* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 5 - Human Activity and Ecosystems - Hitchcock
Conservation biology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Holocene extinction wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
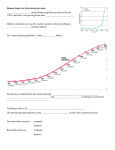
Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems Growing Pains How do humans negatively affect ecosystems? • An ecosystem is all of the living and nonliving things within a given area. • Changing one thing in an ecosystem can affect many other things, because everything in an ecosystem is connected. • Humans can affect ecosystems through pollution. Pollution is caused by any material or condition that harms the environment. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems How do humans negatively affect ecosystems? • The growing human population has created a greater need for natural resources, leading to changes in ecosystems. • The overuse of resources causes them to be depleted, or used up. • Resource depletion occurs when a large fraction of a resource has been used up. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems How do humans negatively affect ecosystems? • Compare the time it took for the human population to grow from 1 billion to 2 billion, and from 3 billion to 6 billion. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems How do humans negatively affect ecosystems? • Human population growth in and around cities is called urbanization. • Urban growth within ecosystems often destroys natural habitats and can bring humans and wildlife into contact. • Every habitat has its own number and variety of organisms, or biodiversity. If a habitat is damaged or destroyed, biodiversity is lost. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems Water, Water Everywhere How do humans impact oceans? • Oceans support various ecosystems that together contain nearly half of Earth’s species. Pollution damages these ecosystems and threatens biodiversity. • Point-source pollution comes from one source, such as an oil spill. • Nonpoint-source pollution comes from many sources, such as when chemical fertilizers and pesticides are washed into oceans. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems How do humans impact oceans? • A greater demand for seafood from the growing human population has led to overfishing of some ocean species. • If a fish population cannot reproduce fast enough, it may become locally extinct. • The local loss of a species can disturb ocean food webs and threaten ecosystem stability. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems How do humans impact oceans? • The growing human population has led to increased coastal development and has increased pollution on shore and in coastal waters. • In some places, development has almost completely replaced natural coastlines, destroying mangrove forests that protect coastlines. • Human activity has also damaged coral reefs, but scientists and others are working to correct this damage. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems How do humans affect freshwater ecosystems? • In many river ecosystems, human activities have decreased the amount of water, or water quantity. • Dams block the flow of river water, leading to less water downstream. • If the natural course of a river is changed by channelization, it changes the water quantity, temperature, and chemistry. This affects river species. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems How do humans affect freshwater ecosystems? • Human activities can also decrease water quality, or how good the water is. Fertilizers contain nutrients that can enter ponds and lakes as runoff. • An increase in the amount of nutrients, such as nitrates, in an aquatic ecosystem is called eutrophication. • Excess nutrients in ponds and lakes cause overgrowth of algae, using up the pond’s dissolved oxygen and causing fish to die. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems How do humans affect freshwater ecosystems? • Water quality is also affected by air pollution. • Burning fossil fuels releases chemicals into the air, and some of the chemicals combine with rain to produce acid rain. • Acid rain can damage both aquatic and land ecosystems. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems Exotic Species • An organism that makes a home for itself in a new place outside its native home is an exotic species. • Exotic species that outcompete native species are called invasive exotic species. • When European rabbits were introduced into Australia, their population exploded because they had plenty of space and food, but no predators. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems Save It! How do humans protect ecosystems? • The careful and responsible management of a resource is called stewardship. • The organisms in an ecosystem depend on each other and interact to form a vast food web. The loss of a species can leave gaps in the web. • Humans can protect habitats and help species survive, thereby protecting the biodiversity and health of an ecosystem. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 2 Lesson 5 Human Activity and Ecosystems How do humans protect ecosystems? • Conservation is the protection and wise use of natural resources. • Practicing conservation means using fewer natural resources and reducing waste. It also helps prevent habitat destruction. • There are “three Rs” for conserving resources: reduce what you buy and use; reuse what you already have; and recycle by recovering materials from waste. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company