* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Characteristics of Islamic law
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
French ban on face covering wikipedia , lookup
Liberalism and progressivism within Islam wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Faisal Kutty wikipedia , lookup
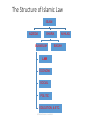
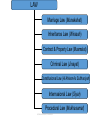
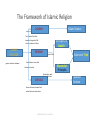
The Characteristics and the Main Objectives of Islamic law By: Dr.Gemala Dewi, SH., LL.M INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI The Structure of Islamic Law ISLAM AQEEDA SHARIA MUAMALAH IBADAH LAW ECONOMI SOCIAL POLITIC EDUCATION, & ETC. INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI AKHLAQ LAW Marriage Law (Munakahat) Inheritance Law (Wirasah) Contract & Property Law (Muamalat) Criminal Law (Jinayat) Constitusional Law (Al Ahkam As Sulthaniyah) Internasional Law (Siyar) Procedural Law (Mukhasamat) INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI The Characteristics • 1. As Part and based on Islamic Teachings • 2. Has a close relations with Iman and Akhlaq • 3. Has two main terms: Syariah and Fiqh • 4. Consist of two major field: - Ibadah and - muamalah. INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI The Framework of Islamic Religion Confidence turned Kalam Science AQIDAH The Creed or faith that becomes the guide of life principles of Ibadah of every adherent of Islam ISLAMIC RELIGION governs relations between SHARIAHRelationship with God Science of Fiqh A set of divine norms that Muamalah Principles Human and nature Relationship with Human & nature AKHLAQ Human behaviour toward God and other human and nature INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI Tasawuf Science The Characteristics 5. Stratified structures: Al-Qur’an, As -Sunnah, Ijtihad and applications (in court or in muslims activities) 6. Make priority to obligations than rights. 7. Can be divided into Taklifi norms and Wadh’i norms (cause, condition and obstruction) 8. Universal 9. Comprehensiveness. 10. The applications of the law is motivated by akidah and akhlaq INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI HUMAN RIGHTS • Universally defined as: A set of rights attached to / inherent in humans, because he is human, it can not live without this right as a human. • According to Article 1 of Law no. 39/1999 about Human Rights is: a set of rights attached to nature and human existence as a creature of God Almighty and it is a gift that must be respected, upheld and protected by the state, law, government and everyone for the honor and protection of human dignity. INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI Islamic Law and Human rights • Human rights in the study of Islamic theocentric view. This is different from other human rights which have anthropocentric view Organization of the Islamic Conference (OIC) issued in the 1990 Cairo Declaration on Human Rights in Islam which states the right to life, property rights, right to dignity, right to education, right in the family, right to equality, rights protection, etc. all of which must based on the provisions of Shari'ah. INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI Islamic Law and Human rights According to Islam, human rights are not only emphasize on human rights alone, but also based on the human obligation to serve God the creator. Rights and obligations of human beings since humans have been conveyed through His revelation. Thus the concept of human rights is not the result of evolution of human thought, but from divine revelation. INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI The Objectives of Islamic Law • From the view of the law Maker (Allah): to prepare the primary (daruriyyah), secondary (hajiyyah) and tertiary (tahsiniyyah) necessities of human beings and to be obeyed by humans as His servants. Whereas from the view of the subject of the Law (humans) is to gain the prosperity in the world and happiness in the hereafter. • According to Abu Ishaq Asy-Syatibi the main objectives (daruriyyah) necessties consist of 5 (five) things as called “Al-Maqasid Al-Khamsah”. INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI The Main Objectives • Al Maqasid Al Shari’ah (Abu Ishaq al Shatibi) The primary (daruriyat) aims is to preserve: Keeping Religion Maintaining Soul Maintaining Intellect Maintaining Descendants Maintain Property INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI Human interests are primary / Darruriyat include Maintenance in: 1. Religion, is the first goal of Islamic law because religion is a guideline of human life, and in the religious creed of Islam other than the component parts of a creed and moral life of every Muslim who is a Muslim way of life, there are also Islamic way of life which is a Muslim with his God & in touch with other human & objects in the community. 2. Soul, is the second objective of Islamic law, Islamic law therefore required to maintain the people's rights to life and for humans to sustain life.thus Islamic law forbids murder (Q 17:33). INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI 3. Intellect, is necessitated by Islamic law, because by Used human minds can think about God, the universe and himself, to develop science and technology.And to maintain the sense that Islamic law forbids any person to drink intoxicating beverages; called Khamar (Q 5:90). INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI 4. Descendants, for pureness Blood can be maintained and the continuation of mankind can be continued, This is reflected in the blood relationship that a requirement to be able to inherit each other (Qs: 4:11), Prohibitionmarriage ban (Q 4:23), and the prohibition of adultery (Qs 17:32). Law of kinship and inheritance laws of Islam are specially created by God to preserve the purity of blood and public descent. 5. Property, according to the teachings of Islam is God's gift to humans, for humans to sustain life.Therefore, Islamic law protects people's rights to acquire property in ways that lawful and legitimate and protect the interests of one's wealth, society and state, instance of fraud (Q 4:29), Embezzlement (Q 4:58), Deprivation (Q 5:33) INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI •Thank You INTERNATIONAL CLASS-FHUI