* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Main page ==> oil-refining http://www.ycysoft.com Copyright ycysoft
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
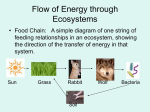
OUR PLANET Unit 1-3a Energy in the Ecosystem I Give Up. What’s black & white and read all over? How Do Ecosystems Work? The Sun - The source of all energy on Earth* Without the sun, our planet would be cold and dark without anything to eat and fresh water would be scarce! Producers (Autotroph) – Make their own food; Photosynthesis change solar energy into chemical energy Without producers there wouldn’t be any food for the… Consumers (Heterotrophs) – Obtain energy from other organisms; Ex: Animals, Fungi and many bacteria Which are these? Consumer Producers ??? Types of Consumers There are four different types of consumers… Types of Consumers Energy Source Examples Herbivore producers cow, turtle Carnivore Omnivore Decomposer other consumers producers & consumers decaying matter snake, vulture people, bears fungi & bacteria Why is a vegetarian still considered an omnivore? *Deep Ocean Ecosystems Without the sun, life on earth could still exist due to… Chemotrophs – Bacteria that get energy from hydrogen sulfide which is released from deep ocean volcanic vents These bacteria support entire ecosystems that have never seen the sun and survive tremendous pressure! This is the basis for the idea that life could exist on Titan, one of Saturn’s moons, that is almost 1 billion miles from the sun. A volcanic core appears to keep it’s ocean from freezing. Storing & Using Energy What does a plant need to survive? Photosynthesis uses Water, Carbon Dioxide and Sunlight to create Sugar (energy stored as glucose) & Oxygen (waste) H2O + CO2 + Energy C6H12O6 + O2 While plants use photosynthesis to create stored energy, plants & animals have another process to use the energy… Cellular Respiration – Plants and animals use Sugar and Oxygen to get energy, releasing water & carbon dioxide C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2 + Energy What do you notice about these equations? Close Your Notebooks… What have you learned in this unit? 1. Describe how energy from the sun can be used by a wolf. 2. Describe the four different types of consumers. 3. How is matter from producers recycled in the environment? 4. How could life exist on one of Saturn’s moons? 5. Explain the similarities and differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. OUR PLANET Unit 1-3b Energy Transfer How Energy Flows Trophic Level – Each step in which energy and matter are transferred within an ecosystem; Ex: Energy pyramid Most of the energy taken in by an organism at one trophic level is used before that energy can be passed to the next level. Organisms use their energy to complete life’s processes. Which level has the highest population? Which has the lowest population? How Energy Flows The 10% Law – Only 10% of the energy at each trophic level is passed on to the next and 90% is used or lost. Carnivores are found at the top. And the remaining ~50 Kcal are passed on to the lion. Next are the herbivores. And only ~500 Kcal are passed on to the giraffes. At the base of every pyramid are producers. They make ~5,000 Kcal of energy/m2 each year. A Closer Look At Trophic Levels Food Chain – A specific diagram that shows how energy flows from one organism to another Why are the bald eagle’s eggs breaking? Thin eggs were being crushed by the mom before they could hatch. A look at the food chain showed that DDT, a powerful pesticide, became more concentrated as it moved up each trophic level. In part, due to the damage caused by DDT, bald eagles were on the endangered species list from 1973-2007. Seeing The Big Picture Food Webs – Shows multiple, interconnected food chains; Show more accurately how organisms survive in an ecosystem Each year, 1-3 million people are killed by a deadly disease known as… Malaria! It is transmitted, person to person, by the mosquito. Wouldn’t it be great if we could kill all the mosquitoes in the world? How many other creatures would be affected if mosquitoes vanished? And who would fill its niche? Where Did All Of These Come From? Invasive Species – A foreign plant/animal that negatively affects an ecosystem; Species grow with few predators • Zebra Mussel – Introduced by ballast water from Russia, they’ve caused $500 million in damage to pipelines each year & as filter-feeders, they poison native species • Asian Long-Horned Beetle – Arrived in wood from China, they burrow holes into the center of Maple, Willow, Birch and Elm trees ultimately killing them; If you see them in New Jersey call… 1-866-Beetle1 Close Your Notebooks… What have you learned in this unit? 1. What is a trophic level? 2. Why does an energy pyramid typically only have 4-5 levels? 3. Which types of organisms are found at each level of an energy pyramid? 4. Give an example of when studying a food chain would be important. 5. Give an example of when studying a food web would be important. OUR PLANET Unit 1-3c Species Interactions What’s A Niche? Niche – A species role in the environment including… (Let’s use squirrels for example…) • Its habitat (Squirrels are common in forests and build nests in trees) • Everything it needs to survive (It eats nuts, bird eggs and other small organisms) • Every interaction it has with other species (It disperses nuts, limits other populations, its waste fertilizes the soil, & it is food for many predators) Overlapping Niches Because squirrels are not the only species to live in trees, eat nuts, or hoard for the winter so this creates… Competition – When species, or individuals, attempt to use the same limited resource Sometimes species don’t even recognize their competition! Indirect Competition – Occurs even when the species may never come into direct contact Ex: An aphid during the day, may feed on the same plant that is eaten at night by a spider mite. How Species Interact There are four types of species interactions Predator-Prey – When one organism uses another as a source of food; Ex: Wolves and rabbits Parasite-Host – A parasite lives on or in a host without killing it immediately; Ex: Dog with ticks & heartworms Why doesn’t the parasite want to quickly kill the host? How Species Interact Mutualism – A relationship between two species in which both benefit; Ex: Acacia trees & ants What are the benefits for the tree and the ants? Commensalism – One organism benefits but the other isn’t helped or harmed; Ex: An orchid and trees How does the orchid benefit by climbing the tree? Who Is Who? Mimicry – When two species have a similarity (in sound, scent, behavior, or appearance) that offers protection • Milk Snake – Harmless but shares the same colors as the deadly coral snake; Red on black-Friend of Jack but Red on Yellow-Kill a Fellow… Can you tell which is which? • Dead Leaf Mantis – What do you think this praying mantis is trying to mimic? Can you see her? Close Your Notebooks… What have you learned in this unit? 1. How big is your niche? 2. What causes competition and who benefits from it? 3. Compare & contrast parasitehost with predator-prey. 4. Describe the mutualistic relationship between a termite and the bacteria in its stomach. 5. Why are there so few examples of relationships that are purely commensalism?