* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics - davis.k12.ut.us
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
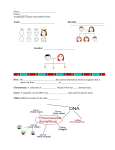
Name_________________________ Genetics Date 270 points Period Directions: On the line before each statement, write correct if the statement is correct or not correct if the statement is not correct. Use proofreading marks to make the statement correct. __________ 8. Genetics is the study of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. __________ LESSON 1 Mendel and His Peas 25 points Directions: On each line, write the vocabulary word or form of a term that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. _____________ 1. Mendel used his pea plants to study the passing of traits from parents to offspring. _____________ 2. Mendel’s research is considered to be the foundation of the study of how traits are passed from parent to offspring. _____________ _____________ 4. Mendel concluded that the haploid cell formed in a female reproductive organ contributed one genetic factor for each trait. _____________ __________ 11. Mendel began his experiments with pea plants that stayed the same from one generation to the next. __________ 12. He then crossed those plants to create truebreeding plants. __________ 13. In Mendel’s studies of the colors of purple pea flowers, none of the first-generation crosses had white flowers. __________ 14. In those same experiments, about threefourths of the second-generation crosses had white flowers. __________ 15. From those results, Mendel concluded that white flowers on pea plants are a dominant trait. __________ 16. In other studies, a trait that showed up in the same proportion of second-generation crosses as white flowers did was yellow pods. __________ 17. One trait that Mendel did not study in pea plants was the shape of the plants’ leaves. __________ 18. Pea plants were a good plant for Mendel to study because they usually self-pollinate and are easy to cross pollinate. 7. The other factor was the one that is blocked by the presence of the dominant factor. 10. Pollination in pea plants can occur in three ways. 6. In some cases, one of the factors, such as purple flower color, was the factor that blocked the other genetic factor. _____________ __________ 5. The other genetic factor for each trait comes from a haploid cell formed in the male reproductive system. _____________ they reproduce slowly and have easily observable traits. 3. Mendel cross-pollinated pea plants with different forms of the same trait to produce offspring with two different forms of the same trait. 9. Gregor Mendel studied pea plants because __________ 19. The Law of Dominance states that in a living thing the dominant trait is expressed and the recessive trait is hidden. Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 1 Name_________________________ Heredity Video Review Date 25 points You Decide! 1. Is surfing an acquired or inherited trait? Period Mendel’s Work Study the figure. Then answer the following questions. P Generation F1 Generation F2 Generation You Predict! 2. What type of offspring would be created from crossing a tall pea plant with a short pea plant? You Decide! 3. What will the pods of these offspring, from these parents look like? You Observe! 4. Describe this hairline formation. Video Quiz: 1. Skin color is an __________________ trait. 2. Playing music is an ___________________ trait. 1. What do the following symbols represent? P Generation = F1 Generation = F2 Generation = 2. What trait in pea plants is being studied in the cross above? 3. _________________ is the process of passing on traits. 4. _________________ is the study of heredity. 3. What are the two alleles of this trait? 5. Gregor __________________ is called the “Father of Genetics”. 4. Which allele is the dominant allele? Explain how you know. 6. Eye color is an example of a _______________. 5. Which allele is the recessive allele? Explain. 7. A ____________________ trait is usually expressed, and a recessive trait is not. 8. According to the Law of Dominance, the dominant trait is expressed and the ________________ trait is “ hidden”. 6. What alleles do the F1 offspring have? Explain which allele was inherited from which parent. 9. A recessive trait is symbolized by a _______________ case letter. 10. ________________ are the basic units of heredity. Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 2 Name_________________________ Fundamentals of Genetics Video Review You Predict! 1. What do you think the second generation of offspring looked like? You Decide! 2. What genes did the short plant have? You Decide! 3. What is this person’s genotype? You Decide! 4. What is their phenotype? Video Quiz: 1. ______________ is the passing on of traits from parents to offspring. 2. A __________________ trait often masks a recessive trait. 3. Dominant traits are usually symbolized by a _______________ letter. 4. Each parent contributes ______________ gene for a trait to each offspring. 5. The _________________ is the visible characteristics of an organism. 6. ___________________ is the term used to describe two unlike genes. 7. A ______________ square illustrates possible combinations of genes in offspring. 8. A _________________ is an organism that is heterozygous for a trait. 9. A ________________ consists of the actual genes for a trait. 10. In this hybrid cross, where T is dominant and lower case t is recessive, the probability of producing short pea plants is Date Period Use Ratios 25 points this page A ratio is a comparison of two quantities. Imagine you have 15 pens and 3 pencils. The ratio of pens to pencils can be written in three ways: 15 to 3, 15:3, and 15 . Like a fraction, a ratio may be simplified. To simplify 3 the ratio 15:3, divide both terms by the greatest common factor, 3. So, 15:3 = 5:1. A cross of two pea plants yields 400 seeds. You count 300 yellow seeds and 100 green seeds. What is the ratio of green seeds to yellow seeds? Step 1 Write the ratio. green:yellow = 100:300 Step 2 Divide by the greatest common factor to simplify. 100 ÷ 100 = 1, and 300 = 100 = 3. 100:300 = 1:3 The ratio of green to yellow seeds is 1:3. Practice: show all work 1. In a garden plot, you count 50 tall 3. In a garden plot, you count 125 redplants and 50 short plants. All the plants are offspring of the same two parent plants. What is the ratio of tall to short plants? 2. In a garden plot, you count 450 yellow-flowered plants and 1,350 white-flowered plants. All the plants are offspring of the same two parent plants. What is the ratio of white-flowered to yellowflowered plants? flowered plants and 125 pink-flowered plants. All the plants are offspring of the same two parent plants. What is the ratio of red-flowered to pinkflowered plants? 4. In a container of seeds, you count 35 dark-brown seeds and 105 lightbrown seeds. All the seeds come from a cross between the same two parents. What is the ratio of dark-brown seeds to light-brown seeds? ______%. Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 3 Name_________________________ Date Period 40 points LESSON 2 Understanding Inheritance Directions: Answer each question or respond to each statement. Use complete sentences. (4 points each sentence) 1. What is the difference between a phenotype and a genotype? 2. Describe the difference between a homozygous genotype and a heterozygous genotype. 3. How does incomplete dominance differ from codominance? dominance pedigree genotype heterozygous chromosomes codominance homozygous incomplete dominance genes environental factors alleles multiple alleles recessiveness polygenic inheritance Punnett square phenotype Directions: On the line before each definition, write the term that matches it correctly. Each term is used only once. _____________ 1. threadlike structures in cells _____________ 2. contain instructions for traits _____________ 3. two different forms of a gene _____________ 4. outward appearance _____________ 5. determines outward appearance _____________ 6. represented by uppercase letters _____________ 7. represented by lowercase letters _____________ 8. RR _____________ 9. Rr _____________ 10. shows possible outcomes of genetic crosses 4. What is the relationship between an allele and a gene? _____________ 11. shows inherited traits in a family _____________ 12. produces a blend of the parents’ phenotypes 5. What is the purpose of a Punnett square? 6. Give an example of a trait that is passed through polygenic inheritance. _____________ 13. when both alleles are expressed _____________ 14. determines human blood type _____________ 15. when multiple genes determine a phenotype _____________ 16. can sometimes influence expression of genes Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 4 Name_________________________ Date Understanding Inheritance 40 points Period Probability and Genetics Key Concept How can inheritance be modeled? Complete the two Punnett squares below, and then answer the questions. Directions: Make the Punnett squares below. 1. Punnett Square A: (4 points) 1. Show a first-generation cross between two true-breeding pea plants— 2. Punnett Square B: (4 points) one with purple flowers (genotype PP) and one with white flowers (genotype pp). 2. Show a second-generation (hybrid) cross between two of the plants from the first-generation cross. 3. In the cross between two black guinea pigs shown in Punnett Square A, what is the probability that an offspring will be black? _____________White?_______________ 4. Is it possible that the cross between two black guinea pigs in Punnett Square A would not produce a white guinea pig? Explain. 3. What percentage of the offspring from the first-generation cross is likely to have purple flowers? White flowers? 5. What color are the guinea pig parents in the cross shown in Punnett Square B? 6. Which guinea pig parent(s) in Punnett Square B is homozygous? 4. What percentage of the offspring from the second-generation cross is likely to have purple flowers? White flowers? 5. What is the chance, in the form of a ratio, that the offspring from the second- generation cross have purple flowers? 6. What is a pedigree? Which is heterozygous? Explain how you know. 7. Calculate the probability that an offspring will be black in the cross in Punnett Square B. What is the probability that an offspring will be white? Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 5 Name_________________________ The Test Cross (15 points) When an organism has a trait controlled by a dominant allele, it can either be a hybrid or a purebred. To find out which, geneticists can use a test cross. In a test cross, the organism with the trait controlled by a dominant allele is crossed with an organism with a trait controlled by a recessive allele. If all offspring have the trait controlled by the dominant allele, then the parent is a purebred. If any offspring has the recessive trait, then the dominant parent is a hybrid. Study the test cross below, then answer the questions. 1. Is the long-haired cat in the P generation a hybrid or a purebred? 2. Is the short-haired cat in the P generation a hybrid or a purebred? 3. If the short-haired cat in the P generation were purebred, what would you expect the offspring to look like? 4. In horses, the allele for a black coat (B) is dominant over the allele for a brown coat (b). A cross between a black horse and a brown horse produces a brown foal. Is the black horse a hybrid or a purebred? Explain. 5. In guinea pigs, the allele for a smooth coat (S) is dominant over the allele for a rough coat (s). Explain how you could find out whether a guinea pig with a smooth coat is a hybrid or a purebred. Date Period Genetic Crosses With Two Traits (10 points) In his work with garden peas, Mendel also set up crosses in which he studied the inheritance of two traits at one time. For example, he crossed tall plants having green pods (TTGG) with short plants having yellow pods (ttgg). The F1 offspring showed both traits controlled by dominant alleles, tall and green. Mendel allowed the F1 offspring to self-pollinate. The F2 offspring had four different phenotypes: tall plants with green pods, tall plants with yellow pods, short plants with green pods, and short plants with yellow pods. These results led Mendel to formulate the Law of Independent Assortment, which states that alleles of one gene separate or assort independently of alleles of another gene. In other words, the distribution of alleles of one gene does not affect the distribution of alleles for another gene. Study the Punnett square of a genetic cross between two pea plants with two different traits. 1. What are all the possible combinations of alleles that each F1 parent can pass on to the offspring? 2. What are the possible genotypes of the F2 offspring? What are the possible phenotypes of the F2 offspring? 3. What is the probability that an F2 offspring will be tall with green pods? What is the probability that an F2 offspring will be short with yellow pods? Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 6 Name_________________________ LESSON 3 Date DNA and Genetics 25 points Directions: Write the correct term in the boxes to the right of each definition. Then unscramble the letters in the shaded boxes to spell a seventh term. DNA RNA mutation transcription nucleotide translation replication 1. a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene 2. the copying of DNA 3. carries the code for making proteins from the nucleus to the cytoplasm Period Should This Dog Be Called Spot??? Imagine this microscopic drama. A sperm cell from a male dog fuses with an egg cell from a female dog. Each dog’s gamete carries 39 chromosomes. The zygote that results from the fusion of the gametes contains 78 chromosomes – one set of 39 chromosomes from each parent. One pair of the zygote’s chromosomes are shown below left. Each chromosome of the homologous pair contains alleles for the same traits. But one chromosome may have a dominant allele and the other a recessive allele. Use the drawings and the table to answer the questions. Trait Hair Length Hair texture Hair curliness Coat pattern Dominant Gene Short (L) Wiry (T) Curly (H) Spotted (A) Recessive Gene Long (l) Silky (t) Straight (h) Solid (a) 1. Will the new puppy have a spotted coat? Explain. 4. process that makes mRNA from DNA 2. Does the female dog have a spotted coat? Explain. 3. Does the male dog have a spotted coat? Explain. 5. nitrogen base + a sugar + a phosphate group 4. What will the texture of the puppy’s coat? Explain. 5. Will the texture of the puppy’s coat resemble that of either of its parents? Explain. 6. organism’s genetic material 7. When they are unscrambled, the letters from the shaded boxes spell , the process that uses RNA to make 6. Will the puppy have curly hair or straight hair? protein. 7. a. Does the female dog have curly hair? b. Does the male dog have curly hair? 8. Explain why you cannot completely describe the puppy’s parents even though you can accurately describe the puppy. Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 7 Name_________________________ 25 points Genetics in Action Video Review You Predict! 1. What did the pea pods of these offspring look like? You Predict! 2. What do you think the flowers looked like from this cross? Date Period A Closer Look at Gene Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis In people with cystic fibrosis, a protein called CFTR is absent from cells in the lungs. Without this protein, mucus builds up in the lungs and causes many of the symptoms of the disease. Gene therapy has been developed to treat cystic fibrosis. The process, which is illustrated in the figure below, involves genetically engineering a cold virus so that it can produce the CFTR protein and then delivering the virus to the patient’s lungs through a tube inserted through the mouth or nose. (10 points) You Observe! 3. What is the shape of this cell? Video Quiz: 1. Genetics is the study of _______________. 2. 3. __________ are the basic units of heredity. A _______________ trait often masks a recessive trait. 4. An offspring, according to the Law of Segregation, generally receives a gene for a trait from each ______________. 5. Different traits are inherited ______________ of one another. 6. The cross of these four-o’clock flowers illustrates 7. 8. ___________ dominance. Blood type is an example of ______________. In ______________ inheritance a group of genes together produces a trait. 9. A ________________ is a change in a gene or chromosome. 10. Sickle cell anemia is the result of a ______________ disorder. 1. What role does CFTR play in the body? 2. Why is it necessary for the viral DNA to enter the cell’s nucleus before it can do its job? 3. Which organelle actually produces CFTR in the treated cells? 4. The cold viruses used in gene therapy for cystic fibrosis are genetically engineered so they cannot reproduce, and thus cannot cause a viral infection in the patient. Because of this, the therapy does not lead to a permanent cure for cystic fibrosis. Explain why this is the case. Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 8 Name_________________________ Genetics Review 1. A nucleotide is to a chromosome as A. music is to words. C. people are to exercise. B. food is to nutrients. D. words are to a paragraph. Date Period Interpreting a Table 25 points Directions: Respond to each statement on the lines or in the space provided. 13. Construct a Punnett square for a cross between parents with the alleles CC and cc. Assume that C is a dominant factor representing a chin cleft and that c is a recessive factor representing a chin without a cleft. 2. A new plant species is discovered. Biologists note that some flowers have royal blue petals and that others have white petals. A biologist cross-pollinated white flowering plants with blue-flowering plants. What color petals will be observed if there is incomplete dominance? A. white B. spotted C. light blue D. royal blue 14. Predict the phenotype of the offspring for the cross in question 13. Directions: On each line, write the term that correctly completes each sentence. 3. The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called _____________. 4. _____________ occurs when multiple genes determine the phenotype of a trait. 5. Offspring that result from the cross of parents with different forms of the same trait are called _____________. 6. A deletion _____________ occurs when one or more base 15. Construct a Punnett square for a cross between parents with the alleles dd and Dd. Assume that D is a dominant factor representing dimples and that d is a recessive factor representing a face without dimples. pair is left out of a DNA sequence. 7. A section of a chromosome that has genetic information for one trait is a(n) _____________. Does either the mother or the father in A have dimples? 8. A(n) _____________ shows the phenotypes of genetically related family members. 9. Different forms of a gene are called _____________. 10. Having two different alleles for a gene results in a(n) 16. Calculate the percentage of offspring who would have dimples. Use the Punnett square in question 15 to explain your answer. _____________ genotype. 11. Having two of the same allele for a gene makes a(n) _____________ genotype. 17. Contrast incomplete dominance and codominance. 12. Base pairs are added to the DNA sequence in a(n) _____________ mutation. Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 9 Name_________________________ Pedigrees of the Rich and Famous Date 15 points The pedigree of Queen Victoria of England shown below is often used as an example of sex-linked inheritance. Victoria was a carrier of hemophilia, a sex-linked disorder that is controlled by a recessive allele. The blood of a person with hemophilia clots very slowly or not at all because the person does not produce one of the proteins needed for blood clotting. Victoria passed the hemophilia allele on to her son Leopold, who had the disease, and to two of her daughters, who were carriers. The allele then passed through successive generations of Victoria’s family, as the pedigree below shows. Period 3. Which of Victoria’s children passed the hemophilia allele on to Queen Victoria of Spain? 4. Assume that a direct descendant of Maria Cristina, daughter of Queen Victoria Eugénie of Spain, has just been found to have had hemophilia. How would this change Maria Cristina’s status? 1. Which of Victoria’s children were carriers of the hemophilia allele? 2. Which of Victoria’s children passed the hemophilia allele on to Empress Alexandra of Russia? ? 5. Explain why males are more likely than females to have hemophilia. 6. The current royal family is descended from King Edward VII. Is it possible for the current royal family to have the hemophilia gene? Explain. On Your Own: Research the maternal pedigree of Queen Victoria and her relationship to Prince Albert. Add to the pedigree. Standard 4: Students will understand that offspring inherit traits that make them more or less suitable to survive in the environment. Buffalo Book 19 Leopard Book iScience Chapter 5 Page 10