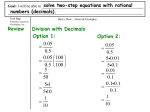
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year 7 Maths AWL Number
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
1. Calculation: Knowledge NUMBER Structure and calculation 1. order positive and negative integers, decimals and fractions; use the symbols =, ≠, <, >, ≤, ≥ 2. apply the four operations, including formal written methods, to integers, decimals and simple fractions (proper and improper), and mixed numbers – all both positive and negative; understand and use place value (e.g. when working with very large or very small numbers, and when calculating with decimals) 3. recognise and use relationships between operations, including inverse operations (e.g. cancellation to simplify calculations and expressions); use conventional notation for priority of operations, including brackets, powers, roots and reciprocals 4. use the concepts and vocabulary of prime numbers, factors (divisors), multiples, common factors, common multiples, highest common factor, lowest common multiple, prime factorisation, including using product notation and the unique factorisation theorem 5. use positive integer powers and associated real roots (square, cube and higher), recognise powers of 2, 3, 4, 5; estimate powers and roots of any given positive number 6. calculate with roots, and with integer and fractional indices 7. calculate exactly with fractions, surds and multiples of π; simplify surd expressions involving squares (e.g. ) and rationalise denominators 8. calculate with and interpret standard form A x 10n, where 1 ≤ A < 10 and n is an integer. Measures and accuracy 14. estimate answers; check calculations using approximation and estimation, including answers obtained using technology 15. round numbers and measures to an appropriate degree of accuracy (e.g. to a specified number of decimal places or significant figures); use inequality notation to specify simple error intervals due to truncation or rounding 16. apply and interpret limits of accuracy, including upper and lower bounds Number Page 1 Place Value & Accuracy: Skills and Threshold Threshold Grade Skill: I can Year Foundation 1 1-3 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 estimate answers to calculations round positive and negative integers to nearest 10, 100, 1000 order positive and negative integers place and indicate an integer on a number line write integers using place value e.g. ‘three thousand and forty seven’ order decimals write the value of a given decimal digit use inequality and ≠ signs estimate answers to calculations (no division) round to decimal places round to 1 significant figure (integer) estimate answers in context (e.g. area) estimate answers to calculations (with division) round to 3 significant figures (integer) use place value in calculations (given 23 x 46 = 1058, calculate 2.3 x 4.6) 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Developing 4 4-5 4 4 estimate answers to calculations (complex) round to significant figures (decimal) round to significant figures (decimal leading zeroes) 7+ 7+ 7+ Key Words place value integer decimal negative positive digit equal = not equal ≠ round decimal place significant figure accuracy inequality <,≤,>,≥ error interval lower bound upper bound estimate calculate find evaluate Number Page 2 Operations: Skills and Threshold Threshold Grade Skill: I can Year Foundation 1 1-3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 know and use multiplication tables to 10x10 know and use the rules of BIDMAS understand and use inverse operations use multiplication tables for mental division (inverse) identify factors and multiples of a number know prime numbers to 100 add and subtract positive and negative integers divide positive integers with integer results using written & mental methods multiply decimals by integers multiply positive integers using standard written methods interpret calculator display in context and round appropriately add and subtract decimals divide integers with decimal results multiply and divide negative integers with integer results multiply decimals by decimals multiply and divide decimals by powers of 10 use BIDMAS correctly on a calculator know and use divisibility rules divide decimals by integers and decimals 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Developing 4 4-5 4 4 4 5 5 know not to use intermediate rounding multiply and divide by a number between 0 and 1 find HCF using factors write an integer as the product of prime factors, including in index form find HCF using prime factor decomposition (PFD) find LCM using PFD 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Key Words equal = not equal ≠ place value integer decimal negative positive digit add sum subtract difference multiply Gelosia divide factor multiple divisible prime number prime factor HCF estimate calculate find LCM inverse operation BIDMAS product of prime factors index form evaluate Number Page 3 Indices & Roots: Skills and Threshold Threshold Grade Skill: I can Year Foundation 1 1-3 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 know square numbers to 144 know cube numbers to 125 calculate square and cube roots use a calculator to evaluate up to powers of 5 use a calculator to evaluate square and cube roots write and understand index notation for positive indices use a calculator to evaluate indices use positive integer indices to evaluate expressions 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Developing 4 4-5 4 5 5 5 use positive integer indices to simplify expressions know and use power 0 estimate the value of a power or root of any positive number write integers with negative indices; understand the relation to reciprocals use negative integer indices to simplify and evaluate expressions 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Key Words integer positive negative term expression reciprocal square cube index power square root cube root index form standard (index) form surd rationalise conjugate evaluate simplify expand equivalent Number Page 4 2. FDP & Ratio: Knowledge NUMBER Structure and calculation 1. order positive and negative integers, decimals and fractions; use the symbols =, ≠, <, >, ≤, ≥ 2. apply the four operations, including formal written methods, to integers, decimals and simple fractions (proper and improper), and mixed numbers – all both positive and negative; understand and use place value (e.g. when working with very large or very small numbers, and when calculating with decimals) 3. recognise and use relationships between operations, including inverse operations (e.g. cancellation to simplify calculations and expressions); use conventional notation for priority of operations, including brackets, powers, roots and reciprocals Fractions, decimals and percentages 10. work interchangeably with terminating decimals and their corresponding fractions (such as 3.5 and or 0.375 or ); change recurring decimals into their corresponding fractions and vice versa 11. identify and work with fractions in ratio problems 12. interpret fractions and percentages as operators. Measures and accuracy 13. use standard units of mass, length, time, money and other measures (including standard compound measures) using decimal quantities where appropriate RATIO, PROPORTION and RATES of CHANGE 2. use scale factors, scale diagrams and maps 3. express one quantity as a fraction of another, where the fraction is less than 1 or greater than 1 4. use ratio notation, including reduction to simplest form 5. divide a given quantity into two parts in a given part : part or part : whole ratio; express the division of a quantity into two parts as a ratio; apply ratio to real contexts and problems (such as those involving conversion, comparison, scaling, mixing, concentrations) 6. express a multiplicative relationship between two quantities as a ratio or a fraction 7. understand and use proportion as equality of ratios 8. relate ratios to fractions and to linear functions 9. define percentage as ‘number of parts per hundred’; interpret percentages and percentage changes as a fraction or a decimal, and interpret these multiplicatively; express one quantity as a percentage of another; compare two quantities using percentages; work with percentages greater than 100%; solve problems involving percentage change, including percentage increase/decrease and original value problems, and simple interest including in financial mathematics 10. solve problems involving direct and inverse proportion, including graphical and algebraic representations 11. use compound units such as speed, rates of pay, unit pricing, density and pressure 12. compare lengths, areas and volumes using ratio notation; make links to similarity (including trigonometric ratios) and scale factors 16. set up, solve and interpret the answers in growth and decay problems, including compound interest and work with general iterative processes. Number Page 5 Fraction: Skills and Threshold Threshold Grade Skill: I can Year Foundation 1 1-3 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 find equivalent fractions understand fraction as division visualise a fraction diagrammatically order fractions simplify proper and improper fractions convert between mixed number & improper fraction convert between fractions and decimals calculate fraction of a quantity understand fraction as an operator add fractions multiply fractions subtract fractions use a calculator efficiently with fractions express one quantity as a fraction of another know the meaning of reciprocals and the relation to division understand and use unit fractions as multiplicative inverse of division 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Developing 4 4-5 4 4 4 understand that terminating and recurring decimals represent fractions recognise common recurring decimals and their fraction equivalents divide fractions operations with mixed numbers 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Key Words fraction numerator denominator fraction bar proper equivalent simplify cancel convert improper mixed number reciprocal common denominator recurring decimal terminating decimal calculate find evaluate of multiply divide Number Page 6 fraction of Percentage: Skills and Threshold Threshold Grade Skill: I can 1st year Foundation 1 1-3 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 understand % as 'out of 100' calculate percentage of a quantity compare and order fractions, decimals and percentage convert between percent, fractions and decimals express one quantity as a percentage of another compare two quantities using percentages understand and use percentages >100% calculate percentage increase and decrease calculate simple interest and VAT write and evaluate simple iterative relations 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Developing 4 4-5 4 4 5 5 5 understand % as a multiplier calculate percentage change given original & final quantity calculate percentage profit and loss calculate compound interest calculate successive percentage change, not using a power solve reverse percentage problems 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Key Words percent percentage denominator percentage of increase decrease simple interest compound interest growth VAT original multiplier decay depreciation profit loss Number Page 7 Ratio & Proportion: Skills and Threshold Threshold Grade Skill: I can Year Foundation 2 1-3 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 understand and write a ratio calculate equivalent ratios convert exchange rates solve exchange rate problems solve problems of ‘best buy’ construct and interpret scale drawings and maps share a quantity in a given ratio solve simple ratio and proportion word problems convert between fractions and ratios 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ 7+ Developing 4 4-5 solve ratio and proportion problems using the unitary method 7+ Key Words ratio part : part proportion equivalent cancel simplify best value scale exchange rate convert calculate find fraction multiplier Number Page 8