the level of 2nd left intercostal space. • Aortic component is heard at the level of the 2nd right interscostal space near the right border of the sternum. Guyton and Hall; Ganong SECOND HEART SOUND (S2) The S2 duration is 0.11 Sec and S1 is about 0.14 second The reason for the shorter S2 is that semilunar valves are more tight than A-V valves, so they vibrate for a shorter time than A-V valve The S2 has higher frequency than the S1 for two reasons: 1. The tautness of the semilunar valves than A-V valves 2. The greater elastic coefficient of the taut arterial walls that provide the principal vibrating chambers for the S2. Chest wall expands during inspiration Intrathoracic pressure becomes more negative to form a vacuum Venous return from the body to the right heart increases, venous return from the lungs to the left heart decreases Guyton and Hall Second heart sound has physiological inspiratory splitting THIRD HEART SOUND (S3) • Occurs at the beginning of middle third of Diastole • Cause of third heart sound • Rush of blood from Atria to Ventricle during rapid filling phase of Cardiac Cycle. • It causes vibration in the blood • Frequency:20-30 Htz • Time: 0.1 sec FOURTH HEART SOUND (S4) OR ATRIAL SOUND • Occurs at the last one third of Diastole [Just before S1] • Produced due to Atrial contraction which causes rapid flow of blood from Atria to Ventricle and vibration in the blood. • Frequency: 20 cycles / sec or less [Htz] • Third and Fourth heart sound are low pitched sounds therefore not easily audible normally with stethoscope • S3 may be heard in children and young adults SUMMARY OF HEART SOUND Heart Sound Occurs during: Associated with: S1 Isovolumetric contraction Closure of mitral and tricuspid valves S2 Isovolumetric relaxation Closure of aortic and pulmonic valves Early ventricular filling Normal in children; in adults, associated with ventricular dilation (e.g. ventricular systolic failure) Atrial contraction Associated with stiff, low compliant ventricle (e.g., ventricular hypertrophy S3 S4 HEART SOUNDS: ASSOCIATION WITH CARDIAC CYCLE VS VD 0.3Sec. 0.5 sec. 1 st Heart Sound 2 nd Heart Sound 3 rd Heart Sound 4 th Heart Sound HEART SOUNDS AS – Atrial Systole; AD – Atrial Diastole ; VS – Ventricular systole; VD – Ventricular diastole CARDIAC CYCLE: ASSOCIATION WITH HEART SOUNDS Guyton and Hall CARDIAC CYCLE: ASSOCIATION WITH HEART SOUNDS Ganongs MURMURS abnormal heart sounds, produced with excessive degree of turbulence of blood flow in the heart chambers. Murmurs occurs when there is an abnormality of the cardiac valves (stenosis and incompetence). Murmurs of aortic stenosis and mitral regurgitation occur only during systole. Murmurs of aortic regurgitation and mitral stenosis occur only during diastole. Systolic types: Pan systolic murmurs, Ejection murmurs, Late systolic murmurs. Diastolic types: Early diastolic murmurs, Mid diastolic murmurs. HEART MURMURS Heart Murmurs Valve Abnormality Timing of Murmur Aortic or pulmonary Stenosis Systolic Insufficiency Diastolic Stenosis Diastolic Insufficiency Systolic Mitral or tricuspid Ganong MURMURS HEART SOUNDS Guyton and Hall SYSTOLIC MURMURS Systolic murmurs: Majority of murmurs are systolic, usually early in systole and disturb the end of S1. S1 often appears slurred, Physicians focus on the end of S1 for soft systolic murmurs. Holo systolic murmur: refers to a systolic murmur that begins during or immediately after S1 and ends with the onset of S2. Mainly heard with mitral valve insufficiency. Pansystolic murmur: Systolic murmur begins during or immediately after S1 and continues into and complicate S2 Guyton and Hall DIASTOLIC MURMURS Diastolic murmurs: Very rare, low frequency, low intensity and best identified with the bell of the stethoscope Continuous murmurs: Common, but less than systolic, typically associated with a PDA and also arteriovenous fistulas. SYSTOLIC STENOSIS] MURMURS [AORTIC Systolic murmurs of Aortic Stenosis: Blood ejected from left ventricle through small fibrous opening of the aortic valve. Because of resistance to ejection the pressure in the ventricle increase while the pressure in the aorta is still normal. Nozzle effect is created during systole, with blood jetting at tremendous velocity through the small opening of the valve. This causes severe turbulence of blood in the root of the aorta and causes intense vibration, loud murmur occurs during systole Guyton and Hall SYSTOLIC STENOSIS] MURMURS [AORTIC Systolic murmurs of Aortic Stenosis [Continued]: Transmitted throughout the superior thoracic aorta and even into the large arteries of the neck This sound is harsh In severe stenosis sound may be so loud that it can be heard several feet away from the patient. Sound vibrations often felt with the hand on the upper chest and lower neck, a phenomenon known as a “thrill.” Guyton and Hall SYSTOLIC MURMURS: REGUGITATION MITRAL Systolic Murmur of Mitral Regurgitation. In mitral regurgitation blood flows backward through the mitral valve into the left atrium during systole. This also causes a high-frequency “blowing,” swishing sound similar to that of aortic regurgitation but occurring during systole rather than diastole. The sound of mitral regurgitation is transmitted to the chest wall mainly through the left ventricle to the apex of the heart. Guyton and Hall DIASTOLIC MURMURS [MITRAL STENOSIS] Diastolic Murmur of Mitral Stenosis: In mitral stenosis, blood passes with difficulty through the stenosed mitral valve from the left atrium into the left ventricle. Because pressure in the left atrium rises above 30 mm Hg, large pressure differential forcing blood from left atrium into the left ventricle does not develop. Consequently, the abnormal sounds heard in mitral stenosis usually weak and very low Guyton and Hall DIASTOLIC MURMURS REGUGITATION] [AORTIC Diastolic Murmur of Aortic Regurgitation. In aortic regurgitation no abnormal sound is heard during systole, but during diastole Blood flows backward from the high-pressure aorta into the left ventricle causing a “blowing” murmur of high pitch with a swishing quality heard maximally over the left ventricle. This murmur results from turbulence of blood jetting backward into the blood already in the low-pressure diastolic left ventricle. Guyton and Hall HEART MURMURS CAUSED BY VALVULAR LESIONS Machinery murmur of patent ductus arteriosis [PDA] In PDA blood flows from the aorta to the pulmonary artery Murmur during systole and diastole. The murmurs during systole is much more tense than in diastole because the pressure in aorta is higher during systole than diastole.