* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ether - TeacherWeb
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Aromatization wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
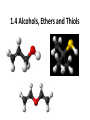
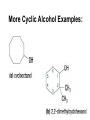
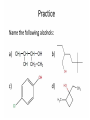
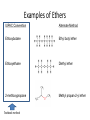
Agenda Today • Lesson on Naming and Structure of: – Alcohols – Ethers – Thiols • Practice Problems 1.4 Alcohols, Ethers and Thiols Hydrocarbon Derivatives Alcohols, Ethers and Thiols • An alcohol contains the hydroxyl (-OH) functional group ethanol • An ether contains an oxygen atom between two carbon atoms in a chain methoxyethane • A thiol contains the sulfhydryl (-SH) functional group ethanethiol dimethyl ether Question??? • Which has a higher melting point? Methane or methanol??? Question??? • Which is more soluble in water? Methanol or ethanol?? • Why are alcohols very useful as solvents? Naming Alcohols •The hydroxyl group can also be attached to an aromatic hydrocarbon. •Phenol: An organic compound that has a hydroxyl group bonded to a benzene ring. **In a case where benzene has multiple hydroxyl groups, benzene is used as the root word. More Cyclic Alcohol Examples: Alcohols Containing More Than One Functional Group: • In some cases, a different functional group takes precedence over the alcohol. In these cases, the –OH group is treated as a substituent, called hydroxy. • This applies later with carboxylic acids, aldehydes, ketones, etc. Naming Alcohols with other Functional Groups • Later, when we begin naming other types of compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids; it will be necessary to name the (-OH) group as a branch. • In this case, the hydroxyprefix is used. • When there is a multiple bond in the chain, the –OH group takes precedence (ex. Pent-4-ene-1-ol) Ethers • Are organic compounds containing an oxygen atom between two carbons atoms in a hydrocarbon chain. Naming Ethers • Identify the two alkyl groups in the chain. • Write the prefix of the shorter alkyl chain, then the suffix – oxy, followed by the complete name of the longer alkyl chain (alkane name). • A number is required to indicate the carbon in which the oxygen is attached to in the longer chain for chains 3 carbons and greater. • An alternate naming system is to use the names of the two hydrocarbon chains, in alphabetical order, followed by the word “ether”. Examples of Ethers IUPAC Convention Alternate Method Ethoxybutane Ethyl butyl ether Ethoxyethane Diethyl ether 2-methoxypropane Methyl propan-2-yl ether Textbook method Intermolecular Forces in Ethers • Ethers lack the hydroxyl group that alcohols have, preventing them from having any type of hydrogen bonding. • However, the C-O bond is polar, thus, ether molecules are somewhat polar, just not as polar as alcohols. • The intermolecular forces in ethers are stronger than those in alkanes but weaker than those in alcohols. • The C-O bond also allows dissolving of polar substances while the C-H bond allows the dissolving of non-polar substances. Uses of Ethers • Ethers were once used as anesthetics to eliminate pain during medical procedures. • Due to its flammability and volatile behaviours, it has largely been reduced in the medical field. • Currently, the majority of its uses comes as a solvent for fats and oils. Thiols • Are organic compounds that contain a sulfhydryl group (–SH). • Cause compounds to be more polar in nature. • Commonly have a strong odour (garlic, skunk). • Are often added to natural gas (methane) to make leaks easier to detect. • To name thiols, add thiol to the ending of the alkane name. HSCH3 methanethiol Practice Questions • Page 34 #1, 2 • Page 39 #1, 2























![Group Activity 3 [10 PTS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010780770_1-3445600a9b56e890a0f283c789afe8fb-150x150.png)










