* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
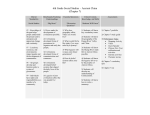
Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Standards: Quarter 1-Unit 1: The Development of Ancient Civilizations Essential Questions: How did river valley civilizations develop? What characteristics did the early civilizations share? 6.3.10 : Explain that cultures change in three ways: cultural diffusion, invention, and innovation. 6.3.11 Define the terms anthropology and archeology and explain how these fields contribute to our understanding of societies in the present and the past WH.1.1 Describe and evaluate social, cultural, and economic changes of small agriculture communities which led to the development of large agricultural settlements such as the movement from hunting and gathering societies, which led to civilization. WH.1.2 Identify the key components that make up a civilization and the key differences between civilizations and other forms of social organization. WH.1.3 Review the key elements of the development of early river valley civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus River Valley, and Shang China. WH.1.4 Examine the development and characteristics of early empires such as Assyria, Persia, Israel, Minoan, and Zhou. (Potential DBQ- Hammurabi’s Code) WH.7.1 Identify patterns of historical change and duration and construct a representation that illustrates continuity and change Content Area Literacy Standards 9-10.LH.1.1: Read and comprehend history/social studies texts within a range of complexity appropriate for grades 9-10 independently and proficiently by the end of grade 10. 9-10.LH.3.1: Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including vocabulary describing political, social, or economic aspects of history/social studies. 9-10.LH.5.1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. Suggested Critical Questions (leading to essential questions): What are the tools and methods historians use to examine the ancient past? 6.3.10, 6.3.11, WH.7.1 What common features did early civilizations share in terms of land, climate and natural resources? (use comparative diagrams) WH.1.1, WH.1.2 How did human communities change over time as they as adopted farming practices during the Neolithic Age? WH.1.1, 6.3.10 How is culture defined and compared across time and space? 6.3.10, 6.3.11, WH.1.2 What ideas or beliefs began to typify most early civilizations? WH.1.3, WH.7.1 What elements of social organization and specialization began to emerge in early societies? WH.1.3, WH.7.1 How did technology aid the emerging civilizations? WH.1.3, WH.7.1 Suggest Document-Based Questions (see digital DBQ file): Hammurabi’s Code (Mini-Q): Was it Just? Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Text-based Resources: World History (Prentice-Hall) Pearson Online Access: www.pearsonsuccessnet.com (use code 94-71-66 to register) Prentice Hall (Historian’s Apprentice Activity Pack C) Chapter 1, pp. 2-24 Infographic: Piecing the Past Together, pp. 6-7 Chapter 2, pp. 28-62 Infographic: Cuneiform Develops in Stages, pp. 32-33 Chapter 3, pp. 66-108 Concept Connector: Belief Systems, p. 83 IDOE Resources for Course: IDOE Home page http://www.doe.in.gov/ IDOE-Social Studies page http://www.doe.in.gov/standards/social-studies IDOE-History/Social Studies Content Area Literacy Standards (linked through ELA page) http://www.doe.in.gov/standards/englishlanguage-arts IDOE Online Communities of Practice (see “Middle Grades”) http://www.doe.in.gov/elearning/online-communities-practice General Resources for Historical Thinking and Assessment Essential World History Questions https://www.ocps.net/cs/services/cs/currareas/soc/IR/Documents/Overarching%20Essential%20 Questions.pdf Stanford History Education Group – Introduction to Historical Thinking (Lessons) http://sheg.stanford.edu/intro-historical-thinking Beyond the Bubble -- Integrating Historical Thinking into Classroom Assessment (assessments available) https://beyondthebubble.stanford.edu/ Reading Quest – Reading, Writing and Research Comprehension Strategies and Handouts http://www.readingquest.org/ Web-based Resources: World History DBQ’s -- Edmodo – IPS World History Group (use school code) https://ips.edmodo.com/ Discovery Education Tech Book – World History – Chapter 1 & Chapter 2 (login required) http://app.discoveryeducation.com/ Five Themes of Geography (on IPS Secondary Social Studies Group 20122013) https://onlinebb.ips.k12.in.us/section/default.asp?id=GROUP-120715160607-FAB General Middle School Geography Resource http://www.sldirectory.com/studf/geography.html Reading Like a Historian (see lessons under “World – Ancient” category) http://sheg.stanford.edu/world Hippocampus.org/History & Government/Presentations (Mesopotamia) http://www.hippocampus.org/HippoCampus/History%20%26%20Governm ent Annenberg Media – Bridging World History – Unit 3 (Human Migrations) and Unit 4 (Agriculture and Urban Revolutions) http://www.learner.org/resources/series197.html Noreen Reale Falcone Library – Compiled listing of primary document sites for ancient history – very complete and diversified http://resources.library.lemoyne.edu/content.php?pid=210266&sid=17645 56 World History for All of Us (a robust web site of fully developed units/lessons for the entire course) – Big Era 2 http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu/ Example Unit Application Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Unit Assessment Question: How did the emergence and refinement of stone tools allow early human populations to spread around the globe? 1) Backgrounder: This is a beginning of the week lesson and helps students how humans came to inhabit so many different regions of the planet. Examine the importance of stone technology as a way of adapting to otherwise harsher environments (building, hunting, gathering, skinning, etc.). See: http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu/eras/era1.php 2) Ask students to create a visual/descriptive cause and effect chart of how this technology led to migration and cultural change 3) Extend this lesson into performance based lesson creating an advertisement or commercial to sell a set of stone tools (remember the Ginsu knives on T.V.!) Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Unit Assessment Question: Using the diagram to the left, can you explain the relationship between population and agricultural (food) production? 1. Ask students to write this relationship down in their own words 2. As they explain, have them try to work out a cause and effect explanation (Which one came first? Can we know? What kind of evidence would historians/archeologists look for to answer that question?) Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Quality 1-Unit 2: Classical Western Civilizations Essential Questions: What enduring traditions, institutions, and cultural achievement did Greek culture influence in the Western world? How did Alexander the Great expand his empire and spread Greek culture? How did Rome grow from a small city into a huge diverse empire, and what led to its downfall? How was Rome impacted by Judaism and Christianity? Standards: WH.7.2 Locate and analyze primary sources and secondary sources related to an event or issue of the past. WH.2.3 Examine the development of Greek civilization including differing political and social structures as well as conflicts such as the Persian and Peloponnesian wars. WH.2.9 Examine the significant achievements of the Greeks and Romans and their impact on the modern world. WH.2.4 Describe the rise of Alexander the Great and the influence of Hellenism in Southwest and South Asia, North Africa, and parts of Europe. (Potential DBQ- Alexander the Great) WH.2.5 Analyze the development of Roman Republican government and society. (Potential DBQ-Athens and Rome-Citizenship) WH.2.6 Trace the changes that culminated in the end of the Republic and the formation of the Roman Empire. WH.2.8 Analyze the causes, conditions, and consequences of the decline and fall of the western part of the Roman Empire WH.2.1 Review the development and key concepts of major world religions and philosophies including Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. WH.2.2 Examine the development of Judaism and the civilization of Ancient Israel, including the origins of monotheism, the significance of the Exodus from Egypt, the Hebrew Bible and the Ten Commandments as the source of many moral and ethical traditions of Western civilization. WH.2.7 Examine the origins, rise, and spread of Christianity including the life of Jesus, and Christianity’s impact on the Roman Empire. (Potential DBQ- Why did Christianity take hold in the ancient world?) Content Area Literacy Standards: 9-10.LH.1.1: Read and comprehend history/social studies texts within a range of complexity appropriate for grades 9-10 independently and proficiently by the end of grade 10. 9-10.LH.3.1: Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including vocabulary describing political, social, or economic aspects of history/social studies. 9-10.LH.5.1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Suggested Critical Questions: What are the specific geographic, environmental and social conditions of the Aegean Sea region that helped give rise to Greek civilization? WH.2.3 What are some of the significant Greek cultural achievements that have influenced later societies, including our own? (use comparative diagrams) WH.2.9 How did competition, conflict and alliance between city-states shape Greek culture? WH.2.3 What issue led to the downfall of Athens? WH.2.9, WH.7.2 What were key Greek notions about government, art, science and logic? WH.2.9 How did Greek colonization into Italy and other parts of Europe influence other cultures? WH.2.4 What made Rome become a republic? WH.2.6 What caused Rome to become an empire? WH.2.6 What was life like for women and slaves in Rome? WH.2.5 How was Rome’s traditional religious beliefs different from Judaism and Christianity? WH.2.1, WH.2.2, WH.2.7 What role did ‘barbarian’ groups play in Rome’s decline? WH.2.8 Suggested Document-Based Questions (Mini Q’s): How Great was Alexander the Great? Citizenship in Athens and Rome: Which was the Better System? Why did Christianity take hold in the ancient world? Text-based Practice: World History (Prentice-Hall) Pearson Online Access: www.pearsonsuccessnet.com (use code 94-71-66 to register) Chapter 1, pp. 2-24 Infographic: Piecing the Past Together, pp. 6-7 Chapter 2, pp. 28-62 Infographic: Cuneiform Develops in Stages, pp. 32-33 Chapter 3, pp. 66-108 Concept Connector: Belief Systems, p. 83 IDOE Resources for Course: IDOE Home page http://www.doe.in.gov/ IDOE-Social Studies page http://www.doe.in.gov/standards/social-studies IDOE-History/Social Studies Content Area Literacy Standards (linked through ELA page) http://www.doe.in.gov/standards/englishlanguage-arts IDOE Online Communities of Practice (see “Middle Grades”) http://www.doe.in.gov/elearning/online-communities-practice General Resources for Historical Thinking and Assessment Web-based Resources: World History DBQ’s -- Edmodo – IPS World History Group (use school code) https://ips.edmodo.com/ Discovery Education Tech Book – World History – Chapter 1 & Chapter 2 (login required) http://app.discoveryeducation.com/ Five Themes of Geography (on IPS Secondary Social Studies Group 20122013) https://onlinebb.ips.k12.in.us/section/default.asp?id=GROUP-120715160607-FAB General Middle School Geography Resource http://www.sldirectory.com/studf/geography.html Reading Like a Historian (see lessons under “World – Ancient” category) http://sheg.stanford.edu/world Hippocampus.org/History & Government/Presentations (Mesopotamia) http://www.hippocampus.org/HippoCampus/History%20%26%20Governm ent Annenberg Media – Bridging World History – Unit 3 (Human Migrations) and Unit 4 (Agriculture and Urban Revolutions) Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Essential World History Questions https://www.ocps.net/cs/services/cs/currareas/soc/IR/Documents/Overarching%20Essential%20 Questions.pdf Stanford History Education Group – Introduction to Historical Thinking (Lessons) http://sheg.stanford.edu/intro-historical-thinking Beyond the Bubble -- Integrating Historical Thinking into Classroom Assessment (assessments available) https://beyondthebubble.stanford.edu/ Reading Quest – Reading, Writing and Research Comprehension Strategies and Handouts http://www.readingquest.org/ http://www.learner.org/resources/series197.html Noreen Reale Falcone Library – Compiled listing of primary document sites for ancient history – very complete and diversified http://resources.library.lemoyne.edu/content.php?pid=210266&sid=17645 56 The British Museum (Interactive Content/Games) http://www.britishmuseum.org/learning/schools_and_teachers/resources/ online_resources.aspx The Greeks – PBS http://www.pbs.org/empires/thegreeks/educational/lesson1.html World History for All of Us (a robust web site of fully developed units/lessons for the entire course) – http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu/ NYC Dept. of Education Global History and Geography Online Resource Guide http://www.p12.nysed.gov/ciai/socst/ghgonline/units.html Nancy Hester’s Pre-World History AP Website with Accessible Materials on all Classical Empires http://www.georgetownisd.org/Page/6470 Collapse – Why do civilizations decline? – Interactive lesson on Annenberg Media http://www.learner.org/interactives/collapse/index.html Example Unit Application Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Unit Assessment Question: Was the Battle of Thermopylae depicted accurately in “300” or does the historical record suggest differently? See this site for documents: http://usf.usfca.edu/classes/AuthEd/Set.Goes/SStudies/Thermopylae/Thermopylae.html 1) Backgrounder: Explain the popularity of the movie “300” was because of its exciting action, but that its historical accuracy is less impressive. Talk to students about whether it’s important to know what really happened at the Battle of Thermopylae and how they might find out. 2) Examine different excerpts of Herodotus’ accounts of the battle (was he really there himself?). Note that Herodotus is one of the West’s earliest examples of an historian. 3) Discuss the event using primary text. Ask students to back up their ideas by pointing to proof or support in these texts (use a Socratic Seminar method/or model it with one group) 4) Ask students to take the role of Herodotus and write their own primary account of what happened. Unit Assessment Question: How did the achievements in Greek theater influence our own style of entertainment today? Visit the site for Greek Theater at Education Portal: http://educationportal.com/academy/lesson/greek-theatre-tragedy-and-comedy.html#lesson Show a portion of the video describing types of Greek Drama/Comedy Ask students to list and describe these types Then have students find a current American entertainment (T.V. show/movie/comedy act) that uses one of these dramatic approaches. Explain this as a connection out culture shares with the Greek past. Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Quarter 1-Unit 3: Classical Eastern Civilizations Essential Questions: What role did Hinduism and Buddhism play in shaping civilizations in the East? How did the schools of thinking – Confucianism, Taoism and Legalism -- affect Chinese society? Standards: WH.2.1 Review the development and key concepts of major world religions and philosophies including Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. WH.2.10 Trace the development and major achievements of civilizations in India such as the Mauryan and Gupta empires. ( Potential DBQ-Asoka) WH.2.11 Compare and contrast the influence of Hinduism and Buddhism on civilization in India and Buddhism’s spread throughout Asia. WH.2.12 Compare and contrast the influence of Confucianism, Taoism, and Legalism on East Asian civilizations. WH.2.13 Trace the developments and achievements of the Qin and Han Dynasties. (Potential DBQ-The Great Wall) WH.3.1 Analyze the impact of trade networks such as the Silk Road and Indian Ocean trade network. Content Area Literacy Standards: 9-10.LH.1.1: Read and comprehend history/social studies texts within a range of complexity appropriate for grades 9-10 independently and proficiently by the end of grade 10. 9-10.LH.3.1: Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including vocabulary describing political, social, or economic aspects of history/social studies. 9-10.LH.5.1: Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. Suggested Critical Questions: What are major historical religions of the eastern hemisphere? WH.2.11, WH.2.12 What is the origin of Buddhism and where did it spread? WH.2.11 What is the origin of Hinduism and where did it spread? WH.2.11 What are the similarities and differences of Buddhism and Hinduism? WH.2.11 How did the Gupta empire create a unique culture? WH.2.10 How did Chandra Gupta create an empire in India? WH.2.10 What did Asoka accomplish during the Mauryan period in India? WH.2.10 What are some of the social and cultural practices that spread with these religions? WH.2.11 What were the major accomplishments and achievements of the civilizations influenced by these religions? WH.2.10, WH.2.13, WH.3.2 How did the Silk road not only a play an economic role the East, but how did help spread the eastern religious ideas to other parts of the world? WH.3.1 What is a dynasty? WH.2.13 Which of the dynasties had the greatest influence on ancient Chinese civilization? WH.2.12, WH.2.13 Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Which “school” of Chinese philosophy was preferred by strict rulers? Why? WH2.13 How did classical civilizations like the Han Dynasty compare with the western civilizations of the day? WH.3.3 Suggested Document-Based Questions (Mini Q’s): Asoka: Ruthless Conqueror or Enlightened Ruler? The Great Wall of China: Did the Benefits Outweigh the Cost? Text-based Practice: World History (Prentice-Hall) Pearson Online Access: www.pearsonsuccessnet.com (use code 94-71-66 to register) Ancient India and China: Chapter 3, pp. 68-108 IDOE Resources for Course: IDOE Home page http://www.doe.in.gov/ IDOE-Social Studies page http://www.doe.in.gov/standards/social-studies IDOE-History/Social Studies Content Area Literacy Standards (linked through ELA page) http://www.doe.in.gov/standards/englishlanguage-arts IDOE Online Communities of Practice (see “Middle Grades”) http://www.doe.in.gov/elearning/online-communities-practice General Resources for Historical Thinking and Assessment Essential World History Questions https://www.ocps.net/cs/services/cs/currareas/soc/IR/Documents/Overarching%20Essential%20 Questions.pdf Stanford History Education Group – Introduction to Historical Thinking (Lessons) http://sheg.stanford.edu/intro-historical-thinking Beyond the Bubble -- Integrating Historical Thinking into Classroom Assessment (assessments available) https://beyondthebubble.stanford.edu/ Reading Quest – Reading, Writing and Research Comprehension Strategies and Handouts http://www.readingquest.org/ Web-based Resources: World History DBQ’s -- Edmodo – IPS World History Group (use school code) https://ips.edmodo.com/ Discovery Education Tech Book – World Geography and Cultures – East Asia -- Chapter 9 -- (login required) http://app.discoveryeducation.com/ Mr. Donn’s Ancient China Resource Page http://china.mrdonn.org/index.html Video Biography of Confucius – 2 minutes http://mongols.mrdonn.org/index.html HyperHistory – Click on “Rome and Han” and “Mongol Empire” – detailed comparative maps http://www.hyperhistory.com/online_n2/History_n2/a.html Silk Road Lessons – China: Exchange of Good and Ideas Along the Silk Road http://orias.berkeley.edu/lessonplans/silkroad.html General Middle School Geography Resource http://www.sldirectory.com/studf/geography.html Reading Like a Historian (see lessons under “World – Ancient” category) http://sheg.stanford.edu/world http://www.pbs.org/empires/thegreeks/educational/lesson1.html World History for All of Us (a robust web site of fully developed units/lessons for the entire course) – http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu/ Example Unit Application Social Studies: World History Pacing Resource Document Unit Assessment Question: Which classical civilization would you want to be a part of?: – Rome, Greece, Han China, Gupta/Mauryan India? 1) Backgrounder: This is an assessment that requires students to do a fair amount of inquiry to decide which ancient empire was – in their view – would be the best to live in. It will give students a broader understanding of ‘empire’ and the incredible achievements each was able to accomplish before reaching their conclusion 2) Look at the World History for Us All and text book to gather research on Rome, Greece (may include Macedonian Empire under Alexander), Han China, Gupta/Mauryan 3) See: http://worldhistoryforusall.sdsu.edu/eras/era1.php , http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/africa/features/storyofafrica/index_section4.shtml and http://www.georgetownisd.org/Page/6470 (find “Decline of Rome word doc and use the Comparing Achievements of Classical Era” handout). Write the achievements in the handout grid 4) Allow students to use statements (1-16) in the handout to guide them with placing information in the correct grid spot 5) Ask groups to present their findings and the require them to cite research evidence to back up their choice 6. Extension: Ask students to use the Hyper History link below to construct a timeline of all the empires of the classical world. (search between periods 500 B.C. to 500 A.D.) http://www.hyperhistory.com/online_n2/History_n2/a.html shares with the Greek past.