* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ORGANIZATION AND CLASSIFICATION
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
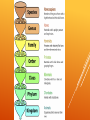
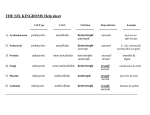
CLASSIFICATION Why Classify? 1) Construct a table with six rows and six columns. Label each row with the name of a different fruit. 2) Observe each fruit and choose four characteristics by which you can tell the fruits apart. Label the columns in your table with these four characteristics. Fill out the chart. 3) Record a description of each fruit in your table. Questions: What characteristics did you use to describe the fruits? Based on your table, which fruits are more closely related? Explain. INQUIRY ACTIVITY A tool that is used to determine the identity of items in the natural world Keys consist of a series of choices that lead to the correct name of a given item “Dichotomous” means “divided into two parts,” so dichotomous keys always give two choices in each step DICHOTOMOUS KEYS Make items: a dichotomous key using the following Bicycle, Automobile. Rock, Tree, Flower, Human, Dog, Pillow, Book, Shark, Bacteria, Pigeon PRACTICE Science of describing, classifying, and naming organisms TAXONOMY Aristotle: system Used First person to develop a classification for more than 2,000 years Classified organisms as plants or animals and then was divided further based on where they lived HISTORY Carolus Linnaeus: 1750’s Swedish scientist considered founder of modern taxonomy Uses observations as basis of classification system Places organisms into groups based on similar observable features such as shape and structure Came up with binomial nomenclature Two-word Genus HISTORY naming system species Linnaean system of classification consists of a hierarchy of groupings, called taxa (singular taxon) Taxa range from kingdom (largest and most inclusive) to species (smallest and most exclusive) Kingdom, Species Species Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, are organisms that are similar enough to produce fertile offspring together LINNAEUS Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia SIX KINGDOMS Kingdoms Eubacteria Archaebacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia unicellular Most unicellular, some multicellular Most multicellular, some unicellular multicellular multicellular prokaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic eukaryotic autotroph heterotroph # of Cells unicellular Nucleus?? prokaryotic Nutrition SIX KINGDOMS auto/heterotroph auto/heterotroph auto/heterotroph heterotroph (absorption) Major change to Linnaean system was the addition of a new taxon called domain (1990). Taxon that is larger and more inclusive than the kingdom Three domains of life on Earth: Bacteria Archaea Eukaryota DOMAINS After Darwin published theory of evolution in 1800s, scientists looked for a way to classify organisms that showed phylogeny The evolutionary history of an organism, or how it has changed over time Cladogram: diagram that shows the evolutionary relationship among a group of organisms Constructed using derived characters Characteristics that appear in recent parts of a lineage but not in its older members EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION Genes of many organisms show important similarities at the molecular level. Similarities in DNA can be used to help determine classification and evolutionary relationships EVOLUTIONARY CLASSIFICATION How are living things organized for study? Describe the system for naming species that Linnaeus developed. What are the seven taxonomic categories of Linnaeus’s classification system? Rank taxa in order starting with largest and ending with smallest BIG IDEAS