* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Elements, Compounds and Mixtures.
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Thermal spraying wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
Sulfur dioxide wikipedia , lookup
Nanoparticle wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Freeze-casting wikipedia , lookup
Geiger–Marsden experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Stöber process wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Sulfur cycle wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Mineral processing wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
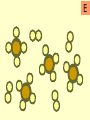
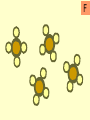
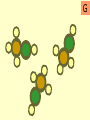
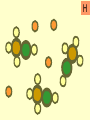
Warm-Up: 2/4 Classifying Elements • Head a sheet of paper and title it: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Notes • Science Binder page 32 • Make a subheading (smaller title under the main title) – Warm-Up: 2/3 Classifying Elements • Write a short paragraph explaining what makes something an element. Include examples. Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Notes Science Binder p. 32 Classification of Substances • • • • Elements Molecules Compounds Mixtures Elements • Elements are substances made up of only one type of atom. • Example Hydrogen, Gold. Elements • Pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. – Pure substance- a substance in which there is only one type of particle (atom or molecule) Periodic Table of Elements Molecule • A molecule is made up of two or more atoms chemically bonded. • Atoms can be the same or different! Compounds • Compounds are pure substances made up of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded. Properties of Compounds • When a compound is formed during a chemical reaction its properties differ from those of the elements it is made of. • Example: Water is made from hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen flammable gas Oxygen colorless gas. Compounds • Represented by chemical formulas with two or more chemical symbols (each capital letter = a new chemical symbol/element) • NaCl = sodium chloride (table salt) • H2O2 = hydrogen peroxide • C6H12O6 = glucose (sugar plants make from photosynthesis) Chemical Formulas • subscript- small number located at the bottom right of a chemical symbol, and gives the number of atoms for the element in that molecule Mixtures • A mixture consists of two or more different substances mingled together but not chemically combined. • Examples: Sea – water and salt Air – nitrogen, oxygen … Soil – sand, clay, humus … Compare mixtures and Compounds. Mixture Compound The amounts of the substances in the mixture can vary. The elements in a compound are always present in the same fixed proportion. A mixture contains two or more substances A compound is a single substance. The properties of a mixture are The properties of a compound similar to those of the substances are different to those of the in a mixture. elements which reacted to form it. There are practically no energy Heat is usually given out or changes when a mixture is made taken in when a compound is formed. It is usually easy to separate the components of a mixture. It is usually difficult to separate the components of a compound. iron particles Key: one iron particle strong bonds between iron particles iron particles held together by strong bonds iron particles iron particles are attracted to a magnet iron particles diagram sulfur particles Key: one sulfur particle strong bonds between sulfur particles sulfur particles held together by strong bonds sulfur particles sulfur particles are not attracted to a magnet sulfur particles diagram iron particles sulfur particles What’s this? A mixture of iron and sulfur particles strong bonds between iron particles strong bonds between sulfur particles A mixture of iron and sulfur particles A magnet attracts the iron particles but not the sulfur particles. The mixture is separated mixture diagram What’s this? A compound between iron and sulfur particles one iron particle one sulfur particle strong bonds between iron and sulfur particles A compound between iron and sulfur particles strong bonds between iron and sulfur particles The magnet cannot separate iron and sulfur particles in a compound compound diagram A B C D E F G H