* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
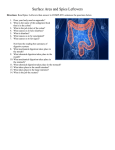
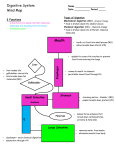
Medical Therapeutics Group of organs that changes food that has been eaten into a form that can be used by the body’s cells. Also known as the gastrointestinal system or GI Track The connecting chain of organs is referred to as the alimentary canal. 1. Ingestion 2. Digestion 3. Absorption 4. Elimination Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Two layers of involuntary muscles When food enters the esophagus, the muscles alternate contract and relax, squeezing the bolus. Together they create the peristaltic movement which moves the bolus to the stomach The whole process takes less than 5 seconds The upper opening to the stomach is controller by a circular muscle called the cardiac sphincter 10 inches long, j shaped Constructed of 3 layers 1. Carbohydrates 2. Proteins 3. Fats A tube about 1 inch in diameter and about 20 feet long Divided into 3 sections 1st is a c shaped section about 9 inches long called the duodenum common area for ulcers known as duodenal ulcer Largest gland in the body Lies below the diaphragm in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen extending into the left upper quadrant Secrets bile at a rate of over a pint a day Gives the fecal material it brown color Small sac attached to the underside of the liver Sole purpose is to store bile for use during digestion Cystic duct empties the GB Hepatic duct from the liver connect to form the common bile duct The common bile duct empties into the duodenum to be added to the chyme during the digestion process Lies behind the stomach with the head in the bend of the duodenum Empties pancreatic juices into the duodenum which aids in digestion Secretes insulin directly into the blood stream No digestion occurs in this area Colon also frames the abdomen Absorbs excess fluid from chyme through capillaries in the lining Only about five feet long Cholecystography-x-ray of the gallbladder after administration of contrast media Colonoscopy- Examination using a fiber optic scope to examine the entire colon Anorectal abscess and fistula- localized infection of the tissue adjacent to the rectum Sings throbbing pain lump which makes sitting and coughing uncomfortable Causes- sharp object in the feces such as fish bone or sea shell, Treatment-surgery to drain the access Inflammation of the colon causing tenderness and discomfort May be acute due to bacteria or chronic due an allergy or emotional stress Treatment-none has to run its course Second leading cause of death (2nd to lung) 93% of cases occur after 50 more in women than men Very slow growing if caught early can be cured 54% cases will occur in the rectum 21% in sigmoind,5% in descending colon, 3% in Splenic flexure, 5% transverse colon, 3% in the hepatic flexure 9% cecum An opening in the wall of the abdomen that allows fecal material to excrete from the body Can be temporary or permanent Indicated when an obstruction of the large bowel occurs near or at the sigmoid colon Sluggish bowel Signs- dry, hard, infrequent bowel movement Causes- diet, meds, dehydration, lack of exercise Treatment- stool softeners, increase fluid intake Add fiber to the diet Inflammation of any part of the colon Most common at the end of the cecum Signs- appendicitis type pain, cramping, pain and tenderness, bloody stool, tenderness in right lower quadrant Treatment- liquid diet, pain meds, steroids for inflammation Runny stools Signs- pain in abdomen followed by urgency with watery loose stool Treatment- antiditreatment of the underlying problem diarrhea meds, decrease fluid intake and fiber, Inflammation of the stomach Signs- pain the term may be applied to such conditions as intestinal flu, diarrhea and food poisoning. Cause- bacteria, food poisoning, drug reaction Treatment- maalox, mylanna, anti gas type meds.