* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transport and cardiovascular systems
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
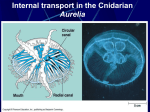
Transport and cardiovascular systems Which of the following does NOT require hemoglobin to deliver oxygen to the tissues. a. Earthworms b. Insects c. Mammals d. Birds e. Amphibians The vessels that return blood to the heart in a closed circulatory system are referred to as a. arteries. b. veins. c. capillaries. d. sinuses. e. auxiliary hearts. Which of a. b. c. d. e. the following is NOT a component of vertebrate blood? plasma. leukocytes. erythrocytes. platelets. myoglobin. Hemoglobin is more likely to release oxygen in metabolically active tissues because a. Metabolically active tissues produce more hemoglobin b. Metabolically active cells are nearer to capillaries c. CO2 is an allosteric regulator of hemoglobin d. CO2 competes for heme binding e. Endorphins released by active tissues trigger oxygen release What allows many marine invertebrates (e.g. corals, jellyfish, sea anemones) to grow large in size even though they have only a gastrovascular cavity for circulation? a. these organisms are only a few cells thick and can rely on diffusion to transport nutrients and oxygen throughout the body b. there are many branches within the gastrovascular cavity that directly transport nutrients and oxygen to various tissues c. a single, large heart provides enough pressure to deliver the blood throughout the entire body d. there are many openings to the gastrovascular cavity that allow nutrients and oxygen to be taken up from all directions Why are respiratory and circulatory systems tightly coupled in organisms with closed circulatory systems? a. all cells in the body require nutrients, oxygen, and waste removal b. organisms with a low surface area:volume ratio cannot only rely on the simple diffusion of nutrients and gases to sustain life c. if these systems weren’t coupled, the blood pressure would be too low to circulate the blood throughout the entire body d. all of the above are true e. only A and B are true Cooperative because a. it b. it c. it sites d. it e. it binding of O2 by hemoglobin is physiologically important overcomes the limitation imposed by diffusion rates allows saturation of blood with O2 at low partial pressure allows hemoglobin to readily give up most of its oxygen at of physiological activity increases the O2 carrying capacity of blood allows efficient exchange of O2 for CO2 Plant gas exchange occurs mainly through which of the following structures? a. companion cells b. trachea c. alveoli d. stomata e. vessels Consider the graphs shown. The center, blue line represents the O2 dissociation curve for adult hemoglobin. The line that represents fetal hemoglobin is a. A because adult hemoglobin has a higher affinity than fetal Hb for O2 b. A because fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity than adult Hb for O2 c. B because adult hemoglobin has a higher affinity than fetal Hb for O2 d. B because fetal hemoglobin has a higher affinity than adult Hb for O2 Which of the following factors contribute to water flow in xylem? a. active transport in root cells and evapotranspiration through stomates b. root peristalsis and evapotranspiration through stomates c. active transport in root cells and capillary action d. capillary action and evapotranspiration through stomates e. active transport in root cells and capillary action What is an advantage for insects to have an open circulatory system rather than a gastrovascular cavity? a. Insects are more efficient with a single heart. b. Insects are terrestrial. c. Open circulatory systems allow high hemolymph pressures. d. An open circulatory system allows coupling of respiratory and circulatory systems. What is an advantage for insects to have an open circulatory system rather than a gastrovascular cavity? a. An open circulatory system provides for more metabolic dynamic range; the animal can respond to changes in energy demands. b. Insects don’t have open circulatory systems. c. Open circulatory systems allow high hemolymph pressures. d. An open circulatory system allows coupling of respiratory and circulatory systems. Which of the following statements about amphibian and mammalian circulatory systems is true? a. Pulmonary circulation occurs at reduced blood pressure. b. Amphibians have 4 heart chambers similar to mammals. c. Oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange only occursin the lungs and skin. d. All of the above are true. e. None of the above are true. Which of the following statements is NOT true about a capillary bed? a. The drop in blood pressure across the capillary is partially due to fluid loss. b. Large proteins diffuse out of the vasculature on the arteriole side and intothe vasculature on the on the venule side. c. The lymphatic system collects water and solutes that are not picked up by the venules. d. The addition of CO2 to the blood decreases the pH of the blood. e. None of the above. All of the above statements are true. Which of the following statements about the blood vessels shown in this figure is NOT true? a. The endothelium provides the conduit for the transport of the blood while allowing small molecules to diffuse into and out of the circulatory system. b. The elastic layers of the large arteries and large veins help to moderate blood pressure fluctuations during and between heart contractions. c. Fenestrated capillaries allow more fluid loss than continuous capillaries. d. The smooth muscle cells contribute to vasodilation and vasoconstriction. e. None of the above. All of the statements are true. Based on what is shown in these oxygen binding curves, which of the following is true? a. At lower temperatures hemoglobin has a lower affinity for oxygen. b. Elevated temperatures increase hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen. c. Increasing exertion at higher altitudes increases oxygen binding to hemoglobin. d. All of the above are true. e. None of the above are true. This question focuses on long-distance transport in the xylem. Which of the following is NOT true? a. Flow of fluids through xylem is not mediated by pressure differences. b. Cohesion-tension theory relies on the polar nature of water molecules. c. Transpiration involves evaporative loss of water. d. None of the above. All of these statements are true. The figure above is from your textbook. Which of the following statements is NOT true? a. Osmosis is a key component of water flow between the xylem and the phloem. b. Developing fruit represents a sucrose source. c. Sink cells uptake sucrose by means of plasmodesmata and concentration gradients. d. Source cells have higher osmotic pressure than sink cells. e. None of the above. All of these statements are true. Stomatal opening is driven by…. a. Water efflux from the guard cells driven by osmosis due to lower extracellular ion concentrations. b. Water influx via osmosis into the guard cells due to pumping of ions and cotransport of sugars into the guard cells. What energy sources drive water transport in the xylem? a. Gravity and photosynthesis b. Stomates and soil pressure c. Gas exchange and xylem vessels d. Sunlight and ATP Where to a. b. c. roots get their sugars? From photosynthesis in the root hairs Via the phloem from the leaves By active transport from the soil Which of the following is NOT an important aspect contributing to water transport through the xylem? a. cohesion among H2O molecules due to hydrogen bonding b. c. d. e. osmosis due to sugar produced in photosynthesizing leaves active transport of mineral ions from the soil into roots transpirational H2O loss from leaves continuous tubes created by dead vessel and tracheid cells Consider the graphs shown. The center, blue line represents the O2 dissociation curve for hemoglobin under normal physiological conditions. The line that represents hemoglobin (Hb) in tissues undergoing intense metabolic demands is a. A because CO2, low pH and high temperatures increase the affinity of Hb for O2 b. A because CO2, low pH and high temperatures decrease the affinity of Hb for O2 c. B because CO2, low pH and high temperatures increase the affinity of Hb for O2 d. B because CO2, low pH and high temperatures decrease the affinity of Hb for O2 Reproduction In plant between a. b. c. d. e. reproduction, alternation of generations refers to alternating male and female embryo and endosperm haploid and diploid epiphyte and halophyte monocot and dicot In mammals, male sex characteristics are determined by all the following EXCEPT a. b. c. d. Having a Y chromosome Having only one X chromosome Testes determining factor Testosterone levels Which of the following is NOT true for both male and female mammalian gametogenesis? a. One primary cell produces four mature gametes. b. Germ line cells multiply by mitosis. c. Primary cells (spermatocytes and oocytes) are diploid. d. Gametes are formed by meiosis. e. Gametes develop in the gonads. In mammalian females, germ cells (oocytes) are a. not produced until puberty. b. nearly all produced in the fetus. c. fully mature gametes at birth. d. produced in the embryo sac. e. arrested in mitosis until puberty. Which of the following is NOT TRUE of the placenta a. It functions in exchange of gases, nutrients and wastes between mother and fetus b. It develops from maternal and fetal tissue c. The fetal portion (chorion) has chorionic villi providing a large surface area for exchange d. Blood of the mother and fetus mix e. It transports drugs and alcohol from mother to fetus In mammals, the primary signal of a successful fertilization is a. the uterus produces chorionic gonadotropin which signals the corpus luteum in the ovary b. the follicle produces estrogen, which signals the corpus luteum to decrease progesterone c. the corpus luteum in the ovary produces estrodiol, which signals implantation in the uterus d. the completion of meiosis II triggers estrogen and progesterone, which signal the uterus e. mechanosensors in the uterine wall are are depolarized by implantation, triggering an action potential Females produce eggs. Which of the following is NOT a feature of meiosis in most female germlines? a. Chromosome number is reduced from 4 to 1. b. Unequal cytokinesis results in a single larger cell with most of the cytoplasm. c. The diploid oocyte is the final product. d. Polar bodies contribute to reduction of chromosome number. e. None. All of the above statements are true. Which of a. b. c. d. e. the following is NOT a form of asexual reproduction? Mitosis Budding Gender switching in fish Regeneration Parthenogenesis Which of a. b. c. d. e. f. the following is NOT an advantage of asexual reproduction? Able to reproduce even if isolated Able to reproduce rapidly Can generate large numbers of offspring Greater genetic variation All of the above None of the above The table above is derived from the Komodo dragon parthenogenesis article. What aspects of this data set support the hypothesis that Sungai’s offspring are the result of sexual reproduction? a. All of the offspring are homozygous at each of the microsatellite loci analyzed. b. The absence of the 133 microsatellite marker in the offspring at the K06 locus. c. All of the microsatellite markers of the offspring are found in Sungai’s DNA. d. None. All of the above statements support the hypothesis that Sungai’s offspring are the result of parthenogenesis. Sex determination in Komodo dragons is based on a system where females are WZ (dissimilar chromosomes) and males are ZZ (similar chromosomes). Based on the observations about parthenogenesis in Komodo dragons, what sex were the offspring produced by parthenogenesis? a. Female b. Male c. The offspring could be either male or female. d. The offspring would be of indeterminate sex. The figure above is from the “Mice without a Father” article. Based on what is shown above and what we discussed in class, which of the following is NOT true? a. Epigenetics does not affect gene expression. b. The maternally contributed genes are necessary for normal development of the embryo. c. Gene expression from the paternal genome is necessary for extraembryonic tissue development. The figure above is from the “Mice without a Father” article. The differentially methylated domain (DMD-Illustrated by the green bar if it is methylated (CH3).) is key to this epigenetic gene regulation. Which of the following is the result if this region is NOT methylated (A nonmethlyated DMD is illustrated by the presence of the blue bar.)? a. The enhancers activate the expression of Igf2. b. The enhancers activate the expression of H19. c. The enhancers fail to activate the expression of either Igf2 or H19. Based on what we discussed about mammalian imprinting, which of the following is a characteristic of epigenetic gene regulation? a. Epigenetic DNA methylation b. is the same between homologous chromosomes in early mammalian embryos. b. Epigenetic imprinting results in the removal of genes from the chromosomes. c. Epigenetic DNA methylation can result in genes not being transcribed. Which of the following is a characteristic of sexual reproduction? a. The embryo is usually the result of the fusion of gametes from different genetic backgrounds. b. The embryo is usually the result of the fusion of diploid gametes from two different parents. c. The species is less able to adapt to changes in the environment due to less genetic diversity within the population. d. The genome is less likely to retain deleterious mutations in critical genes. Recombination occurs… a. as gametes are in the final stages of maturation. b. during the separation of homologous chromosomes in mitosis. c. during the separation of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I. d. as the sister chromatids separate during mitosis. Which of a. b. c. d. the following is a characteristic of asexual reproduction? It is limited to invertebrates. It allows for the maintenance of greater genetic diversity. It allows for the maintenance of successful genotypes. It requires meiotic cell division. In plants, ….. a. 1n individuals b. 2n individuals c. 1n individuals d. 2n individuals produce produce produce produce gametes gametes gametes gametes via via via via meiosis. mitosis. mitosis. meiosis. Double fertilization in flowering plants… a. results in the formation of a 3n endosperm. b. allows for plants to self fertilize. c. is a form of parthenogenesis. d. is a system that improves fertility since only one of the sperm needs to successfully fertilize the egg. In the alternation of generations in flowering plant lifecycles, a. the haploid phase is often free living. b. the diploid phase is dominant. c. the diploid phase produces the gametes. d. the endosperm is haploid. Parthenogenic offspring have been noted in all of the following except: a. lizards b. sharks c. mammals d. bees The figure above is from the “Mice without a Father” article. Based on what is shown above and what we discussed in class, which of the following is NOT true? a. The expression of paternal genes is not required for normal development. b. The maternally contributed genes are necessary for normal development of the embryo. c. Gene expression from the paternal genome is necessary for extraembryonic tissue development. Which of the following outcomes would result if parthenogenesis were the result of either failure of cytokinesis in meiosis II or fusion of the oocyte and the second polar body? a. XX and XX b. XX c. XX d. XX and XX e. XX f. XX Disease Which of the following is the best definition of disease? a. Any condition that leads to cell death. b. Any condition caused by infection with pathogens, such as bacteria or viruses. c. Any condition caused by genetic mutations or inheritance of defective genes. d. Any condition that impairs normal function. e. None of the above. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of cancer a. Cancer cells divide uncontrollably. b. Cancer is a malignant disease, meaning that it progressively becomes worse. c. Cancer is caused by one single mutation that results in increased cell division. d. Cancer is relatively rare at the cellular level, but common among organisms. e. Cancer can metastasize, spreading to other tissues. Activated p53 halts the cell cycle and promotes DNA repair, while inactivated p53 is quickly broken down. p53 is activated in the presence of DNA damage. In the scenario depicted, the p53 gene is mutated and therefore the p53 protein can never be activated. Will this cell divide? a. Yes, because the mutated p53 will induce the expression of genes that promote cell division. b. Yes, because the mutated p53 cannot induce expression of genes that halt the cell cycle. c. No, because the mutated p53 will inhibit proteins that promote cell division. d. No, because the mutated p53 will be detected by the cell, and the cell will not survive. Radiation therapy for cancer induces severe DNA damage. Which of the following cancer cells is this therapy LEAST likely to work on? a. Cancer cells that already have many mutations. b. Cancer cells that have gain-of-function mutations in a growth factor receptor, such that the receptor is always activated. c. Cancer cells that have loss-of-function mutations in p53, such that p53 cannot be activated. d. Cancer cells that still retain “self” signals and can evade the immune system. Consider a genetic mutation in a gene for a death signal receptor, “Y”. In this mutation, a stop codon has been inserted in the middle of the coding region of the gene. What is the most likely outcome? a. Only part of protein “Y” will be translated, and the resulting protein will probably not be functional. b. RNA polymerase will detect the mutation and the gene will not be transcribed. c. The ribosomes will detect the mutation in the mRNA and translation will not occur. d. The ribosomes will recognize the base pair mismatch in the mRNA and correct the mutation. What is genomic instability? a. A mutation in a gene for a protein that detects DNA damage. b. Any mutation that deletes or copies a large chunk of a chromosome. c. When chromosomes break up into many smaller chromosomes. d. The rapid accumulation of mutations over time. Which of directly a. b. c. d. the following cellular processes in cancer cells do NOT promote metastasis? Migration Maintaining survival signals Cell division Apoptosis Consider a gene encoding for a protein important for growth factor signaling. When mutated, this protein becomes constantly active. This gene is most likely a: a. Tumor suppressor b. Tumor promoter c. Proto-oncogene d. Carcinogen Imagine a mutated form of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor. This receptor now signals even when there is no EGF bound to it. What is the result? a. The signal cascade will always be active, so the cell will always behave as if it is receiving growth signals and will divide. b. Since the cell cannot bind to EGF, it cannot receive growth signals and will not divide. c. The signal transduction cascade will always be active, but because there is no EGF the cell will not divide. d. The cell will die because the signal transduction cascade produces toxic byproducts. Which of the following is most likely to be tumor suppressor? a. a gene that increases cell proliferation. b. a gene which codes a fluorescent protein. c. a gene important for repairing DNA damage. d. a gene that enables adaptation to hypoxia (low oxygen). e. a gene that stimulates angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels). The acquired immune system is very effective. Why? a. The cells of the acquired immune system recognize very specific antigens, so only particular pathogens or abnormal cells are targeted. b. The cells of the acquired immune system can recognize very general “non-self” signals, so each cell can target a wide variety of pathogens. c. The acquired immune system can mount an effective response within a few hours of infection. What function does the innate immune system serve? a. The innate immune system takes time to ramp up in response to a specific antigen. b. Innate immune cells are important early in an infection, but after antibodies are produced they no longer contribute to eliminating the pathogens. c. Innate immune cells recognize general “non-self” signals, so they can target pathogens or abnormal cells very early and quickly. d. All of the above. What does “immunological memory” mean? a. The cells of the immune system store antigens from previous infections. b. Acquired immune cells such as B and T cells are primed during the first infection. During the second infection, these cells can respond much more quickly. c. Once antibodies are generated, they never ever break down. The function of B cells is to: a. Produce antibodies, which bind to antigens. b. Activate cytotoxic T cells, which kill abnormal or infected cells. c. Attack antigen-bearing bodies marked with antibodies. d. Help T cells by providing growth signals.