* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Local anesthesia
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Epinephrine autoinjector wikipedia , lookup
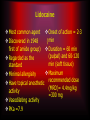
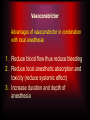
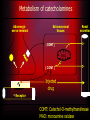
Local anesthesia Lecture 3 Composition of local anesthetic solution • Local anesthetic agent • Vasoconstrictor • Preservative • Reducing agent • Fungicidal agent • Sodium chloride and distilled water Local anesthetic agent Amide Lidocaine Mepivicaine Prilocaine Articaine Bupivicaine Etidocaine Ester Cocaine Procaine Propoxycaine back Lidocaine Most common agent Onset of action = 2-3 Discovered in 1948 ( min first of amide group) Duration = 60 min (pulpal) and 60-120 Regarded as the min (soft tissue) standard Maximum Minimal allergisity Have topical anesthetic recommended dose (MRD)= 4.4mg/kg activity =300 mg Vasodilating activity PKa =7.9 Metabolism and safety Lidocaine metabolized in liver and excreted in urine (10% unchanged completely) On CNS large dose cause initial stimulation followed by depression ( anticonvulsant effect) On CVS large dose cause myocardial depression ( used in ventricular tachycardia) Maximum dose calculation Available concentration =2% =2gm in each 100 ml /100 →→→→ 0.02gm/ml = 20 mg/ml *1.8ml/dental cartridge =36 mg /dental cartridge 300 /36 = 8.3 dental cartridge (MRD) back Mepivicaine Less toxic than Same potency to lidocaine lidocaine Used for child and Similar to lidocaine geriatric patient when in metabolism and vasoconstrictor excretion contraindicated Same onset MRD =4.4 mg/Kg= slight extended 300mg duration (weak 2% → 8.3 cartridge vasodilatation) 3% → 5.5 PKa =7.6 cartridge back Prilocaine (citanest) Same potency to lidocaine Less toxicity Less vasoldilating activity PKa =7.9 MRD =6mg/kg 3% → 7.5 cartridge 4% → 5 cartridge Prilocaine (citanest) Metabolism occur mostly in liver into orthotolidine which can cause methemoglobulinemia in susceptible individual (patient with hemolytic anemia) if used in large dose → poor oxygen carrying capacity resulting in cyanosis Clinically patient may have cyanosis in the lip, mucous membrane and skin. Patient may also have respiratory distress in severe cases Treatment by methyline blue 1% injection 1-2 back mg/kg IV/5min Articaine Slightly more potent than lidocaine Similar toxicity, and vasodilating activity Some literature present a cross allergisity with sulfate so it is best to be avoided in patient allergic to sulfonamide MRD =7mg/kg 4% → 7 cartridge Similar to prilocaine in producing methemoglbulinemia back Bupivicaine Four times more Dental Indication potent than lidocaine 1. Prolonged dental and 4 times less toxic procedure Slower onset (5-10 2. Expected post min) and extended operative pain duration lasting for 90-180 min Contraindication MRD =1.3mg/kg Child and mentally 0.5% → 10 cartridge retarded patient back Etidocaine Similar to bupivicaine except: More toxic than lidocaine MRD= 8mg /kg available in1.5% → 13 cartridge In general surgery both indicated in prolonged procedure when uses of vasoconstrictor is contraindicated systemically or locally back Local anesthetic agent Amide Lidocaine Mepivicaine Prilocaine Articaine Bupivicaine Etidocaine Ester Cocaine Procaine Propoxycaine back Cocaine Oldest anesthetic agent used since 18th century It is the only agent having a vasoconstrictor activity( sympathomimatic activity) and can be used topically because it is rapidly absorbed through mucous membrane It has liability for dependence which makes its uses very limited back Procaine Has 50% potency and toxicity than lidocaine It has prominent vasodilating activity which reduce its duration PKa =9.1 (slow onset) MRD =1000mg Its hydrolyses occurs in plasma by enzyme pseudocholine esterase High incidence of allergisity back Propoxycaine More potent and more toxic than lidocaine Has rapid onset and adequate duration It is available in combination form with procaine to reduce toxicity 0.4% propoxycaine + 2% procaine =24mg/ml MRD =400 mg It is indicated only in patient allergic to amide form of local anesthesia back Composition of local anesthetic solution • Local anesthetic agent • Vasoconstrictor • Preservative • Reducing agent • Fungicidal agent • Sodium chloride and distilled water Vasoconstrictor Advantages of vasoconstrictor in combination with local anesthesia: 1. Reduce blood flow thus reduce bleeding 2. Reduce local anesthetic absorption and toxicity (reduce systemic effect) 3. Increase duration and depth of anesthesia Types of vasoconstrictor 1. Adrenergic agonist agent 2. Vasopressin Adrenergic agonist agent (sympathomimetic agent) - catecholamine Mode of action: 1. Direct (binding) 2. Indirect (displacing) 3. Mixed action Sympathetic receptors: 1. 1 vasoconstriction 2. 2 Reuptake 3. 1 Cardiac stimulation 4. 2 Vasodilatation Affinity of adrenergic agents on receptors 1 2 1 2 Adrenaline ++ ++ ++ ++ Nor - adrenaline ++ ++ - - Levonordephrine + ++ ++ + Phenylphrine + + - - HO HO CH CH NH OH 1 2 1 2 Epinephrine H Levonordefrin CH 3 CH 3 H H Norepinephrine H Adrenergic Receptor Binding + NH 3 VII VI HO V HO O H I N+ IV II III COO – Adrenaline Synthetic or natural abstract from adrenal medulla . It is the most common and potent vasoconstrictor. Concentration: Expressed in ratio gm: ml / 1: 100000 Meaning 1 gm in 100000 ml Concentration 1:100000 means: =1 gm in 100000 ml =1000 mg in 100000 ml = 0.01 mg /ml In single dental cartridge (1.8 ml) = 0.018 mg =18 g (microgram) Adrenaline availability (concentration) 1:1000 (alone) is used for control of bleeding? contraindicated in arterial bleeding- Rebound bleeding 1:50000 for surgery where hemostasis is necessary 1:80000 and 1:100000 commonly used concentration 1:200000 low concentration used for medically compromised patient (vasoconstrictor contraindicated) and where hemostasis is of little importance Maximum recommended dose (MRD) MRD (mg) Available Potency concentration Adrenaline 0.2 100 Nor - adrenaline 0.34 1:30000 25 Phenylphrine 4 1:2500 5 levonordephrine 1 1:20000 15 Other adrenergic agonist vasoconstrictor Nor-adrenaline and phenylphrine have prominent alpha activity comparing to beta activity which may result in severe vasoconstriction (increase blood pressure) and ischemia. It is contraindicated in patients with cardiac problem. It is contraindicated in terminal extremities Metabolism of catecholamines Adrenergic nerve terminal Extraneuronal tissues Renal excretion [ COMT] MAO [ COMT ] Injected drug Receptor COMT: Catechol-O-methyltransferase MAO: monoamine oxidase Side effects and overdose • CNS: Fear apprehension palpitation • CVS: Cardiac stimulant effects , increase blood pressure and rebound bleeding at prolonged dental procedure. Causes of rebound bleeding: Adrenaline selectivity on receptor: Low concentration effect High concentration effect Limitation of adrenergic vasoconstrictor • Precautions/contraindications – Uncontrolled Cardiovascular disease – Uncontrolled thyrotoxic goiter • Drug interactions – Tricyclic antidepressants – General anesthetics – Adrenergic antagonists – COMT inhibitors – Not MAO inhibitors Vasoconstrictors (epinephrine, Levonordefrin) with Tricyclic antidepressants (imipramine, desipramine) Hypertensive and/or cardiac reactions – are more likely. Use epinephrine cautiously; avoid Levonordefrin. Vasoconstrictors (epinephrine, Levonordefrin) with Volatile anesthetics (halothane) Increased possibility of cardiac – arrhythmias exists for some agents. Vasoconstrictors (epinephrine, Levonordefrin) with Nonselective beta blockers (Propranolol, Nadolol) Hypertensive and/or cardiac reactions – are more likely. Use cautiously. Vasoconstrictors (Epinephrine, Levonordefrin) with COMT inhibitors (Tolcapone, Entacapone) Hypertensive and/or cardiac reactions – are more likely. Use cautiously. Consideration MRD for cardiovascular disease patient = 0.04 mg of adrenaline = 2 dental cartridge of 2ml 1:100000 concentration adrenaline Controversy still exists on using adrenaline in controlled cardiovascular diseased patient. Explain why? Uses of small amount available in dental cartridge is better than exposing the patient to failure anesthesia which produce pain and bleeding that can stimulate fear and increase intrinsic adrenaline that may have more dangerous effect than extrinsic adrenaline Vasopressin (Felypressin) Synthetic analogue of posterior pituitary hormone (Octopressin) Act on V1 receptor that is found on venous site of microcirculation It posses mild hemostatic effect and used only when other vasoconstrictor contraindicated Available concentration = 0.03 IU/ml in combination with prilocaine 2% or 3% MRD= 0.27 IU back Preservative Maintains sterility of the solution Caprylhydrocuprienotoxin used for this purpose Methylparaben used in the past but nowadays not used ? back Reducing agent (in vasoconstrictor containing solution) Antioxidant (reducing agent) used to prevent oxidation of vasoconstrictor that may deteriorate on exposure to sunlight (brown discoloration) Sodium metabisulfite used for this purpose On exposure to oxygen it will diffuse through the rubber of the cartridge where sodium metabisulfite will be converted to sodium metabisulfate (oxidized) Oxidized instead of vasoconstrictor Why is an old solution more acidic? Painful back ? Irritant? Fungicide Thymol Sodium chloride and distilled water (ringers solution) For isotonicity of injected solution to reduce edema and discomfort on injection