* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Collision Theory
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembled monolayer wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Equilibrium chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Thermomechanical analysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
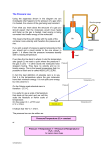
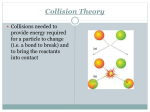
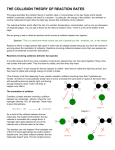
AP CHEMISTRY TUTORIALS–09 AP QUESTIONS Srinivasan G. Srivilliputhur February 24, 2016 Today’s Overview 1 • Review: Chemical Kinetics 2 • AP Examples 1 • Review: Chemical Kinetics: Collision Theory Reaction Kinetics: study of the factors that affect the rates of chemical reactions Collision Theory Summary • Molecules must collide to react • Main Factors: Activation energy, Ea Temperature Molecular orientations 5 Theories of Chemical Kinetics: Collision Theory • Before atoms/molecules/ions can react, they must first collide • An effective collision between two species puts enough energy to break key bonds • The activation energy (Ea) is the minimum energy that must be supplied by collisions to trigger a reaction • A certain fraction of all molecules in a sample will have the necessary activation energy to react • Fraction of molecules that will react increases with increasing temperature. (General rule: 10° (Celsius/Kelvin) increase doubles rate) • The spatial orientation of the colliding species often determine whether a collision is effective. 6 Reactant and Product Concentrations as a Function of Time: H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI (g) Using [H2]: instantaneous rate at 50s: Using [HI]: instantaneous rate at 50s: Plots Rate vs. Concentration Rate = k[A]n Rate constant ‘k’ likely changes with: • Temperature • Catalysts Enzymes are biocatalysts Plots Rate vs. Concentration Rate = k[A]n Rate constant ‘k’ likely changes with: • Temperature • Catalysts 2 • AP 2015 FRQ #5 2015 AP® CHEMISTRY FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS Compound Melting Point (degrees celsius) LiI 449 KI 686 LiF 845 NaF 993 6. A student learns that ionic compounds have significant covalent character when a cation has a polarizing effect on a large anion. As a result, the student hypothesizes that salts composed of small cations and large anions should have relatively low melting points. (a) Select two compounds from the table and explain how the data support the student’s hypothesis. (b) Identify a compound from the table that can be dissolved in water to produce a basic solution. Write the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs to cause the solution to be basic.