* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
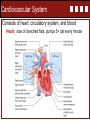
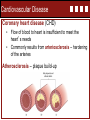
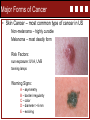
Spencer A. Rathus Jeffrey S. Nevid Chapter 11 Combating Cardiovascular Disease, Cancer, and Other Major Diseases Vicki L Boye, PhD • Concordia University – Nebraska Chapter 11 Combating Cardiovascular Disease, Cancer and Other Major Diseases Learning Outcomes: Describe the cardiovascular systems Discuss the major forms of cardiovascular disease Describe methods of diagnosing and treating cardiovascular disease List and discuss the risk factors for cardiovascular disease Discuss the nature of cancer and how it develops List and discuss the causes of cancer Discuss the similarities and differences among various types of cancer Discuss the nature, incidence, and control of diabetes Discuss the major forms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Cardiovascular System Consists of heart, circulatory system, and blood Heart: size of clenched fists, pumps 5+ qts every minute Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System • The heart pumps an average of 2,000 gallons of blood a day. In a lifetime (65 yr. old) that is about • 46 million gallons or • 72 Olympic Swimming Pools!!! Heart Rate per Minute 60 80 100 60 80 100 Age Total Beats 65 65 65 65 75 75 2,049,840,000 2,733,120,000 3,416,400,000 2,365,200,000 3,153,600,000 3,942,000,000 Circulatory System • System or network of blood vessels that carries blood throughout the body Arteries: funnel oxygen-rich (except for pulmonary arteries) blood away from the heart Capillaries: connect arteries and veins, bring blood directly to cells, exchange with waste products and deoxygenated blood for transport back to heart Veins: Transport deoxygenated blood (except for pulmonary veins) back to heart Blood • Carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and antibodies cells and carts away cellular waste products and carbon dioxide • • • • Blood Plasma – straw-colored liquid part Erythrocytes – red blood cells (hemoglobin) Leukocytes – white blood cells (immune system) Platelets – (blood clotting) Most blood cells produced in blood marrow, lymphocytes (WBC) produced in lymph glands Cardiovascular Disease • Cardiovascular disease describes diseases of the heart and blood vessels such as high blood pressure, coronary heart disease (CHD), heart failure, stroke, and congenital defects. • CVD is the cause of 37% of all deaths in the United States. • Two out of every three people with diabetes die from CVD. • Lifetime risk for CVD is two in three for men and more than one in two for women at 40 years of age. • The best defense against CVD is to prevent it from developing in the first place. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular Disease Coronary heart disease (CHD) • • Flow of blood to heart is insufficient to meet the heart’s needs Commonly results from arteriosclerosis – hardening of the arteries Atherosclerosis – plaque build-up Cardiovascular Disease Coronary heart disease (CHD) • Greatest killer, accounting for nearly one in six deaths in the United States • Myocardial infarction (MI) or heart attack • Approximately 785,000 new heart attacks and 470,000 recurrent heart attacks occur each year. • An MI involves an area of the heart that suffers permanent damage because its normal blood supply has been blocked. Cardiovascular Disease Inflammation – can result in heart attack Know the signs of a heart attack Intense, prolonged chest pain Pain extending beyond the chest Prolonged pain in the upper abdomen Shortness of breath Fainting or weakness Heavy perspiration, nausea, or vomiting Anxiety and fear Don’t wait – Seek medical attention immediately! Cardiovascular Disease Angina Pectoris • Heart pain arising from insufficient blood flow Hypertension – high blood pressure • ‘Silent killer’ • 90% of cases – cause is unclear Cardiovascular Disease Congestive Heart Failure • Heart is unable to pump out as much blood as it receives, leading to pooling of blood in the veins, lungs, and extremities • Signs: swelling (edema), shortness of breath Congenital Heart Defects Arrhythmias – irregular or abnormal heart beat Tachycardia – abnormally fast Bradycardia – abnormally slow Stroke (Cerebrovascular accident) • blood flow blocked to area of brain • Three major types • Cerebral thrombosis (blood clot) • Cerebral embolism (blood clot from another part of body breaks free and travels to brain) • Hemorrhagic stroke – blood vessel ruptures, blood leaks into brain tissue • Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs) • Mini-stroke, resolve quickly • Often early warning signs of stroke Diagnosis of CVD • Diagnostic Tests – different purposes • • • • • • • • Blood tests Chest x-ray ECG or EKG Exercise ECG – stress test Radionuclide imaging MRI Angiogram CT or CAT scan Treatment of Heart Disease Medications Statins, anticoagulants, thrombolytic agents, beta blockers, vasodilators, calcium channel blockers, nitroglycerine Coronary Artery Bypass Coronary Angioplasty Heart Transplants Time is critical for treatment of heart attacks and strokes DON’T WAIT! Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease Factors You Can’t Control Age Controllable Factors Hypertension Blood Cholesterol Gender Triglycerides Heredity Obesity Race/Ethnicity Diabetes Smoking Inactivity Negative Emotions Cancer • Malignant (cancerous) tumors • Begins with change in cell triggered by mutations in cell’s DNA Oncogenes – cause uncontrolled proliferation of body cells – leading to tumors Suppressor genes – normally curb cell division and suppress the development of tumors • Carcinogens – external cancer-causing agents • About half of Americans will develop cancer, ¾ after the age of 55 Cancer (cont.) • More the half of cancer deaths could be prevented by adopting healthy behaviors • • • • Physical activity Avoiding tobacco use Health eating Regular screening • Early detection and treatment critical to surviving • Know the early signs and symptoms (Prevention 11-2) • Self-exams and screenings Causes of Cancer Smoking and Diet 2 out of 3 cancer deaths Other Factors: Obesity Alcohol Environmental Factors Sun Exposure Infectious Agents Genetic Factors Inactivity Types of Cancer • Classified by type of tissue or organ Carcinoma Sarcoma Lymphoma • Classified by location Leukemia Melanoma Major Forms of Cancer • Breast Cancer (1 in 8 women) Risk factors: age, family history, obesity, HRT, Treatment: surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, hormone treatment Prevention: exercise, diet, avoid gaining weight • Ovarian Cancer Detections: Difficulty to detect in early stages Risk Factors: family history, no children, history of other cancer, early menarche, late menopause Treatment: surgery, radiation, chemotherapy Major Forms of Cancer • Cervical Cancer Detection: Pap test Risk Factors: associated with HPV – vaccine available • Uterine (Endometrial Cancer) • Lung Cancer Prevention: Avoid smoking and exposure to second hand smoke, mitigate high levels of radon • Testicular Cancer “young man’s cancer, self-exam critical to early detection Major Forms of Cancer • Colorectal Cancer 2nd leading cancer killer Risk factors: family history, age, diet high in fat – low in fiber; inactivity Prevention: Key is identifying and removing precancerous polyps • Prostate Cancer 2nd most common cancer in men Screening test after 50: Digital rectal exam, PSA, TRUS Treatment: surgery, radiation, hormone therapy Risk Factors: age, family history, race, dietary fat Major Forms of Cancer • Skin Cancer – most common type of cancer in US Non-melanoma – highly curable Melanoma – most deadly form Risk Factors: sun exposure: UVA, UVB tanning lamps Warning Signs: A – asymmetry B – border irregularity C – color D – diameter > 6 mm E – evolving Major Cancer • Oral Cancer Most result from tobacco use Treatment: surgery and radiation • Leukemia – cancer of the blood cells • Lymphoma Hodgkin’s Disease – lymph cells grow abnormally Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma – more prevalent • Pancreatic Cancer Most deadly Higher risk: smokers, high fat diet, diabetes, male Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes Insulin-dependent, body’s own immune system destroys insulin producing cells in pancreas Typically develops in children & young adults Requires daily insulin injections Type 2 Diabetes Non-insulin-dependent, body fails to use insulin properly (insulin resistance), pancreas eventually loses ability to produce insulin Obesity primary risk - epidemic African Americans & Mexican Americans higher risk Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease In COPD, breathing passages are partially obstructed – making breathing difficult Emphysema destruction of air sacs – alveoli causes shortness of breath, especially after exertion Chronic Bronchitis inflammation of lining of the bronchial tubes leads to build up of phlegm, causing hacking cough, shortness of breath, and wheezing