* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendelian Genetics
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
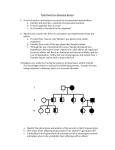
A homozygous recessive blonde dog is crossed with a heterozygous dominant brown dog. What percentage of the offspring do you expect to be brown? ◦ Blonde? “Since chromosomes possess many different genes they are polygenic.” “There is a mutation in the MC1R gene that causes an enzyme to be created which turns pheomelanin into Eumelanin…” “The…shade of your hair is controlled by melanins which are produced by melanocytes, a skin pigment.” Phelan Ch 7 Krogh Ch 11 Male gamete SPERM Female gamete EGG Black Box Offspring “Garden pea” ◦ How might peas be better model organisms than our previous example, Labrador retrievers? Most pea traits have only two phenotypes: ◦ Tall vs. Dwarf ◦ Purple vs. White ◦ Wrinkled vs. smooth seeds Reproduces sexually Female Male (eggs) (pollen) “If you were researching pea plant genetics, what factors would be important to control? How would you control these factors in the pea plant?” Yellow vs. Green seeds Yellow vs. Green seeds No blending of characteristics. Plants retained the potential for passing on recessive phenotypes. This led him to conclude that these plants retained a recessive element (green seed allele). Dominant allele = expressed gene (ex. Purple pigment purple flower) Recessive allele = can be hidden/not expressed (ex. No pigment white flower) Why did the recessive trait show up again in the F2-gen? ◦ “Based on the sum of his results, Mendel determined: 1. Genes are material elements 2. These elements come in pairs. 3. These elements can retain their character through many generations (heritable). 4. That these element pairs separate during the formation of gametes.” ◦Differing characters displayed by organisms result from two genetic elements (alleles) that separate in gamete formation, such that each gamete gets only one of the 2 alleles. ◦ “So far Mendel had looked at pea plants that only differ in one character. smooth, yellow seeds vs. wrinkled, green seeds?” ◦ monohybrid cross. ◦ dihybrid cross. Actual results?? ? “Why do you think these specific ratios were observed? What might these results tell you about the genetics of pea plants?” Why?? “What conclusions can be made based on this data?” This suggested to Mendel that the characters were transmitted independently of one another. Law of Independent Assortment (during gamete formation, gene pairs assort independently of one another.) Used a large number of plants Recorded and drew everything Studied more than one generation of offspring Picked traits that were easy to distinguish “There is a saying that it doesn’t pay to be more than 10 minutes ahead of your time. Gregor Mendel had the misfortune of being about 34 years ahead of his.” ~ David Krogh