* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fats and Proteins
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
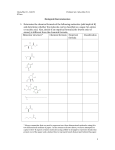
BIOLOGY – Activity Modeling Fats and Proteins Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Date: _____________ Station # _____ Names _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ INTRODUCTION Lipids are a class of chemical compound composed mostly of carbon and hydrogen atoms with very little oxygen. Common examples of lipids are fats, oils and waxes. Generally these compounds are not soluble in water. On a molecular basis, all fats are somewhat similar. Just as carbohydrates are composed of monosaccharide molecules, fats are composed of smaller molecules. The smaller molecules in fats are called glycerol and fatty acid. There are many different fatty acids but they are all similar in several ways. As with all molecules, a molecular formula can be written for a fatty acid by counting the numbers of different atoms and inserting those numbers as subscripts next to the corresponding symbol for the atom. For example, the molecular formula for palmitic acid is C16H32O2. Proteins also consist of many smaller molecules joined together. These smaller molecules are called amino acids. Like many complex carbohydrates, proteins are polymers made of smaller units called monomers. In carbohydrates, the monomers are simple sugars whereas in proteins the monomers are amino acids. There are about 20 different amino acids so there are thousands of different proteins. OBJECTIVE To determine the molecular characteristics of fats and proteins MATERIALS scissors paper models of fatty acids and amino acids glue cardstock PROCEDURE Fats Using the diagram provided: 1. What elements are present in glycerol? _________________________________ 2. Are there elements in glycerol not found in carbohydrates? _________________ 3. What is the molecular formula for glycerol? ______________________________ 4. What is the ratio of H to O atoms in glycerol? ____________________________ 5. Is the ratio of H to O in glycerol the same as in carbohydrates? _______________ 6. What elements are present in all fatty acids? ______________________________ 7. What is the molecular formula for butyric acid? ___________________________ 8. What is the molecular formula for caproic acid? ___________________________ 9. What is the ratio of H to O atoms in fatty acids? ___________________________ 10. Is the ratio of H to O atoms the same in all fatty acids? _____________________ Notice that the end of the butyric acid molecule contains oxygen atoms in a special arrangement of carbon and hydrogen called a carboxyl group as shown below. 11. Is the carboxyl group present in all fatty acids shown ? ___________________ A fat molecule consists of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules joined together. Cut out the models of the glycerol and three fatty acid molecules by cutting along the solid lines only. Next, cut along the dotted lines to remove the –H and –OH groups from each of the paper molecule models. Join each –H you removed with an –OH. 12. What substance is formed when the –H and –OH are joined? ________________ Construct a fat molecule by joining the glycerol model you cut out with the three fatty acid molecules. Production of a fat molecule is a chemical reaction. A chemical shorthand way of expressing the formation of a fat is shown below. Glycerol + fatty acids fat + water Glue your fat molecule and all your water molecules on the card stock provided. 13. How many water molecules are formed when one fat molecules if produced? __________ Many different kinds of fats exist in living things. The wide variety of fats are formed by different combinations of fatty acid molecules. 14. What molecule remains the same in all fats? ______________________________ Proteins Carbohydrates consist of many monosaccharides joined together while fats consist of glycerol and fatty acid molecules joined together. Proteins also consist of many small molecules joined together. In proteins, these smaller molecules are called amino acids. Examine the structural formulas and corresponding models for the four amino acids on the diagram provided. Notice the element nitrogen ( symbol N ) is present in all amino acids. 15. Is nitrogen present in fats and carbohydrates? ___________________________ 16. What is the molecular formula for glycine? _____________________________ 17. What is the molecular formula for alanine? ______________________________ 18. Are the molecular formulas the same for all amino acids? ___________________ 19. What end arrangement of atoms is present in amino acids that are also present in fatty acids? _________________________ Another end arrangement of atoms in amino acids consists of a nitrogen atom and two hydrogen atoms. This arrangement is called an amino group and is shown below. 20. Is the amino group present in all amino acids? _______________ A protein is composed of many amino acids joined together. Cut out the models of the four amino acid molecules provided by cutting on the solid lines only. Next, cut along the dotted lines to remove the –H and –OH groups from each of the paper models. Now join the 4 amino acid models together in this order: valine - threonine – alanine - glycine. Also join the –H and -OH units to each other and glue all your molecules to the card stock provided. Label the molecules you have glued to the card stock and staple the card stock to the back of this packet. Chemists can express the joining of these amino acids as follows: valine + threonine + alanine + glycine protein + water 21. How many molecules of water formed when you combined the four amino acid molecules? _____________ ANALYSIS 1. Dehydration means loss of water and synthesis means putting together. Explain why the chemical process of building fats and proteins is called a dehydration synthesis. ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 2. What are the two types of molecules needed to form a fat molecule? ________________________________________________________ 3. What type of molecule is needed to from a protein? ________________________________________________________ 4. How does a glycerol molecule differ from a carbohydrate molecule? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 5. How does a fatty acid molecule differ from a carbohydrate molecule? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ 6. How do amino acid molecules differ from fatty acid molecules? _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 7. How are amino acids and fatty acids similar? _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 8. How might a human muscle protein differ chemically from a cow muscle protein? _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ 9. Molecules of carbohydrates, fats and proteins can undergo a process called condensation or hydrolysis ( hydro means water and lysis means to break apart ). This process occurs when water molecules are used by cells to break apart the subunits of polymers. For example, 3 water molecules are used to break a fat down into the glycerol and the three fatty acids of which it was composed. What part of the water molecule, -H or –OH, is reattached to the glycerol molecule when a fat undergoes hydrolysis? ___________________________________________________________ 10. How many water molecules must be used in the hydrolysis of a protein that consists of 35 amino acids? ___________________________________________________________ Complete the table below by filling in YES or NO Glycerol carbon present hydrogen present oxygen present nitrogen present 2:1 ratio between H and O has a carboxyl group has an amino group join to form proteins join to form fats Fatty acid Amino acid