* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Normal Blood Cell Morphology PowerPoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
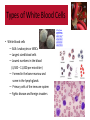
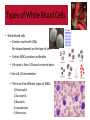
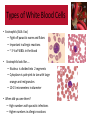
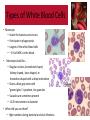
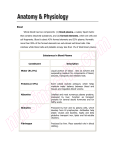
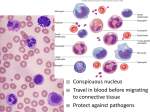
Normal Blood Cell Morphology Types of White Blood Cells • White blood cells — AKA: Leukocytes or WBCs — Largest sized blood cells — Lowest numbers in the blood (4,500 – 11,000 per microliter) — Formed in the bone marrow and some in the lymph glands — Primary cells of the immune system — Fights disease and foreign invaders http://ww w.giantmicr obes.com/ us/product s/whiteblo odcell.html Types of White Blood Cells • White blood cells — Contain nuclei with DNA, the shape depends on the type of cell — Certain WBCs produce antibodies — Life span is from 24 hours to several years —Size is 8-20 micrometers — There are five different types of WBCs 1) Neutrophils 2) Eosinophils 3) Basophils 4) Lymphocytes 5) Monocytes http://ww w.giantmicr obes.com/ us/product s/whiteblo odcell.html Types of White Blood Cells • Leukocytes can be divided into two groups. 1) Granulocytes — Contain granules; inclusions in their cytoplasm — Usually have lobulated or segmented nuclei — Neutrophils — Basophils — Eosinophils 2) Agranulocytes — Do not contain granules — Do not have lobulated or segmented nuclei — Monocytes — Lymphocytes Types of White Blood Cells • Neutrophils (AKA: PMNs, Polys, Segs) — Account for the highest amount of WBCs [~60%] — Fight off bacterial invaders — Fight off fungal invaders — Take part in phagocytosis • Neutrophils look like….. — Nucleus is divided into 2 to 5 segments and stains dark purple (multi-lobed nucleus) — Cytoplasm is pale pink to tan with fine pink-purple granules — 10-15 micrometers in diameter —Mature form = segmented (segs); Nucleus has 2-5 lobes — Immature form = band (bands); no segments in nucleus — Bands are normal in the peripheral blood in low numbers 0-5% • When did you see them? — High numbers during bacterial infections and inflammation Types of White Blood Cells • Eosinophils (AKA: Eos) — Fight off parasitic worm and flukes — Important in allergic reactions — ~ 3 % of WBCs in the blood • Eosinophils look like….. — Nucleus is divided into 2 segments — Cytoplasm is pale pink to tan with large orange and red granules — 10-15 micrometers in diameter • When did you see them? — High numbers with parasitic infections — Higher numbers in allergic reactions Types of White Blood Cells • Basophils — Releases histamine in response to an allergic reaction — Seen with inflammation — Lowest number of WBCs in blood [<1%] • Basophils look like….. — Nucleus has 2 lobes that stains purple and is difficult to see — Cytoplasm is pale pink –tan but contains large purple/blue-black granules —10-15 micrometers in diameter • When did you see them? — High numbers during allergic reactions — High numbers during inflammatory reactions Types of White Blood Cells • Monocyte — Search for bacteria and viruses — Participate in phagocytosis — Largest of the white blood cells — ~ 6 % of WBCs in the blood • Monocytes look like….. — Singular nucleus (convoluted shape); kidney shaped, bean shaped, or horseshoe shaped with a deep indentation — Stains a blue-gray color with “ground glass” cytoplasm, tiny granules — Vacuoles are sometimes present — 12-20 micrometers in diameter • When did you see them? — High numbers during bacterial and viral infections Types of White Blood Cells • Lymphocyte — Fight viral infections — Some produce and secrete antibodies — 2nd most common WBC in blood — ~ 30 % of WBCs in the blood • Lymphocytes look like….. — Large, dark staining nucleus, round or oval — Little to no cytoplasm, blue in color — Occasional purple-reddish granules — About the size of a RBC —8-15 micrometers in diameter — Smallest nucleated cell in peripheral circulation • When did you see them? — High numbers during viral infections — High and atypical form during infectious mononucleosis Platelets • Platelets (AKA: Thrombocytes or PLTs) — Formed from the fragments of a megakaryocyte — Not considered a WBC — Function in hemostasis — Platelets are found in the peripheral blood —Megakaryocytes are found in the bone marrow • Platelets look like….. — Small about 2-3 micrometers in diameter — Fragments — Stains bluish and usually contains small reddish-purple granules — Oval or round but can have spiny projections —Normal is between 7-20 per field Red Blood Cells • Red Blood Cells (AKA: Erythrocytes of RBCs) — Normal sized (oval or round) = called normocytic — If the RBC color is normal = called normochromic