* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
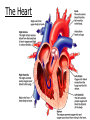
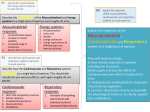
WARM-UP 12/7/11 1. Make a K-W-L chart with 3 columns. And tell me know you Know about the heart, what you Want to know, and after class we will complete the Learned column. 2. Why is the heart important? 3. What is the purpose of the heart? Body’s Transport System OBJECTIVE • SW analyze a demo and take notes in order to explain the cardiovascular system and its3 functions. • Read pp. 79-80 • With a partner, – Define the cardiovascular system – What are the 3 functions of the system – Define the heart and 3 key points • Make outline notes to cover the key points • You have 15 min and then we will review together • Raise you hand if you have any questions! The Cardiovascular system Definition: also called the circulatory system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. 3 functions of the cardiovascular system: 1. Delivers needed material 2. Removes waste products 3. Fighting disease 1. Delivers needed material Most substances that need to be carried from one part to another are carried through the blood. For example, blood carries oxygen from your lungs to your other body cells. Blood also transports the glucose your cells use to produce energy. 2. Removing waste products 1. Cardiovascular system picks up waste from cells. 2. The carbon dioxide is carried by the blood to the lungs to be exhaled. Another example, when cells break down glucose, they produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. 3. Fighting disease Cardiovascular system also transports cells that attack disease-causing microorganisms. This process can help keep you from becoming sick. If you get sick, these disease-fighting blood cells will kill microorganisms and help you get well. - The Body’s Transport System The Heart The Heart Definition- a hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body. Each time the heart beats, it pushes blood through the blood vessels of the cardiovascular system. The heart is made of cardiac muscle, which can contract over and over without getting tired. Your heart is about the size of your fist It is located in the center of your chest. Lies behind the sternum (breastbone) and inside the rib cage. Journal-”Functions of the heart” a. Pick two functions of the heart and describe why these are important functions of the heart b. What type of muscle is the heart composed of? It is voluntary or involuntary? c. How is the type of muscle tissue related to each function of the heart (think of what you listed in part a.)