* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Producers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
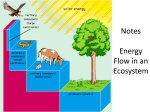
Biology CP Homework • Food Chain and Food Web Quiz 9-4-15 Ch.14.1 p.258 1. What is the difference between a community and a habitat? A community is the organisms that live in a particular place whereas a habitat is the place they live. Ch.14.1 p.258 2. Explain the important role producers play in ecosystems? Producers are the fundamental source of nutrition (consumable energy) in an ecosystem. Ch.14.1 p.258 3. In which trophic level would you place humans? Explain. Omnivore humans would be near the top. Herbivore humans would be near the bottom. Ch.14.1 p.258 4. Why are there fewer lions than zebras on the African Plains? Only 10% of energy is passed to each trophic level. Got Energy Activity • Need: Scissors, tape, Got Energy Worksheet, half sheet of animals • Do: Answer Questions and make food web Energy Flow • Energy is needed to power life! • Energy flows through the ecosystem. Producers • Organisms that make their own food without consuming another living organism are called producers. • Also known as autotrophs Producers: Photosynthesis • Sunlight is the main source of energy for most ecosystems on Earth. • Organisms use a process called photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy. Producers: Photosynthesis Producers: Chemosynthesis • Some ecosystems rely on energy obtained from organisms that store energy in inorganic chemical compounds. • Organisms use a process called chemosynthesis to convert inorganic chemical compounds into energy. Producers: Chemosynthesis Consumers • Organisms that cannot make their own food or energy have to consume (eat) other organisms. This organisms are called consumers. • Also called heterotrophs. Consumers: Herbivores • Eat Producers (plants) Consumers: Carnivores • Eat consumers (meat) Consumers: Omnivores • Eat producers and consumers (plants and animals) Consumers: Detritivores • Eat dead organisms Consumers: Decomposers • Eat/break down decomposing material Energy Flow • Energy flows through an ecosystem in one direction from the sun or inorganic molecules to producers (autotrophs) and then to consumers (heterotrophs). Food Chain • Food Chain is a series of steps in which organism transfer energy by eating and being eaten. Food Web • Food Web is all of the feeding relationships among various organisms in an ecosystem. Food Web • Each step on a food web is a trophic level. Ecological Pyramid • An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows the relative amounts of energy or matter contained at each trophic level of a food web. Ecological Pyramid • Only about 10% of the energy available within one trophic level is transferred to organisms at the next trophic level.