* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TSE diagnostics 4
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
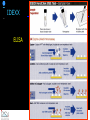
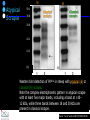
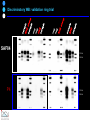
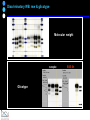
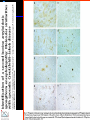
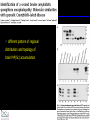
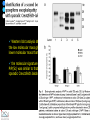
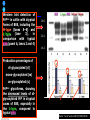
IDEXX ELISA Western Blot I) SDS-PAGE II) Blotting III) Immunodetection and revelation III) Immunodetection and revelation linked protein. weight marker Secondary linked to causes theAbprecipitation of an peroxidase insoluble (luminol product andinoxigen the peroxide), causing the emission nitrocellulose membrane. of able to impress a Thelightquantity of products is photographic plate proportional to the amount of Molecular 1) Blocking: ofsaturation of 2) Incubation the 3) Incubation of the aspecific link sites (non-fat dry nitrocellulose membrane 4a) Signal detection nitrocellulose membrane milk) with aa primary Detection systemAb based on a with enzyme-conjugated secondary linked to an 4b) SignalAb detection secondary Ab (i.e peroxidase, enzyme that acts on its alkaline phosphatase). Detection system based on substrate (DAB); chemiluminiscence. The enzyme-substrate reaction PRIONICS®-CHECK WESTERN SR 1) Preparation of the brain sample and isolation of the scrapie prion protein The test sample is a small piece of obex, a defined region of the brain stem. The homogenized brain sample is incubated with an optimized reagent mixture consisting of digestion enzymes and a buffer solution (I). This solution degrades the normal prion protein. Only the TSEspecific prion protein remains in the test sample. 2) Separation of proteins by gel electrophoresis and immunological detection of scrapie prion protein The proteins in the sample are then separated according to size by gel electrophoresis (II) and transferred to a special blot membrane for detection (III). The scrapie-specific prion protein on the membrane is detected with specific antibodies and is visualized on a digital file or on a film. It is especially designed for the detection of scrapie in sheep and goats. saPMCA Detection of prions in blood Joaquin Castilla, Paula Saa, Claudio Soto Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification (PMCA) for the presymtomatic detection of PrPsc in blood of hamster experimentally infected with scrapie Nature Medicine (Agosto 2005) Confirmatory tests after rapid test Histology Immunohistochemistry Western blot Atypical TSEs Atypical Scrapie BASE (Bovine Amyloidotic Spongiform Encephalopaty) BSE in Sheep/goat Atypical TSEs Atypical Scrapie Atypical scrapie Atypical scrapie was first recorded in Norway (Benestad and others 2003) and reports of other `atypical' TSE phenotypes, including those that are similar to or the same as Nor98 have now been published, from France (Buschmann and others 2004b), Germany (Buschmann and others 2004a, b), Sweden (Gavier-Widen and others 2004), Ireland (Onnasch and others 2004), Portugal (Orge and others 2004), Belgium (De Bosschere and others 2004) and the UK (Everest and others 2005; M. M. Simmons, J. Spiropoulos, H. Elliott, P. Webb, J. Nash, J. Ryan, Y. I. Spencer, personal communication). Atypical scrapie can occur in countries with little or no classical scrapie (for example, Norway and Portugal). Atypical Scrapie in different European Countries Nor98 Not always detected with rapid tests Characteristic neuropathologic pattern (cerebellum, cortex) Not detected in VRQ, particularly in AHQ … other polimorphisms Single case/outbreak No involvement of LRS Characteristic molecular pattern of PrPSc M Atypical Scrapie 58.1 39.8 M Atypical scrapie Classical scrapie 29.0 20.1 14.3 (A) Western blot detection of PrPres in sheep with atypical (A) or classical (B) scrapie. Note the complex electrophoretic pattern in atypical scrapie with at least five major bands, including a band at ≈10– 12 kDa, while three bands between 18 and 30 kDa are present in classical scrapie. Baron T et al Vaccine 2007;25:5625-5630 TSEs typing Titolo presentazione Typing of TSEs strains Lack of appropriate definition of strain “Phenotypic” definition Biological typing – specific, but too long (1-2 yrs) Molecular typing (!?) – rapid, but with limited specificity Tests and laboratories approved for TSEs discrimination VLA (UK) WB M. Stack IHC M. Jeffrey AFFSA (Francia) WB T. Baron CEA (Francia) WB J.P. Deslys ELISA J. Grassi FLI (Germania) WB M. Groschup CIDC (Olanda) WB J. Langeveld ISS (Italia) WB U. Agrimi, R. Nonno Typing of TSEs in conventional mice • Disease characteristics in a panel of inbred mice: RIII, C57BL (PrP-a) VM (PrP-b) C57BLxVM (PrP-ab) • Mean incubation period (Dickinson et al.,1968) • Distribution of vacuolation in brain: “lesion profile” (Fraser & Dickinson, 1968) Biological characteristics of different strains Natural scrapie Lines of mice BSE FSE vCJD Tempi di incubazione (in giorni) days (Bruce et al., 1997) Discriminatory WB: validation ring trial SAF84 25 kDa 20 kDa P4 25 kDa 20 kDa Discriminatory WB: mw & glicotype Molecular weight scrapie Glicotype BSE Sh Atypical TSEs BASE (Bovine Amyloidotic Spongiform Encephalopaty) presence of PrP-immunopositive amyloid plaques, as opposed to the lack of amyloid deposition in typical BSE cases different pattern of regional distribution and topology of brain PrP(Sc) accumulation Western blot analysis showed a PrP(Sc) type with predominance of the low molecular mass glycoform and a protease-resistant fragment of lower molecular mass than BSE-PrP(Sc) the molecular signature of this previously undescribed bovine PrP(Sc) was similar to that encountered in a distinct subtype of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease presence of PrP-immunopositive amyloid plaques, as opposed to the lack of amyloid deposition in typical BSE cases different pattern of regional distribution and topology of brain PrP(Sc) accumulation Western blot analysis showed a PrP(Sc) type with predominance of the low molecular mass glycoform and a protease-resistant fragment of lower molecular mass than BSE-PrP(Sc) the molecular signature of this previously undescribed bovine PrP(Sc) was similar to that encountered in a distinct subtype of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease Western blot detection of PrPres in cattle with atypical forms of BSE, including the H-type (lanes 5–6) and L-type (lane 3), in comparison with typical BSE (panel A, lanes 2 and 4) BSE L-type BSE H-type H-type 29.0 20.1 14.3 Production percentages of di-glycosylated (d) mono-glycosylated (m) un-glycosylated (u) PrPres glycoforms, showing the decreased levels of diglycosylated PrP in atypical cases of BSE, especially in the L-type, compared to typical BSE Baron T et al Vaccine 2007;25:5625-5630 Transmission of new bovine prion to mice Baron et al. (2006) Emerging Infect Diseases 12, 11251128, A recent study indicated that the type of BSE in older cattle in the US (and potentially in Canada) are the same type as the atypical BSE that has been identified in France. Atypical TSEs BSE in goat/sheep BSE in goat/sheep There are only two confirmed cases of BSE in a sheep or a goat that were not infected experimentally. These were in a French goat that died in 2002 and a Scottish goat that died in 1990. BSE in goat/sheep Fig. 1. Western blot detection of PrPres in BSE (arrow) compared to three scrapie sources, in C57Bl/6 mice (panel A) or in sheep (panel B). The lower band corresponding to the unglycosylated PrPres shows a lower apparent molecular mass in BSE-infected animals. Baron T et al Vaccine 2007;25:5625-5630 Differential Diagnosis of Infections with the Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE) and Scrapie Agents in Sheep M. Jeffrey et al. J. Comp. Pathol. 125, 271-284, 2001 LRS tissues BSE Scrapie BSE infected sheep CNS BSE Scrapie BSE Scrapie Scrapie BSE Thank you for your attention Franco Mutinelli Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale delle Venezie e-mail: [email protected]