* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Animal kingdom
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
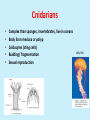
The Animal kingdom Animal diversity • Eagle (bird) and butterfly (insect) both have wings • Animals show diversity in body structures and function Classification of animals • Two main groups • Based on the absence or presence of backbone (vertebral column) • Invertebrates (animals without backbone) • Vertebrates (animals having backbone) Classification of animals Invertebrates Invertebrates • • • • Most animals on the Earth are invertebrates Do not have a backbone Do not have any bones in their body Sponge, spider, snail, jelly fish, worms Invertebrate Phyla • • • • • • • • Sponges Cnidarians Flatworms Round worms Mollusks Annelids Arthropods Echinoderms Sponges • • • • • • Live in ocean Asymmetric body Tube-like body having small pores Sweeps water through pores into the tubes Special cells filter and digest food material Reproduce asexually (fragmentation) and sexually Cnidarians • • • • • Complex than sponges, invertebrates, live in oceans Body form medusa or polyp Cnidocytes (sting cells) Budding/ fragmentation Sexual reproduction Jelly fish Flatworms • • • • Simplest worms, live in water, damp soil, some are parasites More complex body, bilateral symmetry Head with eyespots Reproduce sexually or fragmentation (asexually) Tapeworm Planaria Roundworms • Invertebrates with coelom, bilaterally symmetrical • Fresh water, damp soil, parasites • Some eat other small organisms Ascaris Mollusks • • • • • Invertebrates, oceans, freshwater, land Specialized tissue “mantle” – secretes shell Some have muscular foot to move e.g. snails Others have tentacles e.g. squids Reproduce sexually Snail Oyester Annelids • Found in oceans and on land, bilateral symmetry • Segmented worms (repeated body segments) • Hermaphrodites (have both male & female sex organs in the same organism) Leech Earthworm Arthropods • Most diverse group, presence of exoskeleton, Water, air, land • Segmented body – head thorax, abdomen • Spider, bee, fly, mosquito, grasshopper, centipede, beetle, shrimp, cockroach, crab Echinoderms • Spiny skinned – exoskeleton having spines, live in ocean • Eat organic matter or other organisms Starfish Sea urchin Vertebrates Vertebrates • • • • • • Belong to phylum Chordata Notochord - develops into backbone Backbone – a column of several bones called as vertebrae Backbone is a part of endoskeleton Muscles are attached to bones – movement Divided into five groups – Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals • Live on land or in water • Herbivore, carnivore or omnivore • Separate genders (one gender per individual) Fish • • • • More than half of vertebrate species are fish Jawless, cartilaginous and bony fish Marine and freshwater Ectothermic Cartilaginous Jawless Bony fish Amphibians • • • • • • Water and land Require water to lay eggs As tadpole live in water Frogs, toads, salamanders Thin moist skin Ectothermic Frog Salamander Reptiles • • • • • Live on land, do not require water to lay eggs Crawling animals Turtles, alligators, snakes Reproduce sexually Ectothermic Birds • • • • • Some live on land, others in water, or both Flying birds and flight less birds Feathers – maintain temperature and flying Reproduce sexually Endothermic Parrots Penguin Pelican Mammals • Hair on body, external ears, produce milk • 3 types – monotreme (lay eggs), marsupials (pouched) and placental (fetus is connected to uterine wall through placenta) mammals • Reproduce sexually • Endotherms Lay eggs Pouched Placenta