* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Rhetorical Criticism
MOGUL framework wikipedia , lookup
Ethnoscience wikipedia , lookup
Historical figure wikipedia , lookup
Linguistic insecurity wikipedia , lookup
Style (sociolinguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Linguistic performance wikipedia , lookup
Forensic linguistics wikipedia , lookup
History of linguistics wikipedia , lookup
Speech perception wikipedia , lookup
Honorifics (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Formulaic language wikipedia , lookup
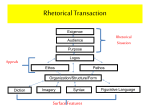
Intro to Rhetorical Criticism Analyzing Historical Context & Rhetorical Text Historical Context Who? – Speaker and audience Why? – Purpose When? – Timing of speech Where? – Placement of speech How? – Production and deliver of speech; who wrote it? How was it delivered? How might the medium have shaped the creation and delivery of the text? Analysis of the Rhetorical Text Characters Place Time Argumentation Structure Style Delivery Evaluation of the Rhetorical Text Effect – How successful was the speech at securing its goals? Artistry – Evaluating the quality of the strategies used Ethics – What are the long-term implications for the social welfare of society? Characters Roles or personas used in the speech; may include the speaker or the audience Place In what places are the characters situated in the speech? Time How is time used to communicate the message? Past, present and future references Argumentation A claim backed by one or more justifications Variety of supports, critical Clear sense of logic Structure How does the text unfold? Historical, chronological? Topical? Logical/Pragmatic? Historical, Chronological The topic is best understood in terms of how it unfolds in time. Sequence is important. Topical Claims that certain elements are critical to understanding the issue Logical/Pragmatic Problem/Solution, Cause/Effect Ideas or situations stand in necessary relation to one another Style What is distinctive about the language of this rhetorical text? Grammar, sentence length, syntax, figures of speech, etc. Delivery The “voice” of the style/language