* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of The Heart
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
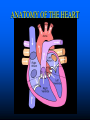
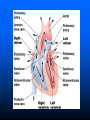
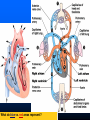
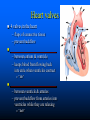
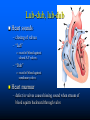
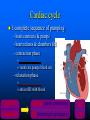
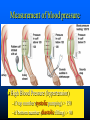
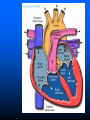
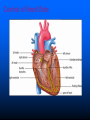
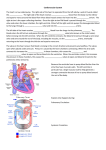
Parts of The Heart The Atria (or Atriums) -Receiving Chambers The Ventricles -Pumping Chambers The Valves -Prevents backflow The Septum -Divides the Heart Right side = incoming blood Left side = outgoing blood ANATOMY OF THE HEART ANATOMY OF THE HEART Label the structures of the heart from your handout. Refer to your text P. 495 You have 10 minutes! PATHWAY OF BLOOD Trace the flow of a red blood cell as it returns to the heart from the body's cells. PATHWAY OF BLOOD 1) a. superior vena cava or 1)b. inferior vena cava 2) right atrium 3) tricuspid valve—(AV valve) 4) right ventricle 5) pulmonary valve—(semilunar valve) 6) pulmonary artery (goes to lungs) PATHWAY OF BLOOD 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) pulmonary vein (from the lungs) left atrium bicuspid valve (left AV valve) left ventricle aortic valve (semilunar valve) aorta to the body’s cells HEART SOUNDS When you hear your heart beating, what are you actually listening to? Normal Sounds (48 sec): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NeMJXMSkA7g (3:30 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H04d3rJCLCE What do blue vs. red areas represent? Heart valves 4 valves in the heart – flaps of connective tissue – prevent backflow ____________________________ – between atrium & ventricle – keeps blood from flowing back into atria when ventricles contract » “lub” SL ____________________________ – between ventricle & arteries – prevent backflow from arteries into ventricles while they are relaxing » “dub” AV AV Lub-dub, lub-dub Heart sounds – closing of valves – “Lub” SL » recoil of blood against closed AV valves – “Dub” AV AV » recoil of blood against semilunar valves Heart murmur – defect in valves causes hissing sound when stream of blood squirts backward through valve Cardiac cycle 1 complete sequence of pumping – heart contracts & pumps – heart relaxes & chambers fill – contraction phase » ______________ » ventricles pumps blood out – relaxation phase » ______________ » atria refill with blood systolic ________ diastolic pump (peak pressure) _________________ fill (minimum pressure) 110 ____ 70 Measurement of blood pressure High Blood Pressure (hypertension) – if top number (systolic pumping) > 150 – if bottom number (diastolic filling) > 90 Control of Heart Rate contraction without brain input Sinoatrial (SA) node, also called pacemaker cells are nerve cells in the right atrium SA node causes the atria to contract sends electrical stimuli to the atrioventricular (AV) node. electrical stimuli are sent through two nerve fibres called Purkinje fibres to the ventricles causing them to contract. Control of Heart Rate Disorders of CV System Plaque – Patchwork of cholesterol, calcium and fat deposits that stick to interior walls Dangers of plaque build up – – – – Atherosclerosis Heart attack Arteriosclerosis Sudden cardiac arrest Atherosclerosis Narrowing of the arteries resulting from plaque building up inside the artery wall Blood pressure increases Sometimes flow completely blocked Heart Attack Blood supply to heart tissue is slowed or stopped Narrowing coronary arteries due to atherosclerosis Heart usually does not stop beating Pain in upper chest, shortness of breath, nausea Heart muscle can die Arteriosclerosis Advanced stage of plaque buildup Deposits on artery wall harden Arteries lose elasticity and ability to stretch Decrease in BP and chance of blood clots Sudden Cardiac Arrest Heart suddenly stops functioning Drowning, electrocution, trauma, choking Coronary heart disease most common CV Disorders Arrhythmia – Irregular heart beat Hypertension – High blood pressure Heart failure – Heart cant pump blood efficiently or send blood with enough force to body Aneurysm – Bulge in artery wall Stroke – Blood clot in artery going to brain Cholesterol A fat that is part of your cell membranes and is used to synthesize hormones, bile and vitamin D Liver manufactures Transported by two lipoproteins made of fat and proteins – HDL and LDL Lipoproteins HDL – Good cholesterol – Helps remove excess cholesterol from tissues and arteries LDL – Bad cholesterol – Becomes part of plaque in arteries – Found in food high in trans and saturated fats